Answer the questions about the text and translate the text in writing.
1. What are the main disorders that affect the heart and the blood vessels?
2. Are all the conditions congenital?
3. What diseases are the most dangerous?
4. What is the difference between Hodgkin’s disease and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma?
Exercises
Look at the diagram and translate all the terms into Russian:
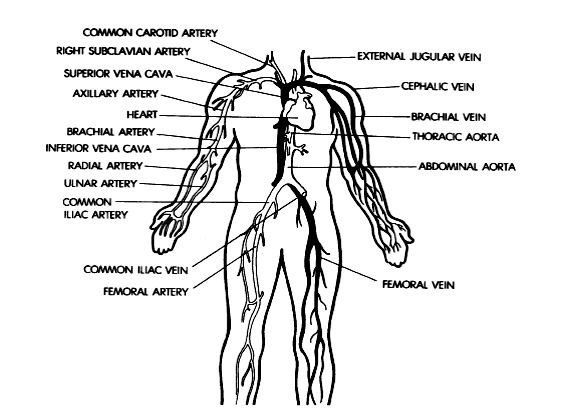
Give the Russian terms and then the English equivalents of the following definitions. Choose from the list of the English terms given below.
1. A localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel, usually an artery, caused by weakness of the vessel wall; may eventually burst.
2. A feeling of constriction around the heart or pain that may radiate to the left arm or shoulder usually brought on by exertion; caused by insufficient blood supply to the heart.
3. Any abnormality in the rate or rhythm of the heartbeat (literally “without rhythm”; note doubled r). Also called dysrhythmia.
4. The development of fatty, fibrous patches (plaques) in the lining of arteries, causing narrowing of the lumen and hardening of the vessel wall.
5. A slow heart rate of less than 60 beats per minute.
6. Sudden damage to the brain resulting from reduction of blood flow. Causes include atherosclerosis, embolism, thrombosis, or hemorrhage from a ruptured aneurysm; commonly called stroke.
7. Enlargement of the ends of the fingers and toes caused by growth of the soft tissue around the nails. Seen in a variety of diseases in which there is poor peripheral circulation.
8. Bluish discoloration of the skin caused by lack of oxygen.
9. Thrombophlebitis involving the deep veins.
10. An aneurysm in which blood enters the arterial wall and separates the layers. Usually involves the aorta.
11. Difficult or labored breathing (-pnea).
12. Swelling of body tissues caused by the presence of excess fluid. Causes include cardiovascular disturbances, kidney failure, inflammation, and malnutrition.
13. Obstruction of a blood vessel by a blood clot or other matter carried
in the circulation.
| aneurysm | angina pectoris | cyanosis |
| clubbing | deep vein thrombosis (DVT) | arrhythmia |
| cerebrovascular accident (CVA) | bradycardia | atherosclerosis |
| dyspnea | dissecting aneurysm | edema |
| embolism |
4. Find the Russian and English equivalents to the following definitions:
|
|
|
- largest artery in the body;
- small artery;
- largest type of blood vessel (carries blood away from the heart to all parts of the body);
- smallest blood vessel;
- the blood vessels that branch from the aorta and carry oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle;
- an artery carrying oxygen-poor blood from the heart to the lungs;
- a vein carrying oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart;
- largest vein in the body;
- small vein.
Complete the following text using words given in the box. Translate the text into Russian orally.
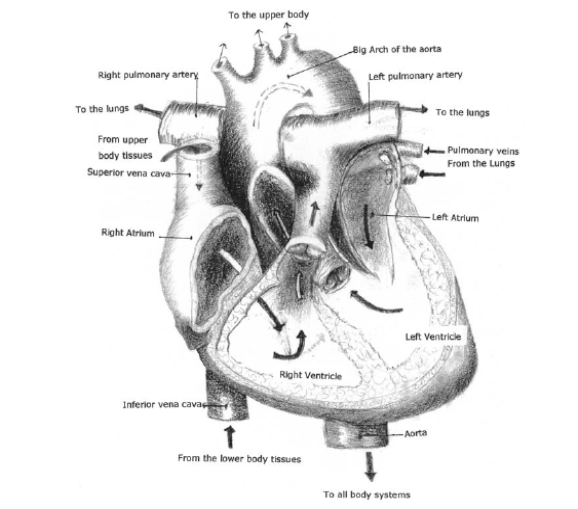
| oxygen-deficient | Heart | oxygen-enriched | ||
| right and left pulmonary | Circulation | arteries | ||
| superior vena cava | right atrium | systemic circuit | ||
| systemic circulation | Pulmonary | circulatory | ||
| cone-shaped | Apex | arteries | ||
| аrteries | the aorta | cavities | ||
| Veins | oxygen-depleted | inferior vena cava | ||
| Rate | Tissues | right ventricle | ||
| pulmonary | left ventricle |
| ||
The ______ is the pump of the _________system. It is about the size of a fist. It’s hollow and ________, with its _________at the bottom. The heart uses ________ to deliver oxygen-rich blood to the cells, tissues, and organs. __________blood returns to the heart via the veins. The heart then pumps ________ blood to the lungs where it becomes ________and returns to the heart for another circulatory round.
Each day, the heart beats about 100,000 times at a _______of approximately 70 beats per minute.
The heart contains four _______, or chambers: two on the right side (pulmonary heart), two on the left (systemic heart). ____________ carries blood to and from the lungs. The _____________ supplies oxygen- and nutrient-rich blood to the body cells, tissues, and organs. After completing the _____________, all blood
returns to the heart through the two main veins, the _______________and the___________. These vena cavae meet at the ___________, a thin-walled chamber that serves as a collecting station. From the right atrium, the blood flows downward into the _____________, the smaller of the two muscular heart chambers. When the ventricle contracts, blood is forced upward. It is pumped through the____________, which lead to the two lungs. This begins the pulmonary circuit. Blood is pumped to the lungs for oxygenation then returns to the heart for distribution to the body.
|
|
|
Blood from the lungs returns to the left atrium of the heart via the________________. From the left atrium (a collecting station) blood flows downward and enters the ___________, which is the larger of the two side-by-side muscular chambers. When the ventricles contract, simultaneously, the oxygenated blood is forced upward from the left ventricle through the big arch and into__________. __________arising from the aorta reach all parts of the head, upper extremities, thorax, abdomen, pelvic cavity, and lower extremities. The blood nourishes the _____________ and returns to the heart to complete the circulation.
Some terms referring to abnormal conditions of the heart or blood vessels can be confusing. Read each definition carefully and select the terms that refer to a condition or procedure involving only the heart.
_ Thrombus is a circulating blood clot.
_ Coronary thrombosis is a heart attack caused by a blood clot that occludes
(closes off ) a coronary vessel of the heart.
_ Embolus is a foreign or abnormal particle circulating in the blood, such
as a bubble of air, a blood clot, or cholesterol plaque.
_ Embolism is the sudden obstruction of a blood vessel by an embolus.
_ Cardiac arrest is the complete cessation of heart function. (If the
heartbeat cannot be restored, the patient dies.)
_ Fibrillation means very fast and irregular heartbeat.
_ Defibrillation means using an electrical spark to shock the heart and
bring about a slower and regular heartbeat.
Now review the terms and their meanings again. This time choose each term that refers to a condition of the blood or blood vessels.
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2019-07-15; просмотров: 578; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
