Determination of end parameters of combustion
Example of the calculation of SI engine
Nominal power:Nе = 73,53 кW (100hp.);
Engine crankshaft speed:n = 3600 min-1;
Compression ratio:ε = 7,2;
Coefficient of excess air:α = 0,9;
Number of cylinders:i = 6 Р;
Piston stroke to cylinder diameter ratio: S/D = 0,95.
Additionaldata selection
1) Ambientpressure:

2) Ambienttemperature
Т0 = 300 0К
3) Residualgaspressure
Рr = 0,12 МPа, [Рr= (1,1…1,25) Р0]
(In square brackets the range is given).
For low-speed engines closer to the lower limit, and for high-speed engines to the upper limit.
4) Residualgastemperature
Тr = 10500 К, [Тr= 900…10500К]
For high-rpm engines - closer to the upper limit.
5) The temperature of the fresh combustion mixture at the time it enters the cylinder

Heating of the fresh combustionmixture charge  [ΔТ = 10…200С].
[ΔТ = 10…200С].
6) The polytrophic exponent n1 and the polytrophic exponents n2 are taken according to the speed regime or statistical data


[  ]; [
]; [  ];
];
7) Coefficient of active heat release  , [
, [  ].
].
8) Gas pressure in the cylinder at the end of the intake
Ра = 0,085 МPа, [Ра = (0,8…0,9) Р0].
9) Lowest calorific value of gasolineНи = 10500 kcal /кg
[1cal = 4,1868 J].
Determination of the end of intake
1) Coefficientofresidualgases
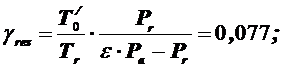 [0,06…0,10].
[0,06…0,10].
2) Determination of the temperature of the gases in the cylinder at the end of the intake.
 [350…3900 К].
[350…3900 К].
3) Fillingratio
 [0,75…0,85],
[0,75…0,85],
where  - charge factor[1,05…1,1].
- charge factor[1,05…1,1].
Determining parameters at the end of the compression
1) The pressure of gases in the cylinder at the end of compression
 [1,0…1,5 МPа].
[1,0…1,5 МPа].
2) The temperature of the gases in the cylinder at the end of compression
 [650…7800 К].
[650…7800 К].
Workingheatcalculation
Composition of gasoline: С = 0,855; Н = 0,145; О2 = 0.
Molecular weight of gasolineμ = 110…120.
1) Theoretically necessary amount of air for complete combustion of 1 kg of fuel
 кg of air./ кg of fuel ,
кg of air./ кg of fuel ,
where 0,23 – mass fraction of oxygen in air;
In moles

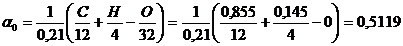 кg of air./ кg of fuel,
кg of air./ кg of fuel,
где 0,21 – volumefraction of oxygen in air;
2) Calculation of the amount of combustible mixture before combustion in kg
 кg.
кg.
3) The amount of the combustible mixture in moles
 kmol.
kmol.
4) Calculation of combustion products atα = 0,9.
|
|
|
Under incomplete combustion (α< 1) the following gas components are released::СО; СО2; Н2; Н2ОandN2.
For the caseα< 1 wetakeК = 0,5, (К – number of moles of hydrogen and carbon monoxide ratio. Whenα> 1- К = ∞ ).
4.1) Number of molesСОin combustion products
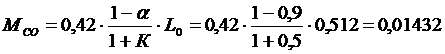 kmol/ кg;
kmol/ кg;
4.2) NumberofmolesСО2in combustion products:
 kmol/ кg;
kmol/ кg;
4.3) NumberofmolesН2 in combustion products:
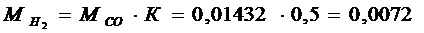 kmol/ кg;
kmol/ кg;
4.4) NumberofmolesН2Оin combustion products:

 kmol/ кg;
kmol/ кg;
4.5) NumberofmolesN2 in combustion products:
 kmol/ кg;
kmol/ кg;
5) Total amount of combustion products:
 =0,5078 kmol/ кg;
=0,5078 kmol/ кg;
6) Calculation of the loss of the net calorific value of gasoline for the case
α< 1due to lack of air:
 kmol/ кg;
kmol/ кg;
7) Calculation of the chemical coefficient of molecular change:
 .
.
8) Determination of the actual coefficient of molecular change:

