The Turboprop/Turboshaft Engine
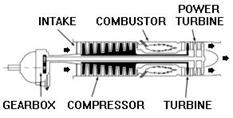
A turboprop, or turboshaft engine.
A turboprop engine uses thrust to turn a propeller. As in a turbojet, hot gases flowing through the engine rotate a turbine wheel that drives the compressor. The gases then pass through another turbine, called a power turbine. This power turbine is coupled to the shaft, which drives the propeller through gear connections.
A turboshaft is similar to a turboprop engine, differing primarily in the function of the turbine shaft. Instead of driving a propeller, the turbine shaft is connected to a transmission system that drives helicopter rotor blades; electrical generators, compressors and pumps; and marine propulsion drives for naval vessels, cargo ships, high speed passenger ships, hydrofoils and other vessels.
The Turbofan Engine
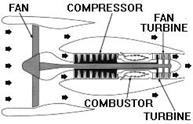
A high bypass turbofan engine.
A turbofan engine is basically a turbojet to which a fan has been added. Large fans can be placed at either the front or rear of the engine to create high bypass ratios for subsonic flight. In the case of a front fan, the fan is driven by a second turbine, located behind the primary turbine that drives the main compressor. The fan causes more air to flow around (bypass) the engine. This produces greater thrust and reduces specific fuel consumption.
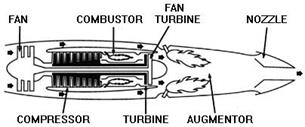
A low bypass turbofan engine.
For supersonic flight, a low bypass fan is utilized, and an augmentor is added for additional thrust.
Дата добавления: 2019-07-15; просмотров: 176; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
