Tonic reflexes of the brain stem
The somatic system of CNS
The somatic system provides motor functions and all kinds of sensitivity.
Structure of the somatic system: sensory and motor departments
The sensory department includes: receptors, pathways, sensitivity centers
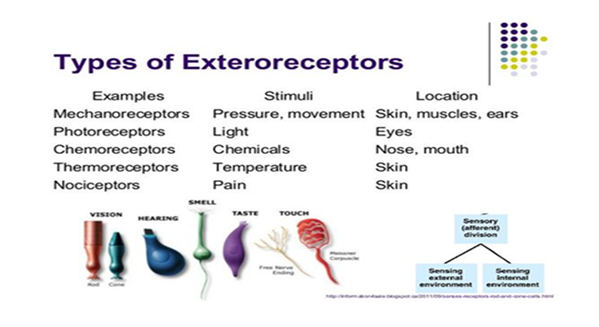
1. Receptors: exteroreceptors, interoreceptors, vestibuloceptors
Exteroreceptors receive irritation from the external environment,
Interoreceptors from the internal environment.
1. Receptors: exteroreceptors, interoreceptors, vestibuloceptors
• Exteroreceptors receive irritation from the external environment,
• Interoreceptors from the internal environment.
2. Afferent pathways:
In the spinal cord:
1) the paths located in the posterior columns conduct impulses from proprioceptors of muscles and tendons;
2) way in the middle columns: spinal-cerebellar pulses - from the muscles to the cerebellum and spinal-thalamic - from the receptors of the skin and internal organs to the thalamus .
In the brain stem:
pass all the above-named paths and they are joined by paths from sensitive cranial nerves.
3. Sensitivity Centers
The thalamus is the subcortical center, where all the afferent pathways are switched, except for the olfactory
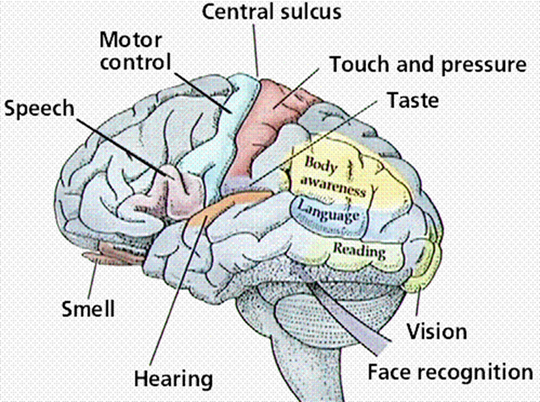
The posterior central gyrus of the cortex of the large hemispheres is the "sensory homunculus," here the sensitivity of the entire body
Types of movements
Movement in space (walking, running, dancing, jumping).
Maintaining the posture, muscle tone.
Communicative movements (facial expressions, gestures, speech).
Workers' movements are labor skills.
Motor department
It is represented by the centers of the spinal cord, brain stem, cerebellum, basal nuclei, cerebral cortex.
Also here are the descending conducting ways: pyramidal and extrapyramidal.
Functions of the spinal cord
Conductor
Reflex
Integrative
The spinal cord contains up to 13 million neurons, 3% - motoneurons (alpha and gamma), intermediate and vegetative
Skeletal muscle control centers are located in all parts of the spinal cord, innervation according to the segmental principle:
Knee reflex - L2 - L4
Achilles - S1-S2
Abdominal reflexes - Th 8 - Th 12
The ulnar reflex is C5-C6
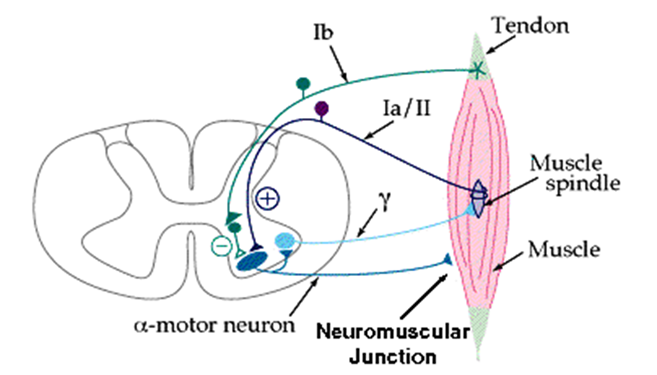
Also in the spinal cord are the centers of reflexes from the Golgi receptors, the stepping reflex, maintaining muscle tone
The stem of the brain
1) The middle brain is represented by the legs of the brain and plate of quadruple.
It contains the nuclei of III and IV pairs of cranial nerves, a red nucleus, a black substance, reticular formation and in the quadruples - primary visual and auditory centers.
|
|
|
The red nucleus and the reticular formation are centers of tonic reflexes.
Here is the center of the orienting reflex – “What is it”
Tonic reflexes of the brain stem
Reflexes, regulating muscle tone, provide a natural posture, its restoration and preservation when moving in space.
Static reflexes
a) Postural reflexes directions to maintain the natural posture.
b) Straightening reflexes consist of raising the head and straightening the neck, and then, the trunk.
Statokinetic reflexes arise with accelerated rectilinear and rotational motions.
Lift reflexes - when stopping the downward moving elevator and at the beginning of the rise, the tone of the extensor muscles of the lower limbs increases
Reflexes of rotation - nystagmus of head and eyes
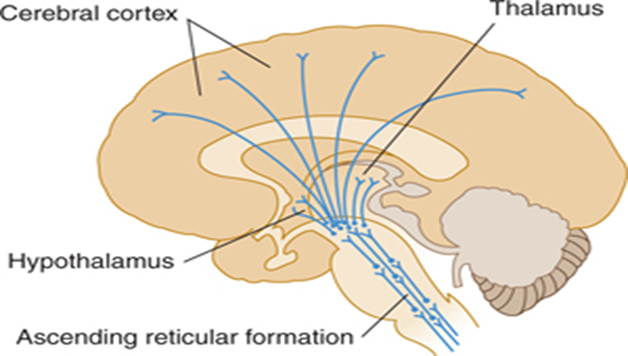
Reticular formation
Reticular formation is an accumulation of neurons, different in function and size, connected by a multitude of nerve fibers that form a network in the brain stem.
RF exerts upward and downward influences on brain structures
Back brain
It is represented by a bridge and oblong brain, contains the nuclei of eight pairs of cranial nerves: from V to XII, the reticular formation, regulates chewing reflexes, sucking, swallowing, postural reflexes, eye movement.
Here is the vital breathing center
Cerebellum
It is located behind the back brain, consists of hemispheres and a worm, has legs, is covered with cortex, which contains Purkinje cells - inhibitory neurons, from them.
The efferent pathways of the cerebellum begin in its cortex, then switch in its nuclei and go to the structures of the brainstem.
Functions: regulation of the tone and posture, slow and fast purposeful movements, vegetative functions, provision of motor programs.
Symptoms of the desease of the cerebellum: 1) ataxia (drunk walk), asthenia (muscle weakness), atony (lack of muscle tone), 2) tremor in motion, 3) nystagmus of the head and eyes, 4) chanted speech, 5) dizziness.
|
|
|
Дата добавления: 2022-12-03; просмотров: 31; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
