Calculationofexpansionparameters
1) Expansionendpressure: 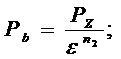
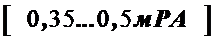 ,
,
2) Expansiontemperature: 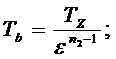
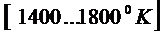 ,
,
3) Mean calculated pressure of the cycle:
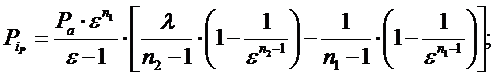
The actual average indicated pressure, taking into account the curvature factor of the indicated diagram.
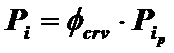 ;
; 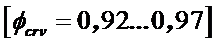
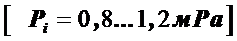 .
.
KeyPerformanceIndicators
1) Indicatedefficiency: 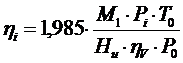 ;
; 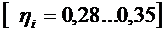 .
.
2) Fuel consumption per one indicator kW. hour:
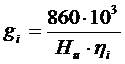 ;
; 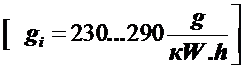 .
.
3) The proportion of indicated pressure used for friction and drive of auxiliary units (pumps, generator, etc.):
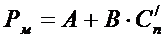 ,
,
whereАиВ – coefficients that depend on the ratio of the stroke of the piston to the diameter of the cylinder (S / D):
atS / D ≤ 1 А = 0,04; В = 0,0135;
atS / D> 1 А = 0,05; В = 0,0155;
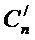 - average piston speed, м/с ,
- average piston speed, м/с ,
[Сп = 9…12м/с, for high-speed motors with
n > 4000min–1we takeСп ≥ 12 м/с].
Mean effective cycle pressure
Ре = Рi – Рм; [Ре= 0,6…0,95 МPа.];
4) Mechanicalefficiency: 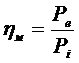 ; [
; [ 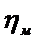 = 0,75…0,82].
= 0,75…0,82].
5) Effectiveefficiency: 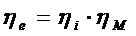 ; [
; [ 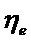 = 0,23…0,29].
= 0,23…0,29].
6) Specificeffectivefuelconsumption:
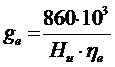 ;
; 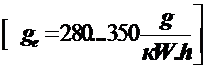 .
.
Basic dimensions of the cylinder
1) Working volume of one cylinder
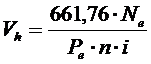 .
.
2) Diameter of the inner surface of the cylinder:
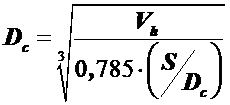 .
.
3) Pistonstroke
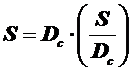 .
.
Finally, for the convenience we round up values to integers.
4) Speed (average) of the piston: 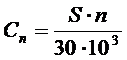 .
.
Speed 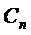 should not differ from the chosen one by more than 5...10 %, otherwise, it is necessary to recalculate the effective indicators.
should not differ from the chosen one by more than 5...10 %, otherwise, it is necessary to recalculate the effective indicators.
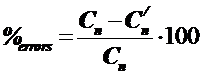 < (5…10 %).
< (5…10 %).
5) Enginedisplacement 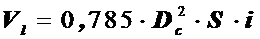 .
.
6) Effectivepower 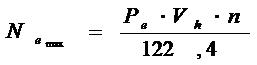 .
.
7) Indicatedpower 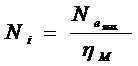 .
.
8) Volumetricpower 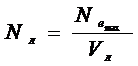 .
.
9) Effective torqueМе = 5266· 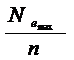 , N·m.
, N·m.
10 ) Indicatedtorque 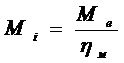 .
.
An example of thermal calculation of a diesel engine
engine type - diesel;
number of cylinders – 8 (row orV – figurative);
Nominal power: 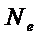 = 110 кW;
= 110 кW;
Engine crankshaft speed:п = 3000min-1;
Compression ratio:ε = 16,5;
Coefficient of excess air: = 1,35;
Piston stroke to cylinder diameter ratio:S / D = 0,9;
type of mixture - with direct injection of fuel;
fuel - diesel, compositionС = 0,87; Н = 0,126; О2 = 0,004;
lowest calorific valueНи = 10000 kcal / kg.
