Read the text and answer the questions.
1. When is an antibiotic tested in human beings?
2. What are the steps of antibiotics production?
3. How are semisynthetic antibiotics produced?
Testing and Producing Antibiotics
Testing. Every year, scientists test thousands of natural and chemically modified microbial substances for potential use as antibiotics. First, these substances are tested against harmful microbes or cancer cells that have been grown either in test tubes or on laboratory plates.
A substance that shows strong antibiotic activity against pathogenic microbes or cancer cells is tested extensively in laboratory animals. Then, if it produces no harmful effects in the animals, the antibiotic is tested in human beings. In the United States, human testing must be approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). If the drug proves to be safer and more effective than antibiotics already being used, it is submitted for approval to the FDA. Finally, if the FDA approves the antibiotic, drug firms begin to produce it commercially.
Antibiotics production involves several steps. First, cultures of the antibiotic-producing microbes are grown in flasks and then transferred to huge fermentation vats. The microbes multiply rapidly in the vats because the environment is controlled to stimulate their growth. After fermentation, the antibiotic substance is extracted from the culture and purified.
Some natural antibiotic substances are modified chemically to produce semisynthetic antibiotics. Many such drugs are more effective than the natural antibiotics from which they came.
Drug companies conduct special tests on antibiotics during and after production to ensure their quality. Finally, the purified antibiotic substances are made into pills, liquids, and ointments for medical use.
Text 6
Read the text and arrange the events in the chronological order.
— Robert Koch developed methods of isolating and growing various kinds of bacteria.
— A new antibiotic called streptomycin was discovered.
— Alexander Fleming observed that a mold of the genus Penicilliumproduced a substance that destroyed bacteria.
— Louis Pasteur discovered that bacteria spread infectious diseases.
— Ernst B. Chain and Howard W. Florey developed a method of extracting and purifying small amounts of penicillin.
History of Antibiotics
For more than 2,500 years, people have treated certain skin infections with molds that form antibiotics. However, modern scientific study of these substances did not begin until the late 1800s. At that time, great French chemist Louis Pasteur discovered that bacteria spread infectious diseases. Then Robert Koch, a German bacteriologist, developed methods of isolating and growing various kinds of bacteria. Koch also identified specific bacteria that cause certain diseases.
|
|
|
Scientists,then began working to develop drugs that could destroy pathogenic microbes, but the substances they produced proved either ineffective or dangerous. A historic breakthrough came in 1928, when British bacteriologist Alexander Fleming observed that a mold of the genus Penicillium produced a substance that destroyed bacteria. He called the substance penicillin. Fleming recognized the potential use of penicillin in treating disease, but difficulty in extracting it from the mold hindered further experimentation.
In the late 1930s, two British scientists, Ernst B. Chain and Howard W. Florey, developed a method of extracting and purifying small amounts of penicillin. The first successful medical treatment with penicillin occurred in 1941, when a British policeman suffering from bacterial blood poisoning received the drug. But the small supply of penicillin prevented physicians from using the drug extensively. A high-yielding type of Penicillium mold was discovered in 1943, and penicillin production increased greatly.
In the early 1940s, American bacteriologist Selman A. Waksman tested about 10,000 types of soil bacteria for antibiotic activity. In 1943, he discovered that some Streptomyces, a type of fungi, produced a substance that had strong antibiotic properties. A new antibiotic called streptomycin resulted from Waksman's research.
Thousands of antibiotic substances have been found in the nature or produced chemically. However, relatively few antibiotic substances have proven to be safe and effective. In addition, certain types of pathogenic microbes have acquired resistance to some antibiotics.
