BUSINESS and ENTREPRENEURSHIP
Міністерство освіти і науки, молоді та спорту України
Київський національний торговельно-економічний університет
Вінницький торговельно-економічний інститут
Яцишин О.М.
АНГЛІЙСЬКА МОВА
ТОРГІВЛІ, ЕКОНОМІКИ ТА БІЗНЕСУ
Навчальний посібник
Вінниця 2012
Поширювати та тиражувати без офіційного дозволу КНТЕУ заборонено
| УДК 811.111(075.8) ББК 81.2Англ.я7 Я 93 |
| Рецензенти: | Латигіна А.Г., завідувач кафедри сучасних європейських мов Київського національного торговельно-економічного університету; |
| Козачишина О.Л., завідувач кафедри зіставного мовознав-ства Інституту іноземних мов Вінницького державного педагогічного університету ім. Михайла Коцюбинського; | |
| Кириленко В.В., завідувач кафедри англійської філології Інституту іноземних мов Вінницького державного педагогічного університету ім. Михайла Коцюбинського; |
| Я 93 | Яцишин О.М. Англійська мова торгівлі, економіки та бізнесу: Навч. посіб. – Вінниця: ВТЕІ КНТЕУ, 2012 р. – 678 с. |
ISBN 966-629-071-5
Навчальний посібник “Англійська мова торгівлі, економіки та бізнесу” розрахований на поглиблене вивчення англійської мови професійного спрямування студентами ВНЗ, які навчаються за торговельно-економічними напрями підготовки.
Мета посібника – забезпечити ефективне засвоєння користувачами базової термінології і понятійного апарату сфери торгівлі, економіки й бізнесу та розвиток на його основі мовних знань, комплексу мовленнєвих навичок і навичок перекладу.
|
|
|
Рекомендовано Міністерством освіти і науки, молоді та спорту України
як навчальний посібник для студентів вищих навчальних закладів
(Лист №1/11-2628 від 28.02.12)
| УДК 811.111(075.8) ББК 81.2Англ.я7 | |
| ISBN 966-629-071-5 | © О.М. Яцишин |
| © Київський національний торговельно-економічний університет, 2012 |
ВСТУП
Навчальний посібник “Англійська мова торгівлі, економіки та бізнесу” – одне із навчально-методичних видань, цільовою аудиторією яких є фахівці / майбутні фахівці торговельно-економічної галузі, що прагнуть оволодіти англійською мовою спеціального вжитку.
Мета посібника – забезпечити ефективне засвоєння користувачами ба-зової термінології і понятійного апарату торговельно-економічної сфери, а також розвиток на його основі мовних знань та комплексу мовленнєвих навичок. Досягнення мети забезпечується системою вправ і завдань навчально-інформаційного, виховного й діагностичного характеру.
Навчальний посібник структуровано за принципом модульності, що дозволяє послідовно й планомірно розкривати і засвоювати зміст його дидактичного матеріалу. Структура модулів надає змогу викладачеві та студентам здійснювати досить точне (поурочне) планування своєї лінгводидактичної діяльності.
|
|
|
Більшість розділів є уніфікованими. На початку кожного уроку представлені вправи довідкового характеру, зміст яких розкриває етимологію, систему значень, специфіку використання одиниць активного словника. Виконання цих завдань є підготовчим етапом до опрацювання текстового матеріалу.
Основою кожного уроку посібника є автентичний текст торговельно-економічної тематики, що слугує джерелом важливої для професійних потреб студентів інформації. Історичні довідки й факти з практики функціонування економічних систем та їхніх суб’єктів, які містяться в текстах посібника, сприятимуть кращому розумінню (майбутніми) фахівцями логіки розвитку і специфіки професійної діяльності підприємців, менеджерів, економістів, обліковців, маркетологів і, відтак, дозволятимуть реалізувати в навчанні міжпредметні зв’язки.
Зміст фахово орієнтованого текстового матеріалу розкривається й розгортається шляхом виконання комплексу мовних і мовленнєвих вправ, що сприяють не лише ефективному засвоєнню активного вокабуляру в різних контекстах, але й дозволяють відпрацьовувати навички перекладу і читання (у тому числі функціонального), а також усного діалогічного та монологічного мовлення.
|
|
|
Наявність у кожному модулі вправ для самоперевірки дозволяє систематизувати вивчений матеріал, реалізувати діагностичну й прогностичну функцію педагогічної оцінки.
