ACTIVATING THE STUDENTS’ BACKGROUND
1. Do you know …
Any words spoken in Stone Age?
Any books written in Proto-Indo-European?
DATE BASE – PIE and Comparative Linguistics
 When there are no documents of language to be traced the pre-written history of any language is studied by methods of comparative linguistics. It is 200 years old. It all started with a publication of an article by Franz Bopp (1816). The talk is about the so-called I-E language. It is now well-supported with evidence from many languages that there was a language spoken by people in pre-historic times. It was given a name PROTO-INDO-EUROPEAN. 10000 B.C. is the most probable time of existing P-I-E homeland. It is based upon linguistic and archeological facts.
When there are no documents of language to be traced the pre-written history of any language is studied by methods of comparative linguistics. It is 200 years old. It all started with a publication of an article by Franz Bopp (1816). The talk is about the so-called I-E language. It is now well-supported with evidence from many languages that there was a language spoken by people in pre-historic times. It was given a name PROTO-INDO-EUROPEAN. 10000 B.C. is the most probable time of existing P-I-E homeland. It is based upon linguistic and archeological facts.
Linguistic facts:
· words denoting the sea (the root mor- denotes the water area)
· names of the trees
· names of the rulers
· names of the devices for cultivating soil (the plough)
Archeological facts:
· the crockery, the pots, the burial places
· people in power were buried with what they possessed
· tools made of stone and absence of metal
· evidences of transition from gathering food to cultivating soil
· megalithic culture. Monuments were reconstructed with huge stones.
P-I-E was the ancestor language of most of the Europe languages and many of those in South Asia.
Match the languages with their language group
| Italic | Russian, Polish, Bulgarian, and Ukrainian |
| Balto-Slavic | Modern Persian, Sanskrit, Hindi |
| Indo-Iranian | English, German, Dutch and Flemish |
| Germanic | Italian, French, Spanish |
REVIEW
Write down in 7 sentences who Franz Bopp is.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Give the subject and purpose of comparative linguistic.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
5. Investigate the map below and list the countries where the following Indo-European languages were spoken:
a) Celtic: _________________________________________________
b) Germanic:_______________________________________________
c) Romance:_______________________________________________
d) Slavic:___________________________________________________
e) Baltic:__________________________________________________
f) Albanian:________________________________________________
g) Greek:__________________________________________________
h) Armenian:_______________________________________________

PROTO-GERMANIC LANGUAGE
| 10000BC | Iron Age | ||||||||||||||||||
| 3000 -250BC |
ACTIVATING THE STUDENTS’ BACKGROUND
1. Do you know …
2.  Do you know who is in the picture?
Do you know who is in the picture?
3. Where was the Roman Empire located in?
4. Who are the so-called barbarians?
5. Who are the Teutons?
6. What Proto-Germanic languages do you know?
7. What Germanic languages do you know?
DATA BASE - PROTO-GERMANIC LANGUAGE
Historically, all the Germanic languages originated from one ancestor language. It is called Proto-Germanic. It developed from P-I-E spoken in pre-historic times. It is believed that this group began as a common language in the Elbe river region about 3,000 years ago.
It was only a spoken language. P-G was most probably spoken just before the beginning of the Christian era. The forms of P-G can only be reconstructed. This was done in the 19th century by methods of comparative linguistics.
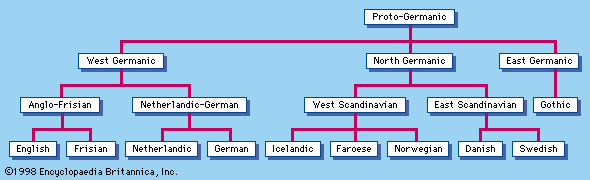 It’s believed that at the earliest stages of history PG was fundamentally one language, though dialectally colored. Dialectal and geographical expansion of the Teutons caused by overpopulation, poor agricultural technique in the areas of their original settlement. Towards the beginning of our era the common period of Germanic history came to an end. The Teutons had extended over a larger territory and the PG languages broke into parts. According to the division PG split into three branches: East Germanic, North Germanic and West Germanic. In due course these branches split into separate Germanic languages.
It’s believed that at the earliest stages of history PG was fundamentally one language, though dialectally colored. Dialectal and geographical expansion of the Teutons caused by overpopulation, poor agricultural technique in the areas of their original settlement. Towards the beginning of our era the common period of Germanic history came to an end. The Teutons had extended over a larger territory and the PG languages broke into parts. According to the division PG split into three branches: East Germanic, North Germanic and West Germanic. In due course these branches split into separate Germanic languages.
The earliest descriptions of the Germans/ Teutons, the ancient tribes that spoke Germanic languages , were known from the writings of Greek and Roman authors. Read the passage below and write out the characteristic features of the Germans.
Pytheas _________________________________________________________
Strabo _______________________________________________________
Plutarch ______________________________________________________
Julius Caesar ____________________________________________________
Pliny _________________________________________________________
Tacitus________________________________________________________
The earliest paper is written by Pytheas who sailed much. It was mentioned that Old Germanic tribes raided the Hellenic countries of south-eastern Europe, Italy and Gall. In the beginning of our era the Greek historian Strabo wrote about Germans nomads. They moved from forest to forest, built houses, and were engaged in cattle bringing.
 The great writer Plutarch described Germans as wild nomadic tribes who had constantly been in war. They were not interested in agriculture or in cattle bringing, but only in war.
The great writer Plutarch described Germans as wild nomadic tribes who had constantly been in war. They were not interested in agriculture or in cattle bringing, but only in war.
The Roman general Julius Caesar fought with them on the Rhine. He took two expeditions against the Germanic tribes who wanted to get hauled on some territories. The Romans defeated the Germans in both expeditions. Caesar wrote that Germans lived in tribal unions. He also gave a detailed description of the structure of their society and peculiarities of their life.
The next great historian Pliny spent many years in the Roman provinces of Low and High Germany. He wrote a book called “Natural History”. He was the first who enumerated and classified the military tribes. It was proved by many scientists.
The Roman historian Tacitus made a detailed description of the life and customs of ancient Germans. Tacitus was a prominent Roman historian. He himself had never been to Germany. Being a Roman senator he got information from military travelers, actions, etc. he also used papers written about the Germans before him. In the time of Tacitus there were constant arm conflicts between the Germans and Romans. Numerous attempts of the Roman generals to conquer the Germanic tribes failed. In the second half of the second century after a short period without wars they began their attacks again. The ancient Germans had a tribal society. In the head of each tribe there was a chief who was called ‘kuning’. Some modern place-names testify to this social structure of the Germans. The whole tribe had the name of the Chief.
According to Pliny there were several Germanic tribes:
V The Vindili
V The Ingvaenoes
V The Istaevones
V The Herminones
V The Hilleviones
Дата добавления: 2018-11-24; просмотров: 448; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
