MUST ( MUST NOT ) настоятельный совет, правило/закон, ты должен, потому что я так решил
Вопросы по грамматике 1 курс
1. Present Simple. Form (statement, negative, question) and uses. Provide examples for each case of use. What is the difference between Present Simple and Present Continuous?. 2
2. Present Continuous. Form (statement, negative, question) and uses. Provide examples for each case of use. What is the difference between Present Simple and Present Continuous?. 3
3. Past Simple. Form (statement, negative, question) and uses. Provide examples for each case of use. What is the difference between Past Simple and Present Perfect?. 4
4. Present Perfect. Form (statement, negative, question) and uses. Provide examples for each case of use. What is the difference between Past Simple and Present Perfect?. 5
5. Present Perfect Continuous. Form (statement, negative, question) and uses. Provide examples for each case of use. What is the difference between Present Perfect Continuous and Present Perfect? What is the difference between Present Continuous and Present Perfect Continuous?. 6
6. Past Continuous. Form (including negative and question) and uses. Provide examples for each case of use. What is the difference between Past Continuous and Past Simple?. 7
7. Past Perfect. Form (including negative and question) and uses. Provide examples for each case of use. What is the difference between Past Perfect and Past Simple?. 8
8. Ways to express future in English (Future Simple, Future Continuous). Forms, uses, examples and difference. 9
9. Ways to express future in English (to be going to, Present Continuous). Forms, uses, examples and difference. 10
10. Modal verbs (can, may) and their negatives. Key features and uses with examples. 11
11. Modal verbs (must, have to, should) and their negatives. Key features, difference and uses with examples. 12
12. Articles (definite, indefinite and zero). Main uses and examples. 13
13. Conditional I, II and III. Uses, examples and difference. 15
14. Nouns and their plurals. Rules and exceptions. Countable and uncountable nouns. Examples. 16
15. Countable and uncountable nouns. Quantifiers (few/little, much/many, a few/a little, number/amount, a lot of). Examples. 17
16. Some, any and no. Rules and examples of use. Indefinite pronouns (somebody/anybody/nobody, something/anything/nothing, somewhere/anywhere/nowhere, etc) 18
17. Personal and reflexive pronouns (my, myself, mine, etc). Difference in use and examples. 21
18. Passive Voice. Form and uses. Examples. 22
|
|
|
19. Comparative and Superlative forms of adjectives. Rules and examples. Adverbs and how they’re formed. Exceptions (late/lately, hard/hardly, fast, etc). Comparative and superlative forms of adverbs. 23
20. Reported speech and sequence of tenses. Reported questions. Rules and examples. 26
1. Present Simple. Form (statement, negative, question) and uses. Provide examples for each case of use. What is the difference between Present Simple and Present Continuous?

We use the present simple
· regular habits or repeated actions:
I get up really early and practice for an hour or so most days.
I use the Internet just about every day.
· permanent situations:
My parents own a restaurant.
· facts or generally accepted truths:
Students don`t generally have much money.
If you heat water to 100 C, it boils.
· to give instructions and directions:
You go down to the traffic lights, then you turn left.
· to tell stories and talk about films, books and plays:
In the film, the tea lady falls in love with Prime Minister.
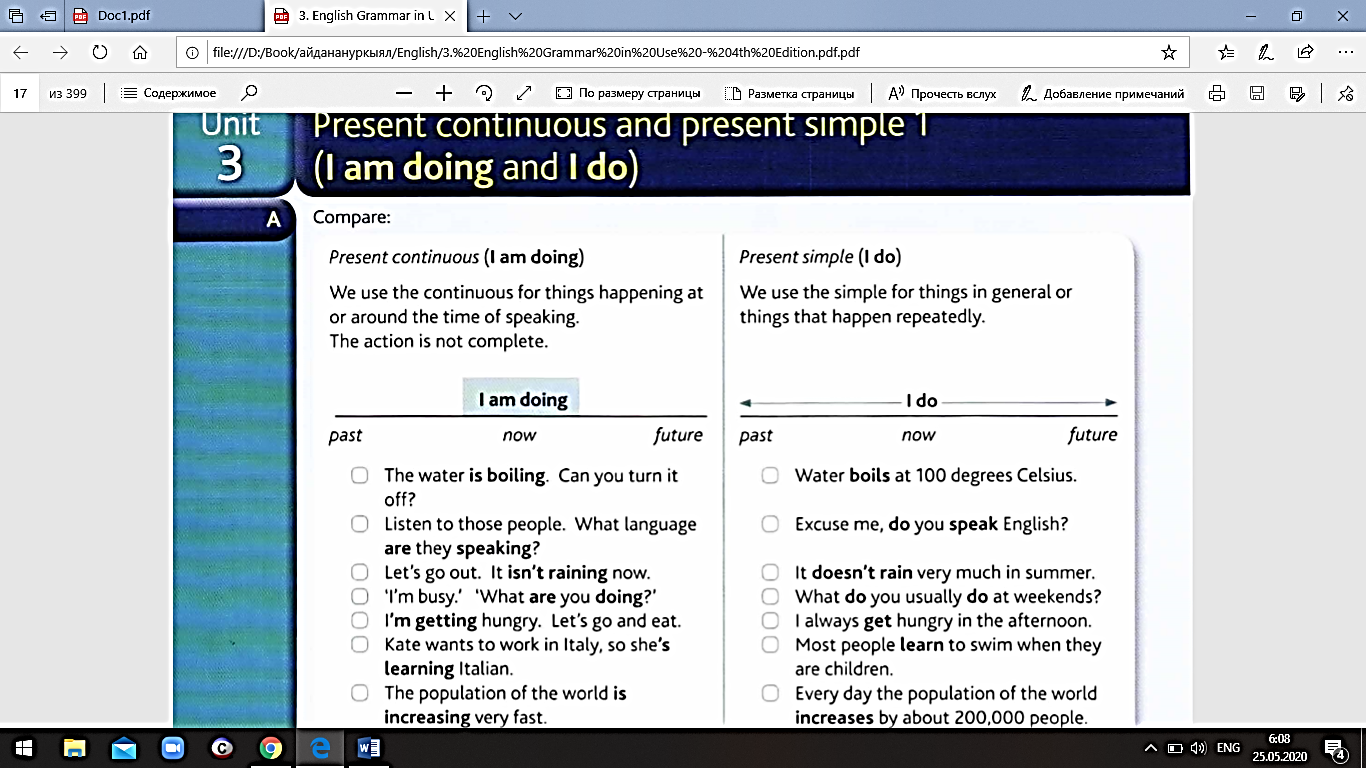
2. Present Continuous. Form (statement, negative, question) and uses. Provide examples for each case of use. What is the difference between Present Simple and Present Continuous?