Посібник містить довідник-глосарій економічних термінів, який стане в нагоді не лише студентам, але й викладачам-філологам (яким з об’єктивних причин може бракувати спеціальних економічних знань).
Зміст і структура посібника жорстко не регламентують конкретні методичні прийоми його використання у навчальному процесі. В залежності від обсягу аудиторного навантаження, кількості годин, відведених на самостійну роботу студентів, конкретних вимог програми навчального курсу користувачі посібника можуть варіювати послідовність вивчення модулів, розділів і вправ, відводити окремі уроки на самостійне опрацювання.
CONTENTS
| INTRODUCTION …………………………………………………………. | 3 |
| CONTENTS ………………………………………………………………. | 5 |
| 1. | MODULE 1. Business and Entrepreneurship |
|
|
|
| 1.1. | Unit 1. Business & Businesses | ||
| Lesson 1. What is Business? ………………………………..…. | 8 | ||
| Lesson 2. Forms of Business Organization …………………..... | 24 |
| 1.2. | Unit 2. Entrepreneurship | ||
| Lesson 1. Entrepreneurs and Entrepreneurship (Part I) .............. | 40 | ||
| Lesson 2. Entrepreneurs and Entrepreneurship (Part II) ............ | 76 |
| 1.3. | Unit 3. Doing Business Internationally | ||
| Lesson 1. International Business ………………………………. | 87 | ||
| Lesson 2. Barriers to International Business …………………… | 105 |
| 1.4. | Unit 4. Communication in Business | ||
| Lesson 1. Modern Means of Business Communication ………… | 111 | ||
| Lesson 2. Cross-cultural Barriers to Business Communication.. | 125 |
| 1.5. | Module Test 1 …………………………………………………. | 135 |
| 2. | MODULE 2. Economy, Economics and Trade |
| 2.1. | Unit 1. Economy & Economics | ||
| Lesson 1. What is Economics? ……………………………..…. | 151 | ||
| Lesson 2. Economy …………………………………………….. | 172 |
| 2.2. | Unit 2. Trade | ||
| Lesson 1. What is Trade?……………………………………… | 191 | ||
| Lesson 2. Forms of Trade ……………………………………… | 205 | ||
| Lesson 3. International Trade …………………………………. | 225 | ||
| Lesson 4. Modern Patterns of International Trade …………… | 236 |
| 2.3. | Module Test 2 …………………………………………………. | 247 | |
| 3. | MODULE 3. Product, Market and Marketing | ||
| 3.1. | Unit 1. Product & Market | ||
| Lesson 1. What is Product? ………………………………..…… | 258 | ||
| Lesson 2. Understanding Information on Products ……………. | 277 | ||
| Lesson 3. Market and Market Relations ………………………. | 295 |
| 3.2. | Unit 2. Marketing & Advertising | ||
| Lesson 1. What is Marketing?…………………………………. | 319 | ||
| Lesson 2. Extended Marketing Mix ……………………………. | 337 | ||
| Lesson 3. Advertising…………………………………………… | 357 |
| 3.3. | Module Test 3 …………………………………………………. | 379 |
| 4. | MODULE 4. Money and Banking |
| 4.1. | Unit 1. Money vs. Currency | ||
| Lesson 1. What is Money? …………………………………….. | 391 | ||
| Lesson 2. Money and Currency ………………………………… | 406 |
| 4.2. | Unit 2. Banks & Banking | ||
| Lesson 1. What is a Bank? (Part I) ……………………………. | 419 | ||
| Lesson 2. What is a Bank? (Part II)…………………………… | 430 |
| 4.3. | Module Test 4 …………………………………………………. | 442 |
| 5. | MODULE 5. Finance and Accountancy |
| 5.1. | Unit 1. Finance vs. Finances | ||
| Lesson 1. What is Finance? (Part I)………………………….…. | 453 | ||
| Lesson 2. What is Finance? (Part II) ………………………….. | 469 | ||
| Lesson 3. Fiscal Years: Year in, Year out …………………….. | 478 |
| 5.2. | Unit 2. Accounting & Accountants | ||
| Lesson 1. Accounting Overview (Part I) ………………………. | 493 | ||
| Lesson 2. Accounting Overview (Part II) ……………………… | 507 |
| 5.3. | Module Test 5 …………………………………………………. | 521 |
| 6. | MODULE 6. Company. Human Resources. Management. |
| 6.1. | Unit 1. A Company and its Staff | ||
| Lesson 1. Talking about Companies …………………………… | 533 | ||
