Christmas Eve and Christmas Day.
In England less emphasis is placed on Christmas Eve than in other countries, much more is made on Christmas Day. Carol singing Christmas songs , midnight church services and going out to the pub are some of the activities that many families enjoy.
After the English Revolution in 1647 the English parliament passed a law that made Christmas illegal. All festivities were banned by the Puritan leader Oliver Cromwell, who considered feasting on what was supposed to be a holy day to be immoral. The ban was lifted only when Cromwell lost power in 1660.
During Queen Victoria's reign Christmas became a time for gift giving and a special season for children.
December 26 is Boxing Day – the day of giving gifts.
Easter is a festival that takes place on the first Sunday after the full moon.
Guy Fawkes Day - November the 5th. Guy Fawkes’ Day is also known as 'Bonfire Night' or 'Fireworks Night'. In 1605 on the 5th of November Catholic Guy Fawkes and his fellow conspirators (60 in all) attempted to kill King James I and the Members of Parliament. This conspiracy arose as a reaction to the persecution of Catholics under the rule of King James, a Protestant. They hid 36 barrels of gunpowder in the cellars of the Houses of Parliament and were going to blow up the Houses of Parliament. But one of the plotters betrayed the conspiracy in a letter to his brother-in-law who told the government about the plotter’s plans. Fawkes was caught with a box of matches in his pocket. Some conspirators fled but many were killed or arrested. Nine members, including Fawkes, were hung and quartered in January 1606.
Parliament made the 5th November a day of Public celebrated with fireworks and bonfires. Today children still make stuffed figures with masks of Guy Fawkes. They call these figures guys and display them in the streets.
November the 5th is also called the Ringing Day because it is appointed for
the church bells to ring for the whole day.
One of the largest events in the UK is the Bridgewater Carnival. The procession is held each year on the Thursday nearest to November 5. It is an illuminated procession that takes about two hours to pass.
Bank Holidays - public holidays when banks, post offices, shops and some attractions are closed. Bank holidays always occur on Monday.
Midsummer Day - 24th June - ceremonies in honour of the Sun have been held from the earliest times. This day is preceded by Midsummer Night when supernatural beings are said to wander about.
|
|
|
Some holidays of different parts of the UK became the public holidays celebrated all over the world.
St. George Day – the Saint of England. According to the legend George was a knight who saved the princess from a dragon. For this her father, the King gave George his daughter to marry and a gold cross to wear. Since that time King Richard 1 (the Lionheart) adopted a cross as a uniform for his soldiers. We can see a red cross on the UK national flag (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({}); 
The flag of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is a combination of more flags.
There is also the theory that the name Union Jack came from King James, whose name is Jacobus in Latin.
The parts of the flag:
1. St George's Cross (England), St.Andrew’s – the Saint id Scotland and St. Patrick the Saint of North Ireland at the time of the Roman Empire. 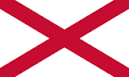
 +
+ 
St.Patrick's Day - March 17th. is celebrated outside too (E.g. in Moscow).
St David's Day - March 1st St. David (520-588), or Dewi as he is called in Welsh, is the patron saint of Wales since the 12th century. He founded twelve monasteries across the country and now about 5 churches are dedicated to him. The flag of Saint David (a gold cross on a black field) is a very important part of the celebrations in Wales.
The Highland games are events held throughout the year in Scotland as a way of celebrating Scottish and Celtic culture and heritage, especially that of the Scottish Highlands. Certain aspects of the games are so well known as to have become emblematic of Scotland, such as the bagpipes, the kilt, and the heavy events. Edinburgh Festival (began in 1947) in August and early September. The whole city turns into carnivals, international theaters, concerts and singing, and music.
| LECTURE № 6 F OLKLORE AND LITERATURE |
The studies of the British culture cannot stand apart from the research of its important product – folklore. The folklore and folk customs of England developed over a long chain of centuries. Some ancient customs were passed from Celtic to Germanic generations and further on. Invaders and settlers brought with them their own beliefs, which mixed with older traditions.
|
|
|
The main system of values, beliefs and traditions of British nations is mostly reflected in the ballads and fairy tales. The old ballads make up a very valuable part of poetical literature. Ballads are a rich source of data connected with history, social life, feelings and values of the people living on the British Isle.
Although the subjects of ballads vary considerably, some major classes of the ballad can be distinguished— among them the historical and heroic such as Beowulf, King Arthur songs and Robin Hood cycle.