Determination of end parameters of combustion
The combustion equation for gasoline engines is:
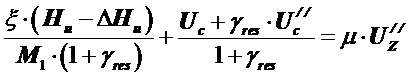 .
.
For the simplicity the internal energies of 1 kmol of fresh mixture and combustion products for different values of α,the following graphs are made.U = f (t)in the temperature range300…8000Си1900…25000С (fig. 2.1; 2.2).
To simplify the calculation, the heat capacity of the fresh mixture is assumed to be equal to the heat capacity of the air.
The values of internal energies of air and combustion products for gasoline under various values α and for diesel fuel atα = 1 in the temperature rangefrom00Сto 25000Сare presented in the table 2.1.
For this enginetс = Тс – 273 = 779 – 273 =5060С.
From the graphs (fig. 2.1) forα = 0,9 sowe have: the internal energy of 1 kmol of fresh mixture at the compression temperaturetс =5060С.
Uc = 2635 kmol/ кg.
The same applies for combustion products attс =5060С–  kmol/ кg;we denote it by "A", then the left side of the combustion equation is:
kmol/ кg;we denote it by "A", then the left side of the combustion equation is:
 kcal/kmol.
kcal/kmol.
When completing a course project, the student must build graphs similar to fig. 2.1. and 2.2. for the temperature ranges calculated for its variant.
|
|
|
Consequently
 kcal/kmol,
kcal/kmol,
where  – internal combustion energy at combustion temperatureТZ.
– internal combustion energy at combustion temperatureТZ.
Maximum combustion temperature valuetZin0Сdetermined from the graph  (fig. 2.2) forα = 0,9.
(fig. 2.2) forα = 0,9.
Table 2.1.
Internal energy of air and combustion products at different temperatures
| Temperature 0 С | Internal energy of combustion products kcal / kmol | Internalenergyofair kcal / kmol | |||
| Petrol α = 1 | Petrol α = 0,9 | Petrol α = 0,8 | Dieselfuel α = 1 | ||
| 0 100 200 | 0 538 1093 | 0 526 1083 | 0 522 1071 | 0 538 1094 | 0 498 1002 |
| 300 400 500 | 1668 2265 2883 | 1651 2241 2851 | 1632 2211 2810 | 1670 2265 2890 | 1520 2052 2601 |
| 600 700 800 | 3522 4182 4860 | 3481 4131 4800 | 3429 4068 4724 | 3530 4200 4870 | 3166 3746 4340 |
| 900 1000 1100 | 5555 6264 6985 | 5483 6181 6892 | 5394 6079 6777 | 5550 6280 7000 | 4946 5561 6186 |
| 1200 1300 1400 | 7720 8465 9219 | 7616 8349 9088 | 7487 8206 8935 | 7740 8480 9240 | 6820 7461 8109 |
| 1500 1600 1700 | 9954 10751 11528 | 9839 10597 11362 | 9673 10416 11167 | 10000 10750 11550 | 8763 9421 10080 |
| 1800 1900 2000 2100 | 12309 13097 13889 14686 | 12131 12907 13687 14472 | 11923 12685 13451 14222 | 12300 13120 13900 14700 | 10750 11420 12100 12780 |
| 2200 2300 2400 2500 | 15488 16291 17098 17907 | 15262 16053 16848 17606 | 14998 15775 16557 17341 | 15520 16310 17100 17920 | 13460 14140 14830 15520 |
U,
kcal / kmol

| α = 1 α = 0,9 α = 0,8 | |||
| Combus-tionproducts | ||||
| Air | ||||
|
|
|
5000
4000
3000
2000
1000
300 400 500 600 700 800 t0C
Fig. 2.1. The values of the internal energy of air and combustion products for various values of α in the temperature ranget = 300…8000С.
(This chart is derived from the table 2.1.)
U,
kcal / kmol

| Combus-tionproducts | α = 1 | |||
| α = 0,9 | α = 0,8 | ||||
| Air | |||||
| α = 1 α = 0,9 α = 0,8 |
16000
15000
14000
13000
12000
11000
1900 2000 2200 2400 2500 t0C
Fig. 2.2. The values of the internal energy of air and combustion products for various values of α in the temperature ranget = 300…8000С.
(This chart is derived from the table 2.1.)
The value 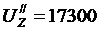 kcal/kmol,corresponds to the combustion temperature
kcal/kmol,corresponds to the combustion temperature
tZ = 24570С,thenТZ = tZ + 273 = 2457 + 273 = 2730 0 К;
[ТZ= 2400…2730 0 К].
Estimated combustion pressure:
 МPа.
МPа.
Increase of pressure:  ,
,
Maximum cycle pressure, taking into account the curvature on the indicator diagram 
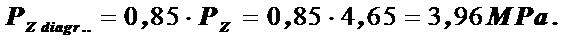
Дата добавления: 2018-02-28; просмотров: 277; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