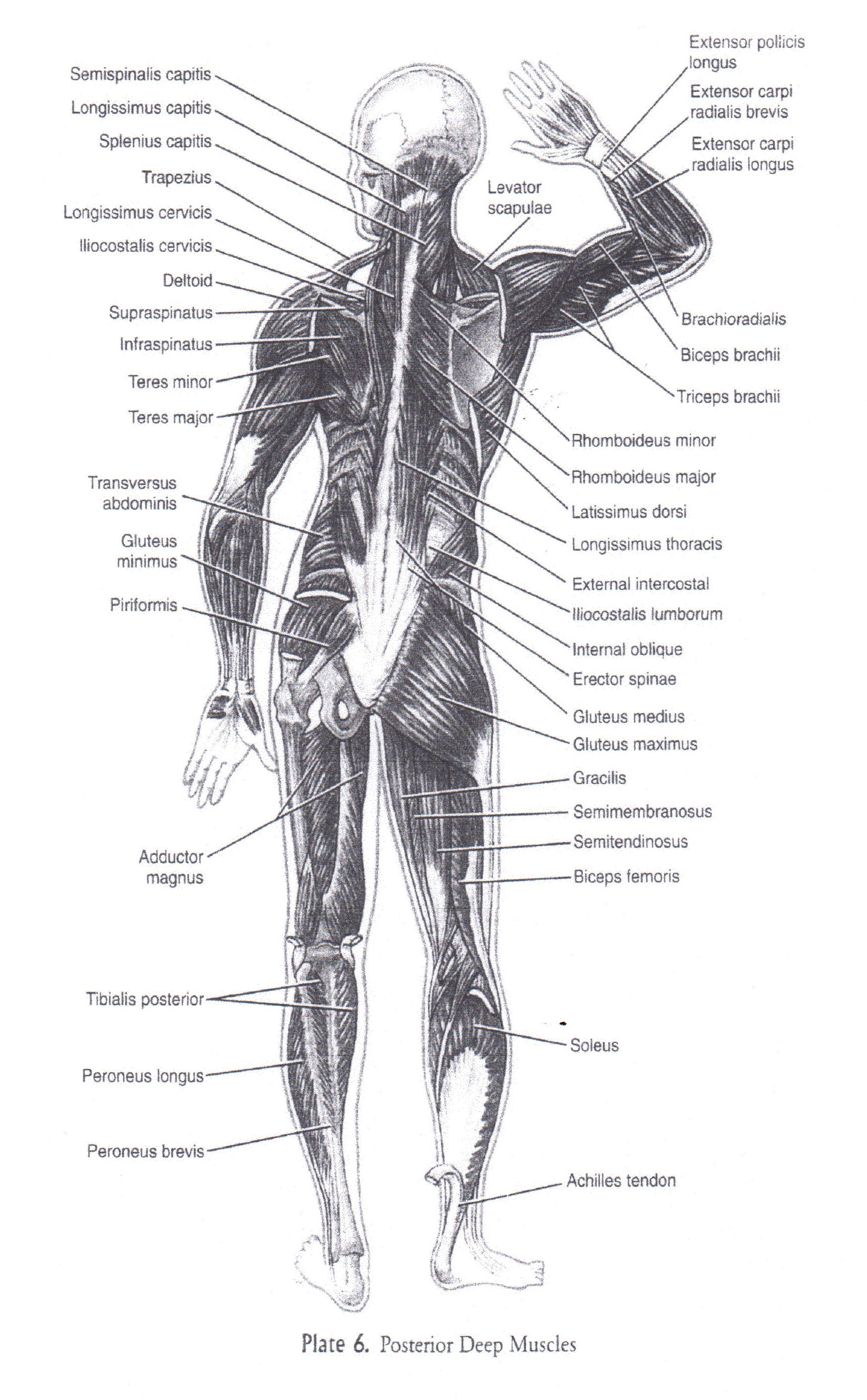
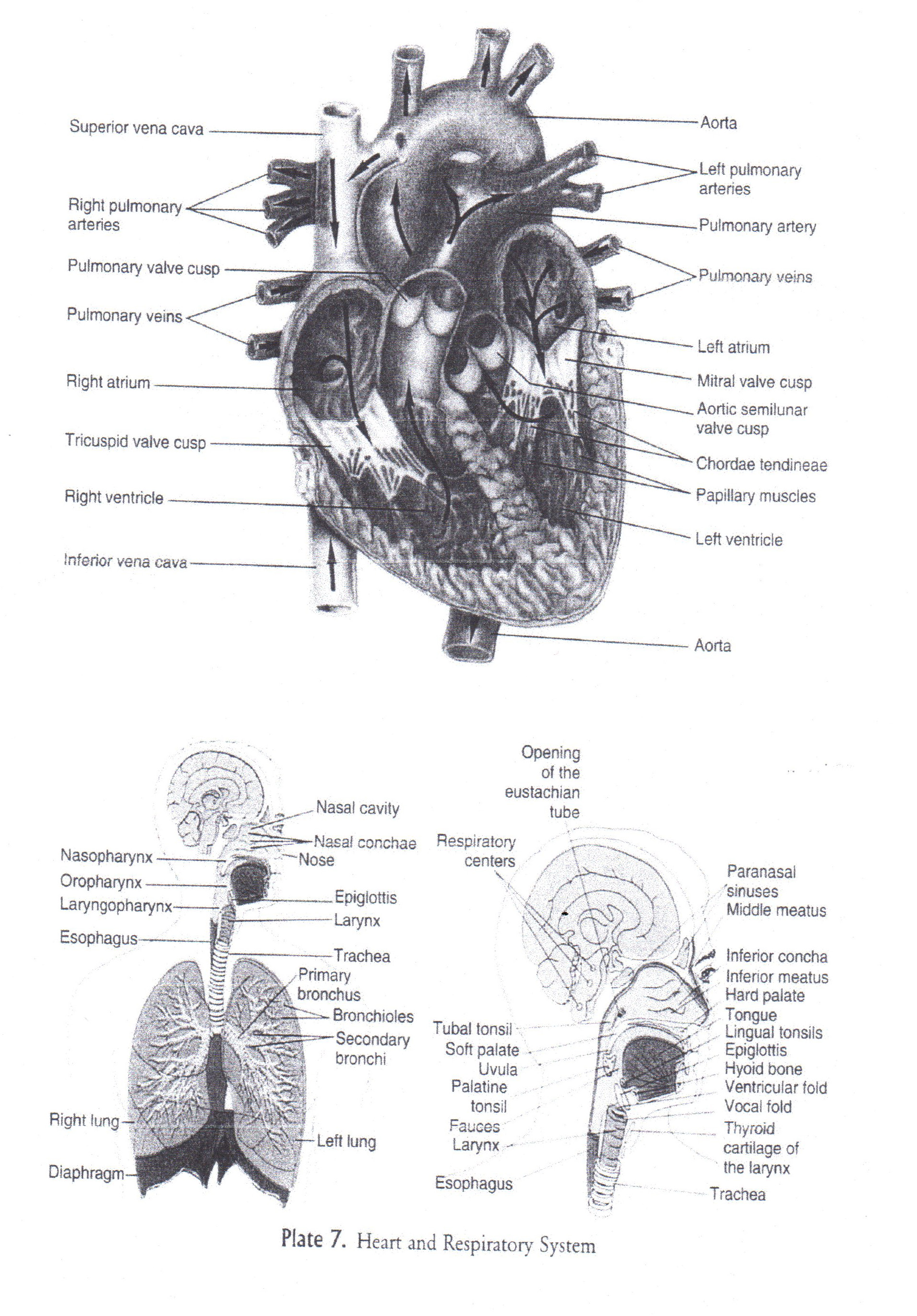
