Explain kinetics of emulsion polymerization.
The monomer is dispersed in the aqueous phase as a homogeneous emulsion.
Benefits:
• High speed of polymerization;
• A slight change in viscosity;
• Easy control of heat transfer;
• Use of water as a solvent;
• The ability to obtain high-molecular compounds with a narrow value of MMP;
• Possibility to adjust the MM by the ratio of monomer / surfactant / water;
• The ability to use the resulting polymer emulsion to produce products by wetting.
Disadvantages:
• The need to use additional substances (surfactants, emulsifiers);
• Wastewater treatment;
• To isolate the polymer from the emulsion, a kaogulant is needed;
Application:
The polymerization of vinyl chloride, butadiene, chloroprene, vinyl acetate, acrylates and methacrylates is carried out.
Explain the mechanism and kinetics of cationic polymerization.
Cationic polymerization is the process of formation of macromolecules, in which the active sites carry a positive charge, and the initiator is a source of positive charge.
The mechanism of cationic polymerization:
Cationic polymerization is characteristic for vinyl compounds with electron-donor substituents: isobutylene, butyl vinyl ether, α-methylstyrene, etc.

Isobutylene polymerizes only by the cation mechanism: 
Stages of cationic polymerization:
1. Initiation:

2. Chain growth:

3. The chain termination reaction (each breakdown reaction proceeds according to its mechanism
- It is possible to stop the chain growth by attaching a negative catalyst ion to the carbonium macroion:

- However, most often the termination of chain growth is due to the detachment of the negative ion of the hydrogen catalyst from the polymer chain: 
4.  Adverse Reactions:
Adverse Reactions:
Explain the mechanism and kinetics of anionic polymerization.
anionic polymerization.— this is the process of formation of macromolecules, in which the active centers carry a negative charge.

Катализаторы анионной полимеризации
1. Alkali metals 2. Amids of alkali metals
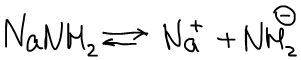
2. Na- и Li-органические соединения, н-р: Na-нафталиновый комплекс.
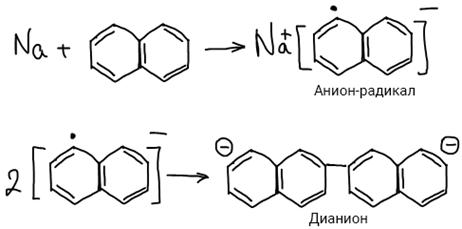
The mechanism of anionic polymerization Anionic polymerization is characteristic for vinyl compounds with electron-withdrawing substituents: acrylonitrile, alkyl acrylates, styrene, etc.


The main stages :
1. Iniciation
And "X" is not a halogen. Halogenated vinyl does not come into this reaction, they are inactive (PVC is obtained by a radical mechanism).
2. Growth chain

3. Reaction of chain termination (proceeds with the participation of a solvent, for example ammonia) 
Дата добавления: 2018-02-15; просмотров: 589; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
