Celtic society consisted of 3 layers. Who are they? Look at the pictures and define the strata of Celtic society.
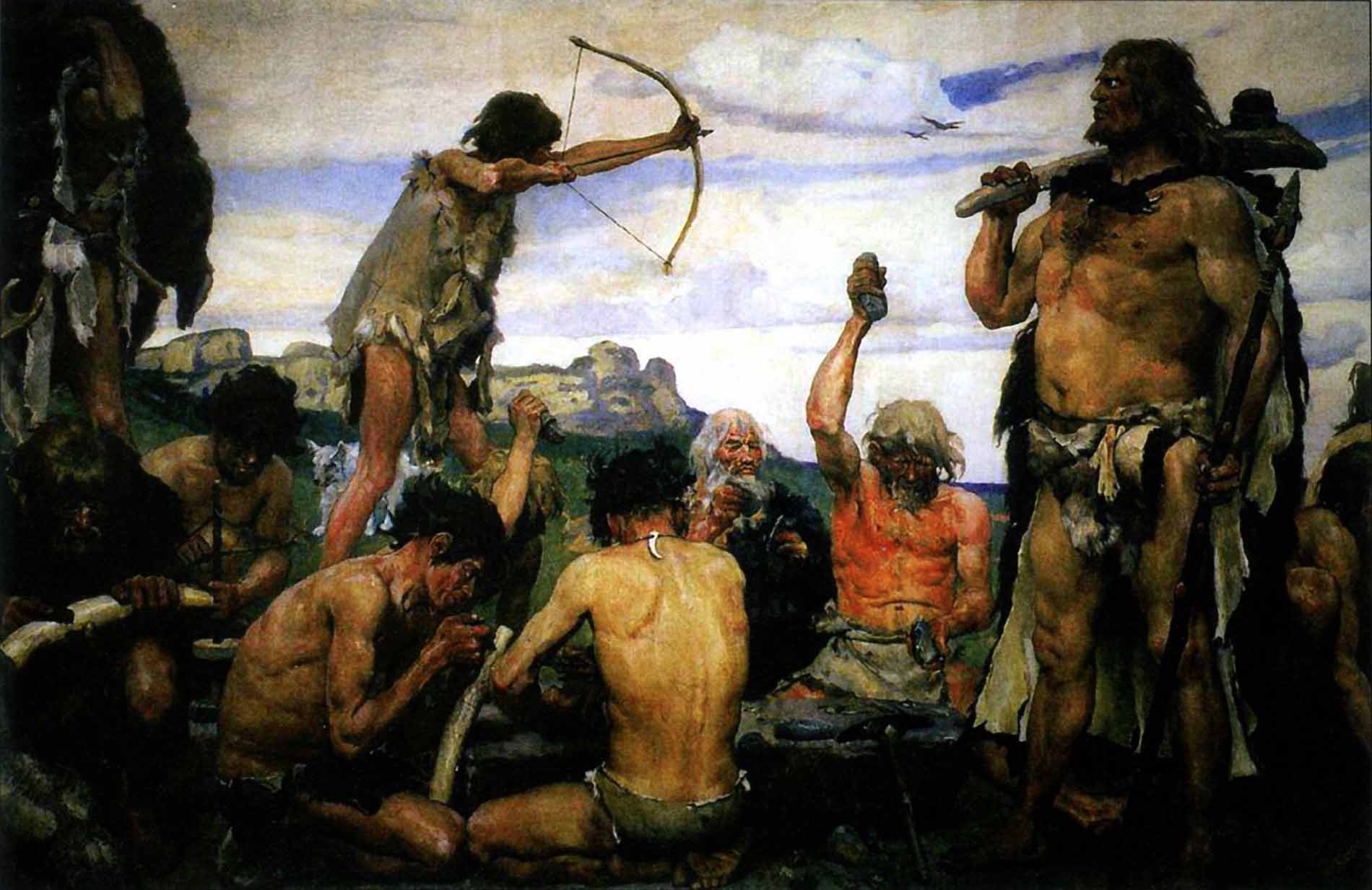


1) ___________________________________
2) ___________________________________
3) ___________________________________
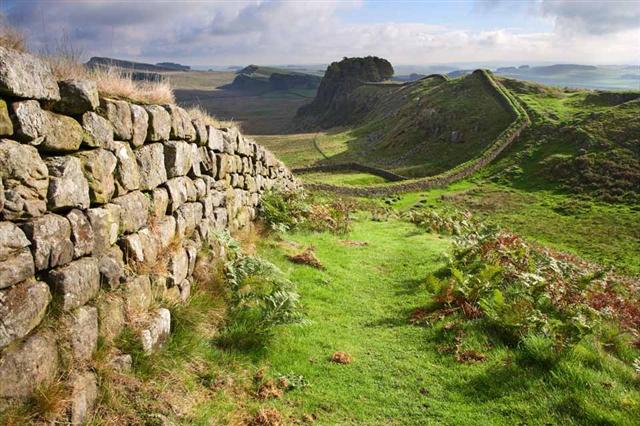
The Celts came to Britain in 3 waves and immediately preceded the Teutons. Economically and socially the Celts were a tribal society made up of kings, kingship groups, clans and tribes, they practiced a primitive agriculture. Brythonic was the spoken language during this time. Like other regions on the edge of the Empire, Britain had long enjoyed trading links with the Romans.