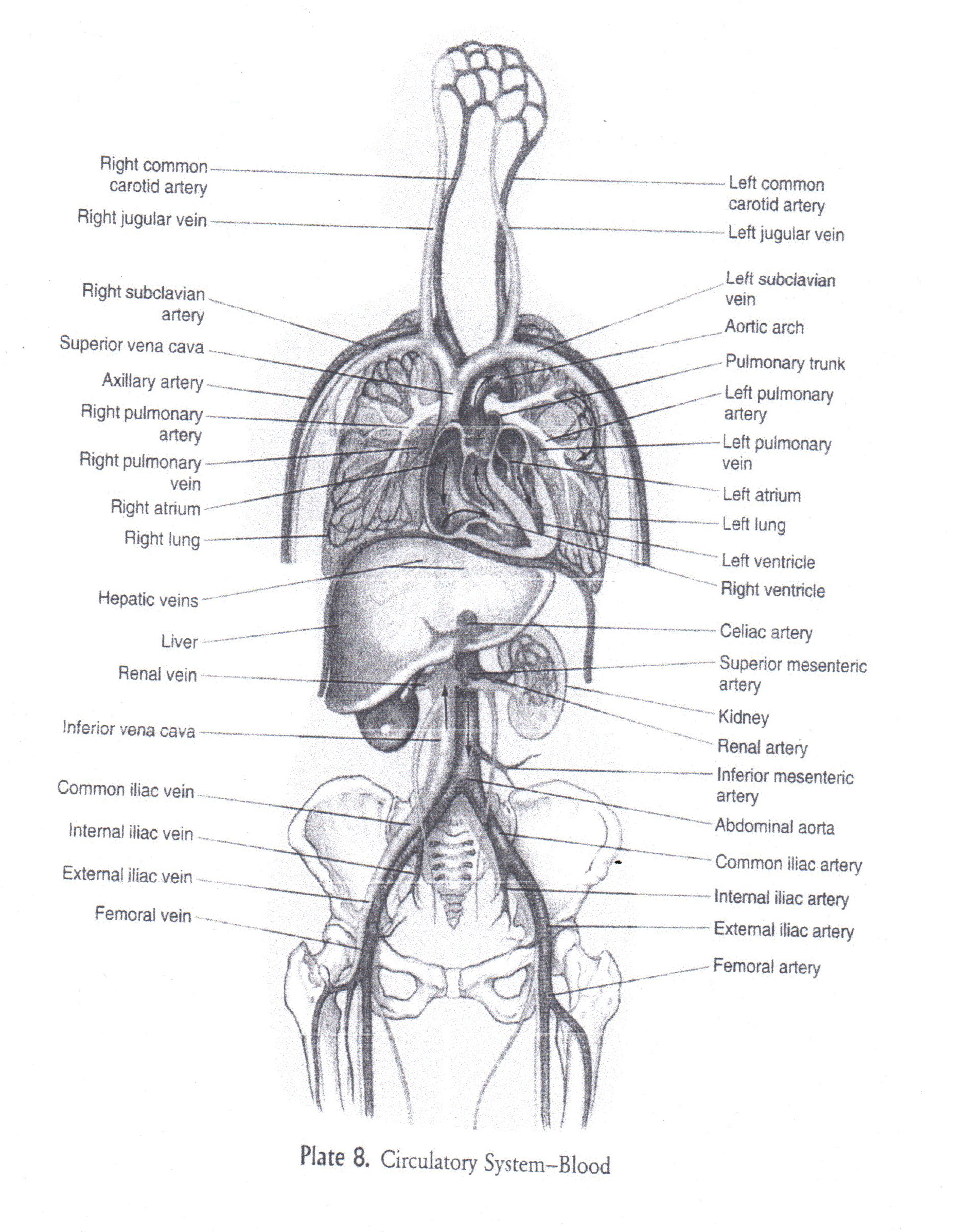
