Look at the list of behaviours typically used by negotiators. Which do you consider to be the most important for a successful negotiator? Are there any you consider unimportant?
A good negotiator is someone who …
· focuses strongly on personal objectives.
· tests the understanding of the other party frequently.
· structures the discussion clearly and flexibly.
· highlights common grounds between the parties.
· spends a lot of time in planning.
· focuses on the long term.
· uses a lot of questions to explore options.
· fixes a clear agenda and stick to it.
As a group, brainstorm the sort of preparations you’d need to make for an international negotiation – think, for example, about goals, alternatives, background research, team-building, venue selection and cultural factors.
The flowchart below shows the principal stages and sub-stages of a formal negotiation. With a partner, complete the different sections using the verbs in the boxes. Fill in the central part of the chart first.

How much do you think negotiating procedure varies from culture to culture? Are the stages listed above sequenced differently or given greater or lesser importance in your culture?
7. Look at some examples of negotiations:
1. negotiating a pay rise with your boss
2. arguing over a price rise with a key supplier
3. buying time to complete a difficult project
4. renegotiating the terms of a multimillion-dollar contract
Discuss in pairs which of the four types of negotiation you have taken part in or will need to take part in. Which would you find the most stressful to do in your language and in English?
Complex negotiations may require several participants and each team member must play a specific role. Complete the team roles model below using the pairs of words in the box.
|
|
|
|
|
|
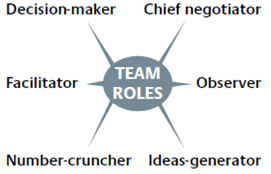
breaks + solutions monitors + movement formulates + authority
notes + calculations conciliates + clarification conducts + spokesperson
A: …………… overall strategy and has the final …………… .
B: …………… and provides …………… of their team’s position.
C: …………… down key figures and does the …………… .
D: …………… the main negotiations and acts as …………… .
E: …………… the other team’s behaviour and looks for signs of …………… .
F: …………… deadlocks by coming up with creative …………… .
|
|
|
Read the text about team negotiations and answer these questions:
1. What are the pros and cons of team negotiation and one-on-one deals?
2. When is it advisable to negotiate as a team and when is it better to negotiate alone?

Wang Mei Ling works for an electronics company based in Shanghai. Listen to Ms Wang talking about her experience of negotiating with an American company (Recording 3.3).
1. What was the purpose of negotiation?
2. What was the most challenging thing for Ms Wang in the negotiation?
3. What was the biggest difference in negotiation style between the two companies?
Listen again and fill in the gaps in the following extracts from the dialogue:
1. Well, they were just very conservative. They didn’t want to ………………. .
2. There were a lot of negotiations between the legal departments. And this slow ……………………. from their side was very frustrating for us.
3. In my organisation people are pretty relaxed. People normally have ……………………. in terms of what they do.
4. So a key lesson is that we have to ……………………………………….. . In the set-up of the negotiation, you need to understand what exactly they are asking before you really begin to negotiate and they need to understand you, and then you can move to …………………………………. .
Ms Wang says that “The really critical part of the negotiation is the start.” Listen to extracts from the openings of three different negotiations (Recording 3.4). In each case note down which proposed objective / agenda point for the negotiation is changed and why.
Дата добавления: 2019-02-13; просмотров: 379; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