Listen and complete the chart
| ………… | Julius Caesar heads first Roman Invasion but later withdraws |
| 43 AD | Romans invade and Britain ………………………………………… |
| 50 | ………………………………………………………………………. |
| 61 | …………….. leads the Iceni in revolt against the Romans |
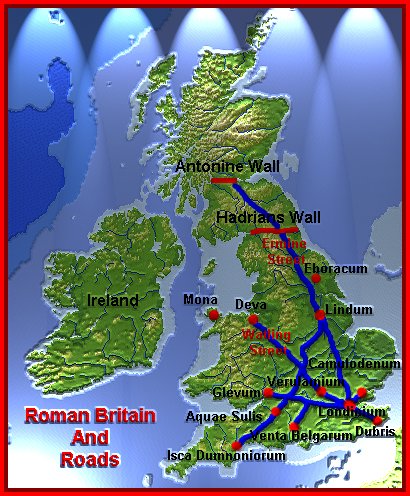
| 122 | …………….. builds a wall on the Scottish Border |
| 140 | Romans conquer ………………………………………………….. |
| ……….... | The Romans withdraw from Britain |
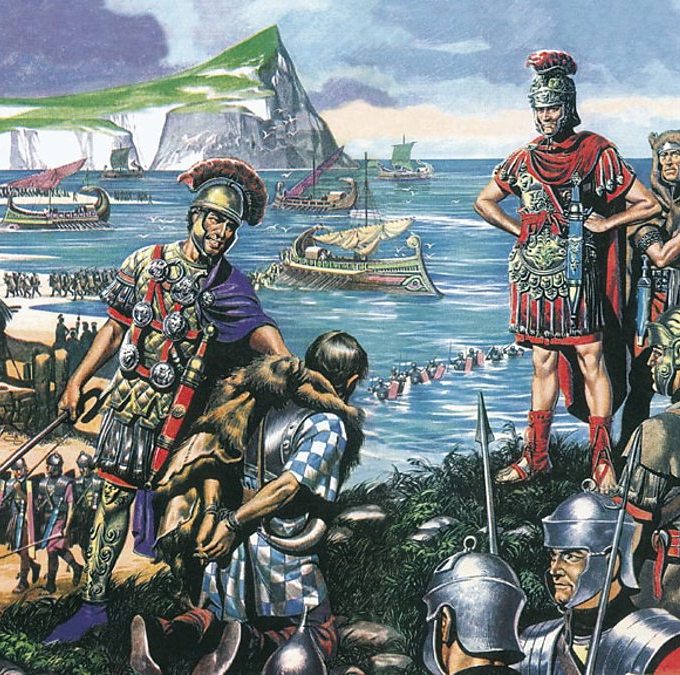
Read the passage below and explain the following series of pictures
| 55BC |

| 
| 
| |

| 
| 
| |

|
| ||
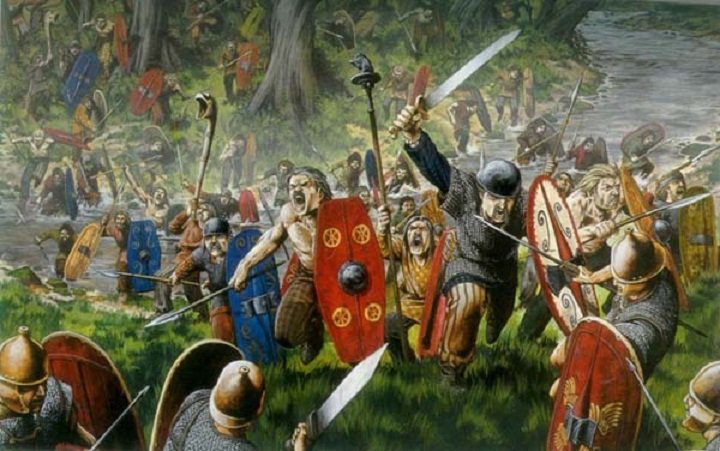
In the 1st century BC the Romans conquered Gaul. Having occupied Gaul Julius Caesar made 2 raids on Britain, in 55 and 54 BC. Caesar attacked Britain for economic reasons – to obtain tin, pearl and corn. Caesar failed to subdue Britain but some hundred years later under Emperor Claudius the Romans s ucceeded in annexing Britain to the Empire. As the province was distant Roman legionaries were followed by numerous civilians. The whole southern part of the island – roughly corresponding to modern day England and Wales – became a prosperous part of the Roman Empire.
The best known of the native tribes who attempted to resist were the Catuvellauni led by Caratacus.
Later, an uprising led by Boudicca, queen of the Iceni, resulted in her death at the Battle of Watling Street.
The Results of the Roman Invasion
6. Read the passage below and find out the answers to the following questions:
1) What are the main results of the Roman Invasion in Britain?
2) What does the word ‘castra’ mean?
3) When did London appear as a settlement?
 This era saw a Greco-Roman high culture prevail with the introduction of law and order, Roman architecture, personal hygiene, sewage systems, education, many agricultural items, and silk.
