Basal nuclei (a stria-pallidar system)
Include: a corpus striatum (a shell and a caudate nucleus), a pale ball (pallidum); functionally belong: the black substance and the subthalamic nucleus of the hypothalamus
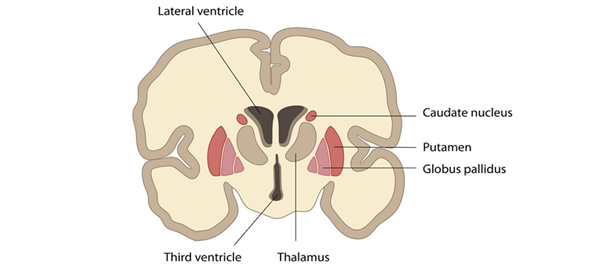
Functions:
provision of motor programs and motor reactions, development and implementation of conditioned reflexes, regulation of ANS activity.
Symptoms of desease:
1) Corpus striatum - hyperkinesia: tremor, athetosis, chorea.
2) Pale ball - "emotional dullness", hypodynamia, tremor when moving.
3) black substance - Parkinson's syndrome - trembling paralysis: tremor, mask-like face, hesitant gait, difficult to start and finish of movements.
Cortex of the great hemisphere
The anterior central gyrus is a "motor homunculus“.
The cortex consists of six layers of cells
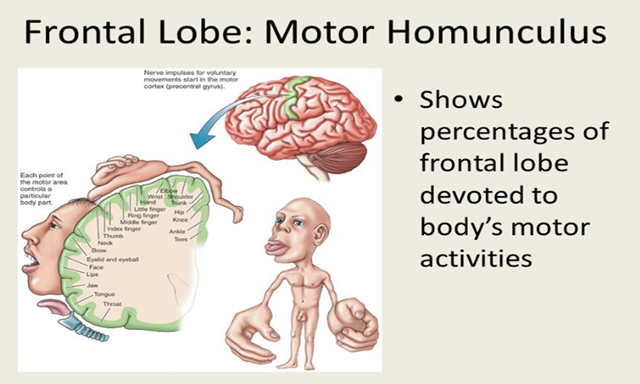
It has motor columns - functional associations of neurons controlling the activity of the muscles of one joint.
In the fifth and third layers of the cortex there are large and small pyramidal cells, descending pathways begin from them.
The function of the cortex is to realize the intentions of the movements. The potential of readiness for movement is detected.
Efferent connections of the motor cortex
Cortico-spinal and cortico-bulbar pyramidal pathways (terminate on alpha-motoneurons, provide rapid activation of motor reactions).
Extrapyramidal pathways are directed to the thalamus, the reticular formation, the red nucleus, the basal ganglia, the cerebellum, and then to the spinal cord and brain stem (end in gamma motor neurons), provide correction of motor programs
Дата добавления: 2022-12-03; просмотров: 29; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