We use the present continuous
· temporary situations:
I`m studying really hard for my exam.
My cousin is living in Thailand at the moment.
· actions happening at the moment of speaking:
I`m waiting for my friends.
· trends or changing situations:
The Internet is making it easier for people to stay in touch.
The price of petrol is rising dramatically.
· things that happen more often than expected, often to show envy or to criticize:
My mum`s always saying I don`t help enough! (complain)
He`s always visiting exciting places! (envy)

3. Past Simple. Form (statement, negative, question) and uses. Provide examples for each case of use. What is the difference between Past Simple and Present Perfect?

We use the past simple
· single past completed actions:
A few weeks ago a woman called to report a robbery at her house.
|
|
|
How did the burglar break in without anybody hearing him?
· a series of actions in the order that they happened:
The burglar came in through the front door, picked up the woman`s handbag, emptied it out and stole her purse.
· past repeated actions:
When her son got older he often went out to visit his friends after school.
· long-term situations in the past which are no longer true:
Bill Murphy worked for the police for over 17 years.
Explorers at that time believed that the world was flat.

We use the past simple for past events or actions which have no connection to the present. We use the present perfect for actions which started in the past and are still happening now OR for finished actions which have a connection to the present.
4. Present Perfect. Form (statement, negative, question) and uses. Provide examples for each case of use. What is the difference between Past Simple and Present Perfect?
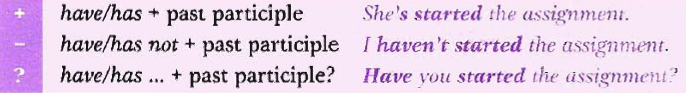
We use the present perfect simple
· to talk about a time period that is not finished (e.g. today, this week):
I`ve written a rough plan this morning.
· to show that something happened at some point in the past before now. we don`t state when it happened:
I`ve collected plenty of information.
It`s the longest I`ve ever had to write.
· present situation which started in the past (for/since):
I`ve worked really hard for the last two weeks.
· smth that happened at an unstated time in the past but it connected to the present:
I`ve read all the books on the reading list.
I`ve just got up.
Have you written your assignment yet?

We use the past simple for past events or actions which have no connection to the present. We use the present perfect for actions which started in the past and are still happening now OR for finished actions which have a connection to the present.
5. Present Perfect Continuous. Form (statement, negative, question) and uses. Provide examples for each case of use. What is the difference between Present Perfect Continuous and Present Perfect? What is the difference between Present Continuous and Present Perfect Continuous?
|
|
|

We use the present perfect continuous
· to show that something started in the past and has continued up until now:
They have been talking for the last hour.
I`ve been feeling tired since I started this course.

| Present perfect continuous · the action was taking place some time ago: He is eating his food. Present continuous · the action that is still going on: I have been telling Francis to do this job. |
6. Past Continuous. Form (including negative and question) and uses. Provide examples for each case of use. What is the difference between Past Continuous and Past Simple?