| Lesson 2. Some Oldest Companies in the World ……………… | 558 | ||
| Lesson 3. Company Structure ……………….………………… | 572 | ||
| Lesson 3. Human resources ………………….………………… | 590 |
| 6.2. | Unit 2. Management & Leadership | ||
| Lesson 1. Management (Part I) ………………………………… | 611 | ||
| Lesson 2. Management (Part II) ………………………………. | 628 | ||
| Lesson 3. Leadership Styles ……………………………………. | 644 |
| 6.3. | Module Test 6 …………………………………………………. | 662 |
| AFTERWORD ……………………………………………………………. | 668 |
| GLOSSARY OF TERMS ………………………………………………… | 669 |
| REFERENCES ……………………………………………………………. | 683 |

BUSINESS and ENTREPRENEURSHIP
UNIT 1. BUSINESS & BUSINESSES
Lesson 1
Task 1. What do you think the English equivalents of the following Ukrainian sentences have in common?
1. Після університету він розпочав свою власну справу.
2. На війні як на війні (У торгівлі сентименти зайві).
3. Гарненькі справи! (Гарненька історія!)
4. Гірка праця – солодкий відпочинок.
5. Я керую малим підприємством.
6. Не пхай носа до чужого проса.
7. У семи няньок дитя без ока.
8. Це нікого не стосується.
9. Що вам тут потрібно?
10. Я кажу серйозно.
Task 2.Study the etymology of the word “BUSINESS” and its equivalents in some modern languages.
| Etymology: | BUSY + NESS | |
| Old English(before year 950) bisig (busy) + -nis → bisignis | ||
| bisignis– solicitude (заклопотаність, турботи); attentiveness (пильність) | ||
| The word got its modern two-syllable pronunciation in the 17th century. | ||
| Language | Equivalents of “BUSINESS” |
| Ukrainian | – бізнес, підприємництво, справи, комерція, виробництво; |
| Russian | – бизнес, предпринимательство, коммерция, производство; |
| Danish | – business, forretning; |
| German | – Busineß, Business, Geschäft, Unternehmen; |
| Finnish | – bisnes, liiketoimi[nta]; |
| French | – business, affaires, activité commerciale; |
| Italian | – business, affari, attività commerciale, imprenditoriale; |
| Spanish | – business, negocio, atenciones; |
| Turkish | – biznes, iş, ticaret. |
Task 3. a)The word “BUSINESS” has a wide range of meanings:

b)Which meaning of the word is revealed in the following sentences?
1. After graduating from the university he started his own business.
2. Business is business.
3. A pretty business!
4. Business before pleasure.
5. I run a small business.
6. Mind your own business.
7. Everybody’s business is nobody’s business.
8. It’s nobody’s business.
9. What is your business here?
10. I mean business.
Task 4. Compare the following meanings of “BUSINESS”:
|
|
| · A business (also called a firm or an enterprise) is a legally recognized organization designed to provide goods and / or services to consumers, governments or other businesses. A business needs a market. A consumer is an essential part of a business. · Business is the activity of making, buying, selling or supplying goods or services for money. |
Task 5.Distribute the following sentences into two groups according to the meaning of the word “BUSINESS”:
1) невелике промислове чи торговельне підприємство; фірма, компанія;
2) бізнес, підприємницька діяльність; справа, що приносить прибуток.
1.Their little shop has turned into a thriving business. 2. He may be a friend, but business is business and he’s not the man for the job. 3.He runs a small business in the town. 4.It’s a pleasure to do business with you. 5.How’s business? – Business is booming. 6.The company has been in business for almost 100 years. 7.Her parents own a small clothing business. 8.Many small businesses fail in their first year. 9.It was a mistake to go into business with my brother. 10. She didn’t want to work in the family business.
