Oxidation of nonsaturated fat acids
Enoyl-CoA Hydratase, a key enzyme in 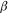 -oxidation of saturated fatty acids, acts on trans double bonds, but cannot act on the cis double bonds of unsaturated fatty acids. Instead, cells must rely on two additional enzymes, enoyl-CoA isomerase and 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase, to complete the
-oxidation of saturated fatty acids, acts on trans double bonds, but cannot act on the cis double bonds of unsaturated fatty acids. Instead, cells must rely on two additional enzymes, enoyl-CoA isomerase and 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase, to complete the 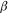 -oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids.
-oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids.
1. Enoyl-CoA Isomerase catalyzes conversion of cis double bonds at positions 3-4 to trans double bonds at positions 2-3.
2. 2,4-Dienoyl-CoA Reductase catalyzes the reduction of the conjugated double bonds, cis 4-5 and trans 2-3 to a single cis double bond between carbons 3-4. This reaction uses electrons from NADPH.
In each case, enoyl-CoA isomerase and 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase converts an intermediate with a cis double bond into an intermediate with a trans double bond. Moreover, the trans double bond has the appropriate structure to be handled by the enzymes involved in the 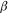 -oxidation of saturated fatty acids.
-oxidation of saturated fatty acids.
It should be noted that enoyl-CoA isomerase and 2,4-dienoyl-CoA reductase only help metabolize dietary unsaturated fatty acids with double bonds in the cis configuration. Dietary fatty acids with trans double bonds are not readily metabolized and may pose a health hazard.
β-Oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids poses a problem since the location of a cis bond can prevent the formation of a trans-Δ2 bond. These situations are handled by an additional two enzymes,Enoyl CoA isomerase or 2,4 Dienoyl CoA reductase.
Whatever the conformation of the hydrocarbon chain, β-oxidation occurs normally until the acyl CoA (because of the presence of a double bond) is not an appropriate substrate for acyl CoA dehydrogenase, or enoyl CoA hydratase:
· If the acyl CoA contains a cis-Δ3 bond, then cis-Δ3 -Enoyl CoA isomerase will convert the bond to a trans-Δ2 bond, which is a regular substrate.
· If the acyl CoA contains a cis-Δ4 double bond, then its dehydrogenation yields a 2,4-dienoyl intermediate, which is not a substrate for enoyl CoA hydratase. However, the enzyme 2,4 Dienoyl CoA reductase reduces the intermediate, using NADPH, into trans-Δ3 -enoyl CoA. As in the above case, this compound is converted into a suitable intermediate by 3,2-Enoyl CoA isomerase.
Дата добавления: 2016-01-04; просмотров: 23; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
