Explain the mechanism and kinetics of free-radical polymerization.
Explain the mechanism and kinetics of free-radical polymerization. 2 Explain kinetic features of alternating copolymerization. 3 Explainfeatures of three-dimensional free-radical polymerization. 4 Explain kinetics of emulsion polymerization. 5 Explain the mechanism and kinetics of cationic polymerization. 6 Explain the mechanism and kinetics of anionic polymerization. 7 Coordination polymerization. Explain monometallic and bimetallic mechanisms of stereoregular polymerization in the presence of Ziegler-Natta catalysts. 8 Explain the mechanism of inhibition of alternating copolymerization. 9 Living radical polymerization. Give definition, classification and characteristics of iniferters. 10 Explain features of three-dimensional living radical copolymerization. 11 Explain features of organometallic radical polymerization 12 Explain the mechanism of reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer process. 13 Explain the general atom transfer radical polymerization mechanism. 14 Explain the general stable free radical polymerization mechanism. 15 Describe techniques of living cationic polymerization. Give examples. 16 Discuss diffusion phenomena in radical polymerization. Gel-effect in radical polymerization. 17 Evaluate advantages and disadvantages of spin traps in comparison with other reversed inhibition methods of controlled/living radical polymerization. Give example. 18 Evaluate advantages and disadvantages of Ziegler-Natta catalysts. 19 Evaluate advantages and disadvantages iodine transfer radical polymerization technique in comparison with other methods of controlled radical polymerization. Give example. 20 Evaluate advantages and disadvantages of reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer process in comparison with other methods of controlled radical polymerization. Give example. 21 Evaluate advantages and disadvantages of atom transfer radical polymerization in comparison with other methods of controlled radical polymerization. Give example. 22 Evaluate advantages and disadvantages of nitroxide-mediated radical polymerization in comparison with other methods of controlled radical polymerization. Give example. 23 Evaluate advantages and disadvantages, common features and differences between radical and controlled/living radical polymerization. 24 Evaluate advantages and disadvantages of radical polymerization in the presence of alkoxyamines in comparison with other methods of controlled/living radical polymerization. Give example. 25 Compare efficacy of low-molecular and polymeric RAFT-agents for control of molecular-mass characteristics of polymers. Draw appropriate equations and graphs. 26 Evaluate advantages and disadvantages of alkoxyamines used in three-dimensional living radical copolymerization. 27 Evaluate major difference between radical and ionic polymerization. 28 Evaluate advantages and disadvantages and major difference between cationic and living cationic polymerization. 29 Find the key differences between anionic and cationic polymerization. 30 Discuss gel point in three-dimensional free-radical polymerization. 31 Use of RAFT-polymerization for controlled synthesis of liquid crystal polymers. 32 Use of nitroxide-mediated radical polymerization for controlled synthesis of gradient copolymers. 33 Use of stable free radical polymerization for synthesis of low-molecular acrylates. 34 Propose mechanism of ATRP in the presence of titanium complexes. Draw appropriate formulas. 35 Propose mechanism of initiation in the presence of Ni complexes. Draw appropriate formulas. 36 Specify the factors influenced on the mechanism of controlled radical polymerization in the presence of organometallic compounds. Draw appropriate formulas. 37 Use of spin traps technique for kinetic investigation of elementary steps of RAFT-polymerization. 38 Propose method of determination of relative constants of chain transfer to monomer and initiator in free-radical polymerization. 39 Study of the mechanism of alternating copolymerization by spin traps method. 40 Study of the mechanism of alternating copolymerization by electron paramagnetic resonance method. 41 Evaluate organometallic compounds as reversible spin traps and molecular weight regulators in processes of living radical polymerization. 42 Study of chain transfer reactions to the polymer by spin trap. 43 Draw the scheme of the mechanism of radical polymerization inhibition by quіnons. 44 Write the main reactions of chain transfer and chain break of acrylonitrile polymerization in the presence of butyl lithium. 45 Find the major difference between reactions of photochemical and chemical initiation of radical polymerization. Write the appropriate equations.
|
|
|
Explain the mechanism and kinetics of free-radical polymerization.
|
|
|
Radical polymerization is the process of obtaining high-molecular compounds from low-molecular compounds without the isolation of by-products, where the active center is a free-radical particle (a particle with an unpaired electron). This process is realized due to multiple bonds (C = C, C = O, etc.) cycles containing heteroatoms (N, S, O). The polymerization products have the same elemental composition as the original monomers.
The compounds containing at least one multiple bond, as well as cycles, are capable of polymerization. The reactivity of the monomer depends on its structure, the conjugation of the double bond in the monomer molecule, the number and relative position of the substituents, their polarization phenomenon on the double bond.
Radical polymerization proceeds along a chain mechanism and is described by the kinetics of an unbranched chain reaction.
The main stages of the chain reaction:
I. Initiation - formation of active centers;
II. Growth of the chain - sequential attachment of monomers to the active center;
III. An open circuit - the death of the active center;
IV. Transmission of the chain is the transfer of the active site to another molecule.
To study the kinetics of radical polymerization, it is necessary to consider the dependence of the reaction rate and the degree of polymerization on the concentration of the starting materials, pressure and temperature.
Concentration on initiator
Concentration of monomer
Let's consider each stage:
I. Initiation

II. Growth of the chain
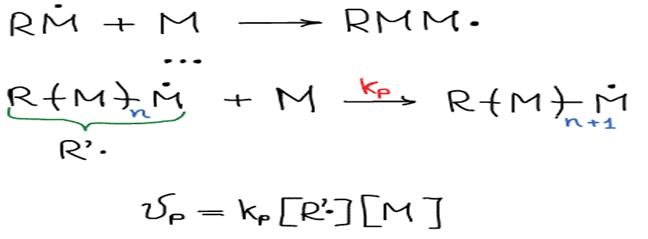
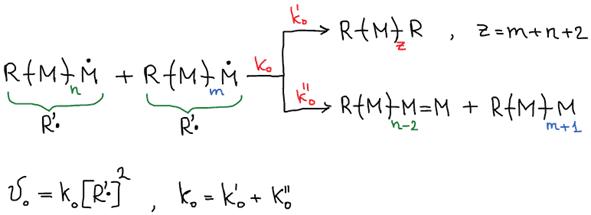
III. Chain Termination
Дата добавления: 2018-02-15; просмотров: 583; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