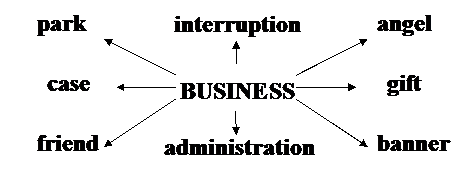
Task 6. a)The words below frequently occur after “BUSINESS”:
|
b)Which of the above word-combinations means:
· a type of advertising in the form of a banner which contains a company name, its site and other items related to its business;
· a client, customer or firm that is related to a given firm; a correspondent (that carries out missions on behalf of another person or organization);
· an investor who helps new companies develop by lending them his / her own money, which may involve a lot of risk;
· a document that presents the reasons that show why a product, project, etc. would be successful and make money, used to try to get people to invest in the project;
· a small item that a company gives free to people in order to advertise itself; an amount of money that a company gives to a charity (it may be used to obtain a reduction in the amount of tax a company has to pay);
· a situation where a company loses money when it has to stop work because of a disaster;
· the study or practice of planning, organizing and running a business;
· an area of land, usually outside a town or city that is especially designed for offices and small factories?
Task 7. Translate into English.
1.Зупинення діяльності підприємства; 2.“бізнес-ангел” (“ангел бізнесу”; “діловий ангел”); 3. діловий подарунок; 4. бізнес-баннер (реклама у формі баннера, що містить назву компанії, її сайт, та будь-які найменування, що пов’язані з її бізнесом); 5. клієнт; замовник; фірма, пов’язана з даною компанією; 6. обґрунтування ділової пропозиції; аналіз господарської ситуації; завдання щодо підприємництва; 7. бізнес-адміністрування; 8.комерційно-промислова зона.
Task 8.Translate into Ukrainian paying special attention to the words in italics.
1. Tens of millions of dollars were paid out on business interruption insurance claims as a result of the computer virus [`vaıərəs].
2. In their early stages many businesses raise money from business angels.
3. Business gifts are indispensable part of business practice.
4. Business banner is an important tool of advertising.
5. We need to expand the circle of business friends.
6. The website teaches you how to build a business case for a new product range.
7. Harvard Business School invented the Master of Business Administration degree (MBA) in 1921.
8. The plant is located on a nearby business park.
Task 9. Think and answer:
1. What can cause business interruptions?
2. Is it risky to be a business angel? Why?
3. Have you ever got business gifts? What is their expected effect?
4. What can make a business banner attractive?
5. Does the old saying “One who has many friends never needs a full purse” apply to business friends?
6. Can well prepared business cases facilitate business?
7. Are you studying for a degree in business administration (BA)?
8. Are there business parks in your neighbourhood?
Task 10. a)Translate some possible answers to the question “How’s business?”
| All is well.* All write [O:l `raıt].** Sour. Not too hot. Growing. Right on the money. | Heavenly. Up and down. Right on the line. Having no pains. All washed up. Sew-sew [`səu `səu].*** |
* well– добре, гарно, відмінно; здоровий;
**[O:l `raıt] – all write / all right
***[`səu `səu] – sew-sew / so-so; sew – шити, пришивати, зашивати.
b)Classify the answers into two categories:
1) Those reflecting well-being and success;
2) The ones which denote troubles and problems.
c)Can the above answers reflect the essence of some professional activities?Relate the answers to the following occupations.
1. The architect; 2. the author; 3. the banker; 4. the cook; 5. the dentist; 6. the doctor; 7. the farmer; 8. the laundryman; 9. the lift operator; 10. the milkman; 11. the minister; 12. the tailor.
Task 11.Think and answer.
1. What makes many people go into business?
2. What are the most common words for those who transact business?
3. Is it easy to start your own business these days?
4. Who usually runs a business?
5. Does it take much time and effort to build up a business?
6. Why do many firms go out of business?
7. What can help business owners expand their business?
Task 12. Practice reading the following words.