Beowulf is an Old anonymous English heroic epic poem.Its creation dates to between the 8th and the 11th centuries. It is long, as there are 3183 lines, devoted to brave and strong hero who fought for the good of his people, killing two monsters.
Beowulf has been adapted a number of times in cinema, on the stage, and in books.
Another old recorded ballad in the English language is the legend devoted to King Arthur who was a legendary British leader of the late 5th and early 6th centuries. According to medieval histories he led the defense of the Celts against the Saxon invaders.  The magical sword Excalibur, his castle Camelot, and the Lady of the Lake also play great associated with King Arthur. In Arthurian legend King Arthur had a round table so that none of his knights, when seated at it, could claim precedence over the others.
The magical sword Excalibur, his castle Camelot, and the Lady of the Lake also play great associated with King Arthur. In Arthurian legend King Arthur had a round table so that none of his knights, when seated at it, could claim precedence over the others.
Countless new legends, stories, revisions, books, and films have been produced in Europe and the United States about King Arthur and his Round Table (the film with R. Geer)
Other ballads printed in the late 15th or early 16th centuries are devoted to “Robyn Hood". Robin Hood is a heroic outlaw in English folklore, and, according to the legends, was also a highly skilled archer, assisted by a group of fellow outlaws known as his “Merry Men”. Traditionally, Robin Hood and his men lived in Sherwood Forest, wearing Lincoln green clothes.
Robin Hood became a popular folk figure in the medieval period as the one who was fighting with the unscrupulous sheriff. Robbing the rich he gave everything to the poor. The earliest Robin Hood manuscript is “Robin Hood and the Monk’ (1450) kept in Cambridge University. The first printed version is “A Guest of Robyn Hode” (1475).
|
|
|
Robin Hood continues to be widely represented in modern literature, films and television.
Like ballads English Fairy Tales circulated in England in oral form. One of the oldest printed fairy tales in England was Tom Thumb.In this fairytale a childless poor couple asked Magician Merlin to give them a son even if he were no bigger than his father’s thumb. Tom Thumb met many adventures. The last of them was being eaten by a fish which was then caught for King Arthur’s table. Tom became a knight and when he died was mourned by the whole Arthur’s court.
The English fairytales were mostly humorous ones, except for the more magical Three Heads in the Well. Later Victorian collectors found some other oral examples, including Tom Tit Tot and Cap o' Rushes from Suffolk, the Small-Tooth Dog from Derbyshire, and the Rose Tree from Devon.
In the 18th century English fairy tales were published mainly by French Perrault. Selections from these were quickly translated and cheaply printed. Such fairy tales as Cinderella, Bluebeard, Sleeping Beauty, Beauty and the Beast, Frog Prince, Red Riding Hood, Snow White, and The Little Mermaid were totally absorbed into English culture, staged and made into numerous films.
Theatre
Theatre was introduced to the UK from Europe by the Romans. In the middle Ages it was mostly in a street form, concentrating on dance and on the themes such as Saint George and the Dragon and later on Robin Hood. The plays were retelling old folklore stories. The groups of actors were travelling from town to town performing not only for money but also for hospitality. There were also religious plays on Christian themes performed at religious festivals.
The difference came during the reign of Elizabeth 1 in the 16th-17th centuries. The flowering of English drama is associated with William Shakespeare, of course. William Shakespeare wrote about 40 plays that are still performed in the theaters all over the world.
|
|
|
His plays include tragedies, such as Hamlet (1603), Othello (1604), King Lear (1605), Romeo and Juliet. There are also famous comedies, such as A Midsummer Night’s Dream (1594-96) and The Twelfth Night (1602). Among his plays there are popular historic plays, such as Henry 1V.
The Elizabethan age is sometimes nicknamed “The age of Shakespeare” for the amount of influence he held over the era.
During the years after the Revolution headed by Cromwell the theater was practically closed. It was resumed under Charles 11. A lot of new authors and professional actors and actresses appeared who attracted the audiences (at the time of Shakespeare all female roles were played by boys). There even appeared a woman playwright Aphra Benn.
In the 18th century Restoration comedy was replaced by sentimental comedy and by overwhelming interest in Italian opera.
A restoration and an interest in theatre of drama came in the 19th century with the plays by the Irishman playwright George Bernard Shaw and English playwrite Oscar Wilde.