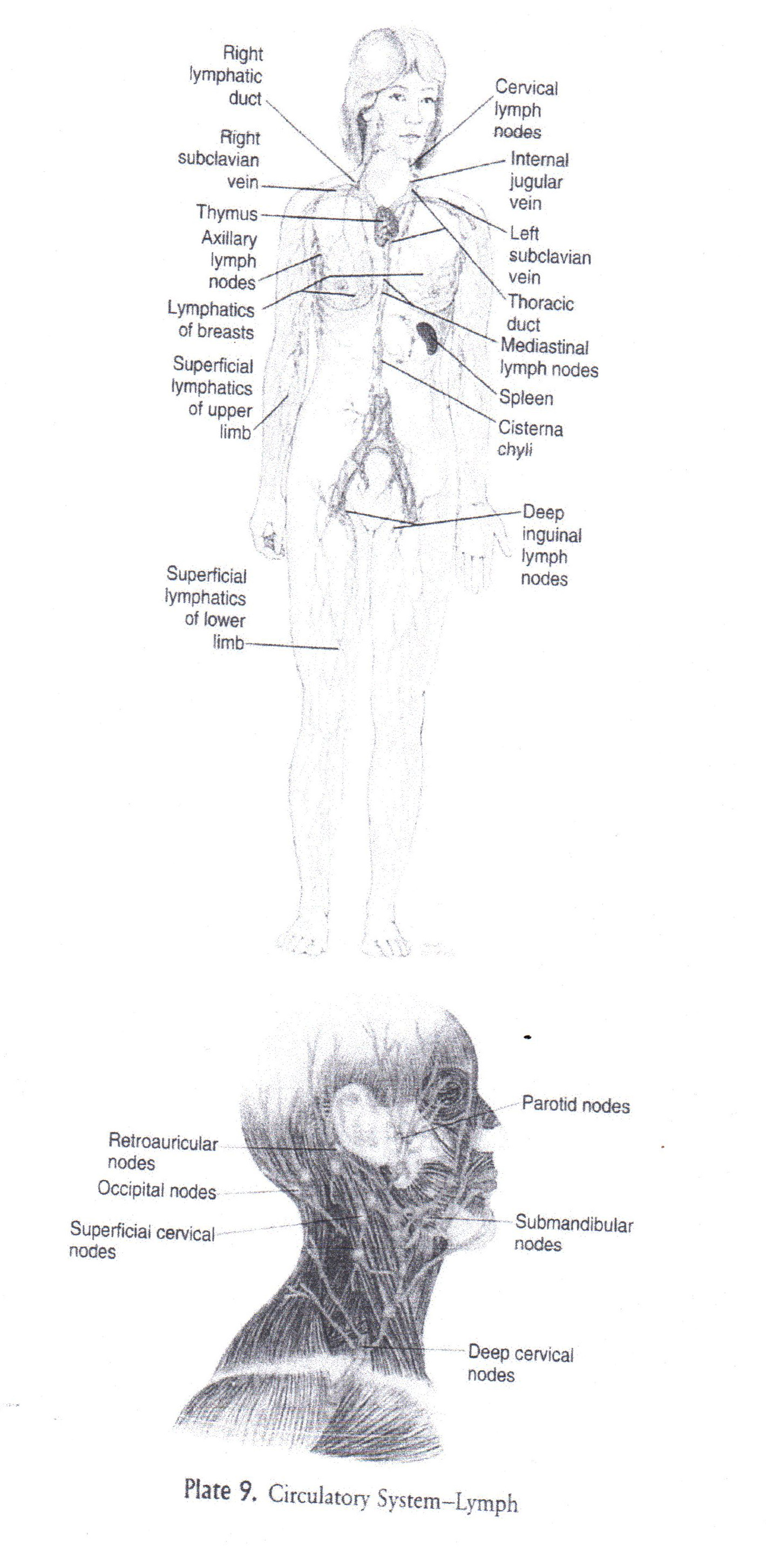
Appedix.
Додаток.


Дата добавления: 2019-07-17; просмотров: 119; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