| 1. to acquire [ə`kwaıə] / [ə`kwaıər] 2. all-inclusive [ֽO:l ın`klusıv] 3. among [ə`mAŋ] 4. commercially [kə`mə:∫əli] 5. continuous [kən`tınjuəs] 6. to contribute [kən`trıbju:t] 7. cycle [`saıkəl] 8. debaten [dı`beıt] 9. either[`aıðə] BrE 87%; AmE 16%; [`i:ðər] BrE 13%; AmE 84% 10. to encompass [ın`kAmpəs] 11. to ensure [ın`∫O:] / [ın`∫u:ər] 12. to excel [ık`sel] 13. enterprise [`entəpraız] 14. etymology [ֽetı`mOləGi] 15. exact [ıg`zækt] 16. generalized [`Gənərəlaızd] 17. giant [`Gaıənt] 18. however [hau`evə] / [hau`evər] 19. increasingly [ıŋ`kri:sıŋli] 20. manufacturing[ˏmænju`fækt∫ərıŋ] 21. to occur [ə`kə:] | 22. particular [pə`tıkjulə] 23. period [`pıəriəd] / [`pıriəd] 24. persuit[pə`sju:t] / [pər`su:t] 25. primary [`praiməri] 26. profit[`prOfıt] 27. prosperity [prO`sperəti] 28. series [`sıəri:z] / [`sıri:z] 29. singular[`sıŋgjulə] / [`sıŋgjələr] 30. social [`səu∫əl] / [`sou∫əl] 31. society [sə`saıəti] 32. sophisticated [sə`fıstıkeıtıd] 33. successful [sək`sesfəl] 34. to supply [sə`plaı] 35. therefore [`ðeəfO:] / [`ðerfO:r] 36. though[ðəu] / [ðou] 37. through [θru:] 38. throughout[θru:`aut] 39. unfortunatelly[An`fO:t∫ənətli] 40. venturesome [`vent∫əsəm] 41. viable [`vaıəbəl] 42. violence [`vaıələnts] 43. whole [həul] |
Task 13. Read the text.
What is Business?
“Business” (informally “biz”) is a word which is commonly used in many different languages. Its etymology relates to the state of being busy either as an individual or society as a whole, doing commercially viable and profitable work.
This broad, all-inclusive term can be applied to many kinds of enterprise. Business encompasses a broad range of action, from individual pursuits to the work of giant corporations. The term covers manufacturing, trade and other economic activities of individuals and institutions.
However, the exact definition of business, like much else in the philosophy of business, is a matter of debate.
The term “business” has at least three usages, depending on the scope:
1) the singular usage to mean a particular company or corporation;
2) the generalized usage to refer to a particular market sector, such as “the music business” and compound forms such as “agribusiness”; and
3) the broadest meaning to include all activities by the community of suppliers of goods and services.
Business is an increasingly important activity throughout the world. Millions of people are involved in making, buying, selling or supplying goods or services for money. They go into business to get a maximum profit. Profit, also known as an economic surplus, is the money that remains after all the expenses are paid. Creating an economic surplus is a primary goal of business activity.
Business is like life itself, a cycle – a continuous series of challenges, obstacles, economic movements and above all increasing and sophisticated competition that will always occur. An enterprise, therefore, must continually re-invent and develop itself if it is to remain relevant and successful.
Unfortunately, business is not always brisk. There are periods when it drops off and businessmen sustain losses or even go out of business.
A well-known saying holds “Nothing venture, nothing have.” Business always involves risk-taking. Still some ventures are more risky than others. Business angels or venture capitalists are among those involved in venturesome undertakings of providing capital for new commercial enterprises.
Though business is sometimes defined as the art of removing money from a person’s pocket without using violence, its importance cannot be overestimated. Business is the means through which society’s standard of living improves. It provides the bulk of our employment as well as the products we enjoy. Above all, business is a place where anyone can excel by deploying the learning, skills and standards they have acquired to ensure not only their own prosperity but to contribute to the social welfare.