The Irish playwright Bernard Show (1856-190) wrote a great number of satirical, witty and psychological plays that became well known not only in Britain, but also all over the world, including Russia. Among Shaw’s best-known plays are Heartbreak House, Saint Joan and Pygmalion, based on the Greek myth about a sculptor who carved a statue of a woman and fell in love with her. The adaptation of Pygmalion is a very popular musical “My Fair Lady”, successfully staged in Broadway and many Europeans theaters.
Today the West End in London has a large number of theatres, particularly centered on Shaftesbury |Avenue. There are over 200 theaters in Britain: 40 of which are situated in London’s West End. The most famous British theaters are The Royal Opera and Royal Ballet, both based at Covent Garden, the National Theatre and the Barbican Theatre. The National is a part of the South Bank Arts Centre, located near the River Thames. The Centre contains three theatres, cinemas, an art gallery, and concert halls. The diamond of the National is the 1.160-seat Oliver Theatre, named after famous actor and director Laurence Olivier. The Royal Shakespeare Company performs at the Barbican in London and in Shakespeare's birthplace Stratford-upon-Avon.
A prolific composer of the 20th century Andrew Lloyd Webber dominated the West End for a number of years, and his musicals travelled to Broadway in New York and around the world.
Important modern playwrights include Alan Ayckbourn, John Osborne, Harold Pinter, Tom Stoppard, and Arnold Wesker.
LECTURE № 7
Literature.
British literature is so rich that it is absolutely impossible to describe its history and its main writers, poets and dramatists in any detail. Like many other world literatures English literature grew up from the rich and diverse folklore of the nations in this country. Rich narrative traditions of ballads, songs and tales come to us through literature, writings of English authors ranging from Chaucer, Shakespeare and Ben Johnson, to William Yeats, Burns and Bernard Shaw and John Milton.
Everyone in the childhood read Robinson Crusoe by Daniel Defoe (1660-1731), Gulliver’s Travels by Jonathan Swift (1667-1745), historical novels of Walter Scott, Oliver Twist and David Copperfield by one of the greatest English writers of the 19th century Charles Dickens (1812-1870).
| Charles Dickens |

|
The Bronte sisters were exceptional writers of poetry as well as fiction. Wuthering Heights by Emily Bronte and Jane Eyre by Charlotte Bronte are read and enjoyed even now.
Thomas Hardy’s and Jane Austen’s novels reflected different sides of English life of the 19th century. It was not easy for 19 century women writers to sell their books under their real names. Many of them used male pseudonyms: George Eliot (1819-1880) never used her real name which was Mary Ann Evans. Her books show a detailed picture of provincial Victorian society with humour and feeling.
A Scottish writer Robert Stevenson (180-94) wrote famous adventure novels, and an English novelist William Thackeray (1811-63) in his brilliant satire Vanity Fair became the master of great individuality.
Jerome, K. Jerome (1859-1927) wrote two humorous books, one of which Three Men in a Boat is favourite with the Russian students.
Rudyard Kipling (1865-1936) wrote a lot of poems, stories and tales, which children of all the countries still enjoy today. His stories about Mowglii and finest animal stories inspired American Walt Disney to create wonderful cartoon films. Kipling was the first English writer to be awarded with the Nobel Prize in 1907. An Irish-born author Oscar Wilde (1854 - 1900) created novels, stories and plays, still staged in Russian theatres.
There were many wonderful poets in Britain. Romantic poets Baron and Shelly influenced the poetry of Alezander Pushkin.
Scottish poet Robert Burns (1759-1796) whom we know in wonderful translations by Marshak  grew up on the folklore traditions of his land. R.Burns managed to combine in his simple poems tenderness, rich humour, lyric and love for freedom of the Scottish folklore heroes. His birthday is celebrated in Scotland as the national holiday and his statue and house in Dumfries are the places, visited by his numerous admirers.
grew up on the folklore traditions of his land. R.Burns managed to combine in his simple poems tenderness, rich humour, lyric and love for freedom of the Scottish folklore heroes. His birthday is celebrated in Scotland as the national holiday and his statue and house in Dumfries are the places, visited by his numerous admirers.
The 20th century gave a great number of talented British writers, poets and dramatists: poet Thomas Eliot (1888-1965), novelist and dramatist John Galsworthy (1867-1933), David Lawrence, satirist Aldous Huxley (1894-1963), Sean O’Keisi, Richard Oldington, novelist, dramatist and essayist John Priestly (1894-1984), Evelyn Waugh (1903-66), Graham Green (1904-91), Irish novelist James Joyce (1882-1941) and many others.