Additionaldata selection
1) Ambientpressure:Р0 = 0,1 МPа;
2) AmbienttemperatureТ0 = 3000 К;
3) Residual gas pressureРr = 0,12 МPа;
4) Residual gas temperatureТr = 8500К
[Тr=700…9000 К];
5) The air temperature at the time it enters the cylinder
|
|
|
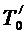 = Т0 +ΔТ = 300 + 30 = 3300 К;
= Т0 +ΔТ = 300 + 30 = 3300 К;
[ΔТ = 20…400].
6) The polytrophic exponent n1 and the polytrophic exponents n2 are taken according to the speed regime:
[п1 = 1,28…1,4]; п1 = 1,38;
[п2 = 1,18…1,28]; п2 = 1,23.
7) Coefficient of active heat release
ξ = 0,78; [ξ = 0,7…0,85].
6) Gas pressure in the cylinder at the end of the intake
Ра = 0,089 МPа, [Ра =( 0,85…0,95) Ро].
For high-speed diesels take the lower limit.
Determination of intake properties
1) Coefficientofresidualgases
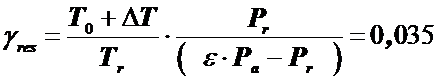 ,
,
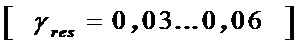 .
.
2) Determination of the temperature of the gases in the cylinder at the end of the intake.
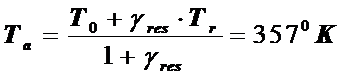 ,
,
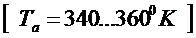 .
.
3) Fillingratio
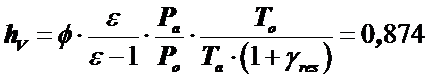 ,
, 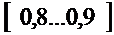
where 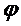 - charge factor,
- charge factor, 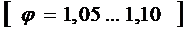 .
.
Determiningof the compression parameters
The pressure of gases in the cylinder at the end of compression
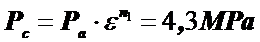 ,
, 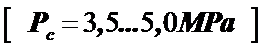 .
.
The temperature of the gases in the cylinder at the end of compression
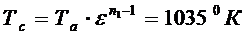 ,
, 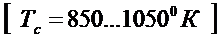 .
.
Workingheatcalculation
Theoretically necessary amount of air for complete combustion of 1 kg of fuel
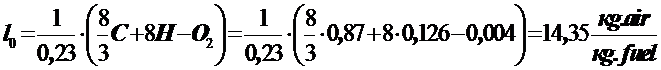 ,
,
orin moles 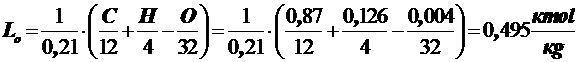 .
.
1) The total amount of air
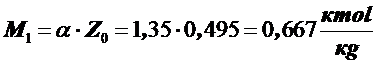 ,
,
The total amount of combustion products M2 will consist of combustion products at α = 1 and excess air which is not participating in combustion 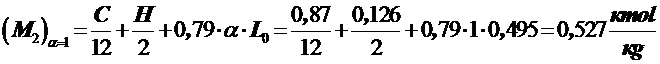 .
.
Excess amount of fresh air
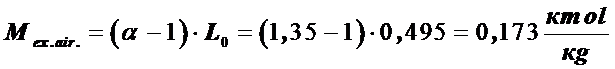 ,
,
Total amount of combustion products
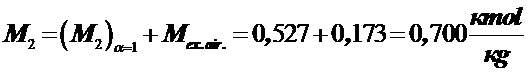 .
.
Chemical coefficient of molecular change
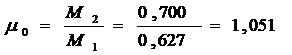 .
.
The actual coefficient of molecular change
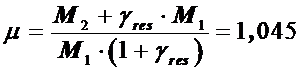 .
.
Дата добавления: 2018-02-28; просмотров: 271; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