Vocabulary Notes:
1. etymology [ֽetı`mOləGi] – етимологія, наука про джерела й походження слів і морфем;
2. viable [`vaıəbəl] – життєздатний; такий, що спонукає ефективну життєдіяльність;
3. profitable [`prOfıtəbəl] – прибутковий, вигідний, дохідний;
4. all-inclusive [ֽO:l ın`klusıv] – комплексний; всеохоплюючий; такий, що включає усе;
5. to encompass [ın`kAmpəs] – містити в собі; охоплювати;
6. action [`æk∫ən] – діяльність, активність, заходи;
7. pursuit [pə`sju:t] / [pər`su:t] – заняття, справа; професія;
8. to cover [`kAvə] / [`kAvər] – охоплювати, містити в собі;
9. scope [skəup] / [skoup] – масштаб, розмах, сфера;
10. to supply [sə`plaı] – постачати (with); поставляти, доставляти; давати;
11. economic surplus [ֽi:kə`nOmık `sə:pləs] – економічний надлишок;
12. expenses [ık`spentsız] – затрати; витрати; те, що підлягає відшкодуванню;
13. challenge [`t∫ælınG] – виклик; складне завдання, проблема;
14. obstacle [`Obstəkəl] – перепона, перешкода, завада;
15. increasing [ıŋ`kri:sıŋ] – зростаючий; такий, що збільшується;
16. sophisticated [sə`fıstıkeıtıd] – складний, тонкий; витончений (про смак, манери); оманливий;
17. relevant (to) [`reləvənt] – релевантний; доречний; що стосується справи;
18. brisk [brısk] – жвавий, пожвавлений; моторний;
19. to sustain losses [sə`stein lOsız] – зазнати втрат, збитків; терпіти збитки;
20. venturesome [`vent∫əsəm] – сміливий; відважний, хоробрий; ризикований, небезпечний;
21. undertaking [ֽAndə`teıkıŋ] – підприємство, справа; зобов’язання, угода, гарантія;
22. to overestimate[ֽəuvər`estımeıt] – переоцінювати; оцінювати занадто високо;
23. standard of living [`stændəd əv `lıvıŋ] – рівень життя;
24. employment [ım`plOımənt] – зайнятість (робочої сили); робота, служба;
25. to enjoy products [`prOdAkts] – користуватися (володіти) продукцією;
26. to deploy[dı`plOı] – використовувати, застосовувати; вводити в дію;
27. to excel [ık`sel] – відзначитися;
28. to acquire [ə`kwaıə] / [ə`kwaıər] – набувати, здобувати; досягати, оволодівати;
29. to contribute (to) [kən`trıbju:t] – сприяти (чомусь); робити внесок.
Task 14. Agree or disagree with the following statements. Correct false statements.
1. In many cultures the word “business” does not need translation.
2. Etymology of the word “business” relates to the state of being rich.
3. Business people are involved in commercially viable and profitable work.
4. Manufacturing and commercial trade are not the only components of business.
5. Philosophy suggests the exact definition of business.
6. The term “business” has several usages, depending on the country.
7. The importance of business is gradually decreasing in the world.
8. Business is like life itself.
9. Most people go into business to contribute to the social welfare.
10. Fortunately, business is not always risky.
Task 15. Match items in column A with their antonyms in column B.
| A | B |
| 1.to go into business | a)to sustain losses; |
| 2.profitable | b)fruitless, defective; |
| 3.to drop off | c)crude, naïve; |
| 4.employment | d)risk-free; |
| 5.increasing | e)earnings, gains; |
| 6.expenses | f)to underestimate; |
| 7.viable | g)to be brisk; |
| 8.to get a profit | h)to go out of business; |
| 9.venturesome | i)to lose; |
| 10.sophisticated | j)unemployment; |
| 11.to overestimate | k)loss-making; |
| 12.to acquire | l)decreasing; |
Task 16. Complete the sentences with the words and phrases from Task 15.
1. Business angels are involved in _____ activities.
2. Loss-making companies often have to _____ business.
3. When business is _____ a company gets high profits.
4. Those who ______ business risks will surely sustain losses.
5. The _____ of loss-making enterprises are higher than profits.
6. When business drops off the rate of _____ increases.
7. Not all business people are involved in commercially _____ and profitable work.
8. People go into business to get a maximum _____.
Task 17. a) Match the terms in column A with their definitions in column B:
| A | B |
| 1. enterprise 2. competition 3. employment 4. business cycle 5. manufacturing 6. venture capitalist | a)the business or industry of producing goods in large quantities in factories, using parts or raw materials; b)a company or business; a business project, especially one that is difficult or involves taking risks; the activity of starting and developing businesses; c)the usual pattern of a country’s economy over a period of time, with periods of success (growth) and periods of difficulty (recession) happening regularly one after another; d)a private investor or a financial business that invests money in new companies, which may involve a lot of risk and bring good profits; e)a situation in which people or organizations compete with each other for something that not everyone can have; f)work, especially when it is done to earn money; the state of being employed; the situation in which people have work; the act of employing somebody; |
b) Translate into Ukrainian.