This era saw a Greco-Roman high culture prevail with the introduction of law and order, Roman architecture, personal hygiene, sewage systems, education, many agricultural items, and silk.
|
|
|
The Romans brought to ‘barbarian’ Britain their administration, their way of life and their language. The Romans founded the military settlements or camps – ‘castra’ (Manchester, Lancaster, Colchester, Lincoln). Along the trading centres of Roman Britain Londinium stood the first; from a small settlement it turned out into an extensive town. The Roman occupation lasted nearly 400 years, it came to an end in the early 5th century.
7. Read the following Latin words and give their English equivalent:
1. accomŏdo, 1 приспособлять
2. accūso, 1 обвинять
3. admĭnistro, 1 руководить
4. adōro, 1 поклоняться
5. advŏco, 1 призывать
6. armo, 1 вооружать
7. cito, 1 приводить
8. cōgito, 1 думать
9. compăro, 1 сравнивать
10. condemno, 1 осуждать
11. conservo, 1 хранить
12. conspīro, 1 составлять заговор
13. corōno, 1 венчать
14. declāro, 1 объявлять
15. demonstro, 1 указывать
16. destīno, 1 назначать
17. dicto, 1 диктовать
18. dubĭto, 1 сомневаться
19. edŭco, 1 обучать
20. emĭgro, 1 переселяться
21. erro, 1 ошибаться
22. exclāmo, 1 восклицать
23. expecto, 1 ожидать
24. firmo, 1 укреплять
25. formo, 1 формировать
26. frequento, 1 часто посещать
27. guberno, 1 править
28. hābĭto, 1 обитать
29. honōro, 1 уважать, почитать
|
|
|
30. ignōro,1 быть в неведении
31. illustro, 1 освещать
32. impĕro, 1 править
33. importo, 1 ввозить
34. judĭco,1 судить
35. libĕro,1 освобождать
36. milĭto, 1 воевать
37. ministro, 1 прислуживать
38. muto,1 меняться
39. narro,1 рассказывать
40. navĭgo, 1 плыть
41. nomĭno,1 называть
42. numĕro,1 считать
43. porto,1 переносить
44. probo,1 одобрять
45. regno,1 царствовать
46. salūto,1 приветствовать
47. signo,1 обозначать
48. spiro,1 дышать
49. tolĕro,1 терпеть
50. vibro,1 дрожать
Дата добавления: 2018-11-24; просмотров: 433; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!