Joyce’s novel Ulysses started the development of modernist literature in Britain. In this novel and later in Einnegan’s Wake Joyce revolutionized the techniques of fiction – writing, introducing the “stream of consciousness,” inventing words and experimenting with syntax. Virginia Woolf (1882-1941) in her novels also experimented with the stream-of-consciosness narrative technique.
An Irish playwright Sean O’Casey wrote a number of tragicomedies, blending realism with symbolism and poetry with vernacular speech.
The poetic writings of William Yeats (1865-1939), marked with the Nobel Prize in 1923, had a great influence on the development of the British poetry of the 20th century. All his books of verses were full of the Irish spirit, brilliant vigorous technique, the combination of western viewpoint with national philosophy and traditions.
The War of the World by H. Wells (1866-1946) became the first great works of science fiction.
William Somerset Maugham (1874-1965) is considered to be the best short-story writer in English. Many of his stories, together with novels and plays have been dramatized and became very fashionable and successful.  Agatha Christie, the world’s most successful and best-known detective writer, occupies a special place in British literature. During her long writing career she wrote over 83 books. Her detective novels were translated into every major language and tens of millions of her books were sold. Her little Belgian detective became as popular as Sherlock Homes by Arthur Conan Doyle. Poirot and her other detectives have also appeared in many of the popular films, radio programmers and stage plays, based on her books.
Agatha Christie, the world’s most successful and best-known detective writer, occupies a special place in British literature. During her long writing career she wrote over 83 books. Her detective novels were translated into every major language and tens of millions of her books were sold. Her little Belgian detective became as popular as Sherlock Homes by Arthur Conan Doyle. Poirot and her other detectives have also appeared in many of the popular films, radio programmers and stage plays, based on her books.
In the late 1950s John Osborne, one of a group of so-called Angry Young Men, achieved fame as an author of tough realistic drama about working class life. Iris Murdoch gained an international reputation for her “psychological detective stories’. Sir Arthur Clarke created a number of science fiction books but probably became best known for his book A Space Odyssey which was made into an extremely popular film.
English literature influenced the literatures of America, Europe, Russia and many other world countries. It also gave rise to the young literatures of former British colonies. For example, Paul Scot’s novels show the last years of the British presence in India, Alan Paton, Jack Cope, Alex La Guma wrote about the racial relationships in South Africa. Chinua Achebe described the tribal life in Nigeria. Nadina Gordimer, a white author from South Africa, was rewarded with the Nobel Prize in 1991 as the greatest English writer of her time.
.
During the Revolution of 1642—1660, English theatres were closed by the Puritans.When the London theatres were opened again with the Restoration of the monarchy in 1660, they flourished under the personal interest and support of Charles II. The audiences were attracted by the introduction of the first professional actresses (in Shakespeare's time, all female roles had been played by boys). New genres of the Restoration were heroic dramas and comedies.
In the 18th century, the Restoration comedy was replaced by an overwhelming interest in Italian opera. A change came in the late 19th century with the plays by the Irishmen George Bernard Shaw, Oscar Wilde and Norwegian Henrik Ibsen, all of whom vitalised English drama again.
Today there are over 200 theaters in Britain: 40 of which are situated in London’s West End. The most famous British theaters are The Royal Opera and Royal Ballet, both based at Covent Garden, the National Theatre and the Barbican Theatre. The National is a part of the South Bank Arts Centre, located near the River Thames. The Centre contains three theatres, cinemas, an art gallery, lecture and concert halls. The diamond of the National is the 1.160-seat Oliver Theatre, named after famous actor and director Laurence Olivier. The Royal Shakespeare Company performs at the Barbican in London and in Shakespeare's birthplace Stratford-upon-Avon.
Pop music in Britain is an important part of British culture. It is mainly a mixture of styles. It is difficult to find people who don’t listen to music at least for pleasure so it is not surprising, that music can be an instrument of social influence and change. A prolific composer of the 20th century Andrew Lloyd Webber has dominated the West End for a number of years and his musicals have travelled to Broadway in New York and around the world, as well as being turned into films.
In the 20th century American influences became most dominant in popular music, with young performers producing their own versions of American music, developing a parallel music scene. This led to the explosion of the 'British Invasion' of America of the early 1960s, headed by The Beatles, with movements on one side of the ocean being exported to the other. As a result of these factors the United Kingdom remained a major source of musical innovation and participation in the modern era.
Дата добавления: 2019-11-25; просмотров: 236; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
