HISTORICAL DEVELOPMENT OF ENGLISH LANGUAGE
DATA BASE – TRADITIONAL PERIODIZATION
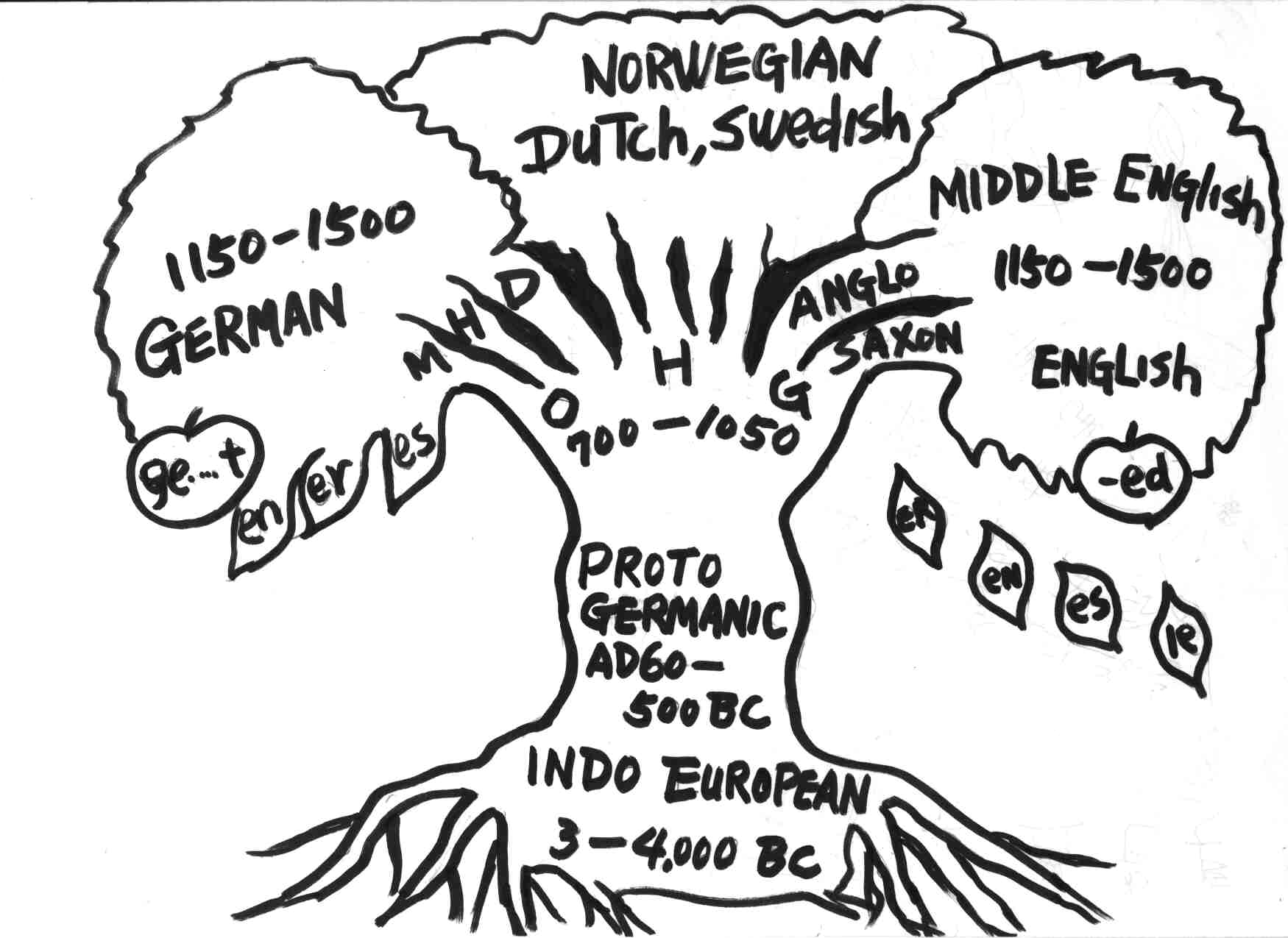 The historical development of a language is a continuous uninterrupted process without sudden breaks or rapid transformations. The commonly accepted, traditional periodization divides English into 3 periods:
The historical development of a language is a continuous uninterrupted process without sudden breaks or rapid transformations. The commonly accepted, traditional periodization divides English into 3 periods:
· Old English (OE)
· Middle English (ME)
· New English (NE)
Ø OE begins with the Germanic settlement of Britain (5th c.) or with the beginning of writing (7th c.) and ends with the Norman conquest (1066);
Ø ME begins with the Norman conquest and ends on the introduction of printing (1475), which is the start of the Modern or NE period;
Ø the NE period lasts to the present day.
Classification of Henry Sweet
H. Sweet suggested to divide all the history into Early, Classical and Late.
Division into chronological periods should take into account both aspects: external and internal.
Pre-written or pre-historical period, which may be called Early Old English. It lasts from the West Germanic invasion of Britain till the beginning of writing that is from the 5th to the close of the 7th cc. It is the stage of tribal dialects of the West Germanic invaders (Angles, Saxons, Jutes and Frisians). The tribal dialects were used for oral communication, there was no written form of English.
· The second historical period extends from the 8th c. till the end of the 11thc. The English language of that time is named as Old English or Anglo-Saxon, it can also be called Written OE.
· The third period Early Middle English lasts from 1066 till the middle of 14th c. the official language of this period was French (Anglo-French or Anglo-Norman)
· The fourth period extends from 14th to the 15th c. and is usually called Classical Middle English. H. Sweet called this period as the period of ‘leveled endings’
· The chronological frames of the Early New English Period are from 1475 to 1660. During this period the first book was printed.
· The 6th period lasts from the middle of the 17th c. to 18th c. it’s usually called ‘the age of normalization and correctness’, or ‘neo-classical age’
· The 7th period extends from 19 to 20th c. Late New English or Modern English.
Language change is gradual, and cannot be as easily demarcated as are historical or political events.
· 450–1100: Old English (Anglo-Saxon) – The language of Beowulf and Alfred the Great.
· 1100–1500: Middle English – The language of Chaucer.
· 1500–1650: Early Modern English (or Renaissance English) – The language of Shakespeare and the King James Bible.
· 1650–present: Modern English (or Present-Day English) – The language as spoken today
REVIEW
Investigate the given texts and suggest what period do they belong to?



Дата добавления: 2018-11-24; просмотров: 1089; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