We use the past continuous
· to provide the background scene to an action or event (when/while/as):
It happened at five in the afternoon while she was watching the news on TV.
· when we want to emphasize the activity without focusing on its completion:
| In a story which is told in the past tense, the main events are expressed with the past simple, while the past continuous is used for background events. |
7. Past Perfect. Form (including negative and question) and uses. Provide examples for each case of use. What is the difference between Past Perfect and Past Simple?

We use the past perfect
· when we are talking about the past and want to mention smth that happened earlier (just/already):
His father was a composer and his grandfather had also been a musician.
· with words when, as soon as, by the time, after to show the order of events:
When Mozart was born, five of his siblings had already died.
· to talk about an indefinite time before a particular point in the past:
By the time he was six, the little boy had written a composition of his own.
· to report past events using reporting verbs:
The man told me he had met my father a long time before.
| We use past perfect to talk about something that happened before another action in the past, which is usually expressed by the past simple. |
|
|
|
8. Ways to express future in English (Future Simple, Future Continuous). Forms, uses, examples and difference.

FUTURE SIMPLE
We use future simple
· predictions, usually based on our opinions or our past experience:
I think it`ll be extremely hot there.
· future events we haven`t arranged yet:
We`ll probably stay in some sort of mountain lodge there.
· future events or facts that are not personal:
The best player on the tour will get a special trophy.
· smth we decide to do at the time of speaking:
Tell me all about it and I`ll pass on the information to the rest of the team.
· offers, promises, suggestions:
Don`t worry, I`ll let everyone hnow.
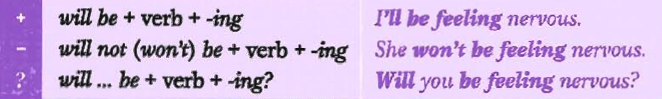
FUTURE CONTINUOUS
We use future continuous
· to describe or predict events or situations continuing at a particular point in the future or over a period of time in the future:
I`ll be working on the report all next week.
I`ll be thinking of you in Rome.
· events that are planned or already decided:
I`ll be seeing Sarah at lunch.
| The future continuous tense, sometimes also referred to as the future progressive tense, is a verb tense that indicates that something will occur in the future and continue for an expected length of time. The simple future tense is a verb tense that is used when an action is expected to occur in the future and be completed. |
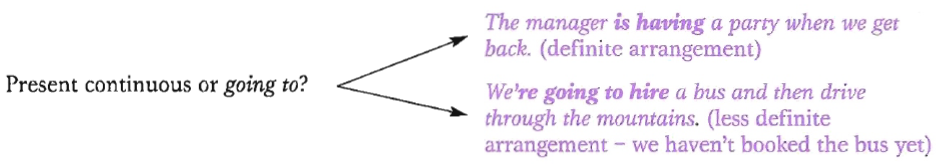
9. Ways to express future in English (to be going to, Present Continuous). Forms, uses, examples and difference.
PRESENT CONTINUOUS
We use present continuous
· plans or definite arrangements for the future
We`re staying in a small hotel. (we have made the arrangements)
GOING TO

We use going to
· events in the future we have already thought about and intend to do:
We`re going to hire a bus.
We`re going to get a boat to a couple of the islands.
· to make predictions when there is present evidence:
We`re certainly going to have a varied trip.
10. Modal verbs (can, may) and their negatives. Key features and uses with examples.
CAN, CAN`T (COULD, COULDN`T)
ability:
I can`t swim.
They could find out his name.
· we use can to mean sometimes:
People can do funny things when they`ve experienced smth terrible.
· we use can to ask for and give permission:
Can I borrow the car this afternoon?
You can borrow it, but I need it later this evening.
MAY (MAY NOT) возможно
possibility:
He may remember some things already. (possible)
· present
may + infinitive without to (to talk about possibility in the present)
He may remember some things already.
may + be + -ing (to talk about things happening or in progress at the time of speaking)
She may be talking to her sister on the phone.
· past
may + have + past participle (to talk about possibility in the past)
In the attack he may have hit his head.
may + have been + -ing (to talk about things possibly happening or in progress in the past)
He may have been trying to run away from his past.
· future
may + infinitive without to (to talk about possibility or uncertainly in the future)
He may make a total recovery one day.
may + be + -ing (to talk about things happening or in progress at a time in the future)
She may be meeting John later.
11. Modal verbs (must, have to, should) and their negatives. Key features, difference and uses with examples.
MUST ( MUST NOT ) настоятельный совет, правило/закон, ты должен, потому что я так решил
possibility:
He must remember all the things. (very likely)
obligation and necessity:
You mustn`t dress too casual for work.
You mustn`t wait here. (= it is not allowed)
· the obligation comes from the speaker:
You must invite me to visit you.
· must is usually used on signs, notices and printed information:
All employees must hold a valid work permit.
· use must in present, not use in questions
suggestions and advice:
· to give strong advice:
You must phone me when you get there.
Дата добавления: 2021-01-21; просмотров: 71; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