1. He really wants the job, but he will be facing stiff competition.
2. We are in competition with four other companies for the contract.
3. Graduates are finding it more and more difficult to find employment.
4. She has negotiated a five-year employment contract with a company.
5. How do you turn a loss-making enterprise into a profitable concern?
6. The country has been selling off its state enterprises.
7. Many jobs in manufacturing were lost during the recession.
8. The manufacturing sector is starting to recover.
9. Successful venture capital investment is harder than it sometimes looks.
10. The model isn’t all that complicated: develop a good idea, raise venture capital, grow rapidly, and then go public or sell out.
Task 18. In the text “What is Business?” (Task 13) find the words similar in meaning.
1. To get, to obtain; 2. majority, major part; 3. engaged, occupied; 4. popularly, usually, ordinarily, generally; 5. discussion; 6. occupation; 7. to assure, to guarantee; 8. company, firm; 9. production, making; 10. obstruction, hindrance, barrier; 11.to take place; 12. precise, exact; 13. fundamental; 14. range, scale; 15. prosperity, well-being.
Task 19. a)Translate the following nouns. Find the paronymous (related) adjectives in the text “What is Business?” (Task 13).
| 1. Difference; | 3.profit; | 5.risk; | 7.relevance; |
| 2. society; | 4.economy; | 6.venture; | 8.success. |
b) Use the derived adjectives to make up word combinations with the following nouns. Try to make up as many word combinations as possible.
| _____ welfare; _____ undertakings; _____ enterprise; | _____ languages; _____ work; | _____ venture; _____ activities. |
c) Which of the above word combinations were used in the text “What is Business?” (Task 13)?
Task 20. a)Match the verbs (column A) with the nouns (column B) to make up phrases.
| A | B |
| to be in | |
| to take | risk |
| to run | loss |
| to incur | work |
| to share | profit |
| to make | goods |
| to cover | business |
| to do | expenses |
| to be out of |
b) Translate into English.
1. Укладати угоди, вести справи, торгувати;
2. керувати підприємством, вести справу;
3. займатися торговельними справами;
4. викликати, спричинювати витрати;
5. виконувати, здійснювати роботу;
6. зазнати збитків, проторгуватися;
7. збанкрутувати; бути банкрутом;
8. покривати витрати, збитки;
9. брати участь у прибутках;
10. отримувати прибуток;
11. розподіляти витрати;
12. виготовляти товари;
13. бути безробітним;
14. зазнавати ризику;
15. покривати ризик;
16. мати роботу.
Task 21. Translate into Ukrainian paying attention to the italicised words.
1.What kind of work do you do? 2.It’s not the best piece of work you’ve ever done. 3.He’s someone I can do business with. 4.We do business with many domestic companies. 5.The factory makes luxury goods (предмети розкошу) for the export market. 6.There’s no way you can make a loss on this deal. 7.We made a loss on the house sale. 8.He’s only interested in making a quick profit. 9.A businessman will catch at (схопиться за) any chance of making a profit. 10.I’m afraid I won’t be able to cover all the expenses when this bill matures (настане час оплати цього рахунку). 11.The insurance will cover all expenses incurred during your time in hospital. 12.He was given a sum of money to cover his travel expenses. 13.Will £20 cover your expenses? 14.The insurance policy (страховий поліс) covers a range of risks. 15.Who will cover the risk of our property damage? 16.The economy is growing fast and more people are in work than ever before. 17.He’s in business in a small way. 18.They have been in business, not for love, but to make money. 19.The percentage of people out of work has fallen. 20.Many small shops are out of business these days. 21.I’m not prepared to run the risks. 22.You have to run a lot of risks if you want to succeed in business. 23.It was my dream to run my own business. 24.Owners of the partnership share their profits. 25.A plan was brought forward to allow workers to share in the profits. 26.They established a rule that everyone must share the expenses. 27.It was my understanding that we would share the expenses. 28.The company has incurred huge losses over the past three years. 29.Each stage of the process incurs an additional risk. 30.I take calculated risks but never gamble (граю в азартні ігри). 31.I was taking a big risk in lending her the money. 32.A good pilot never takes a risk.
Task 22.Make up sentences with the following word combinations.
| 1.To take a risk; | 7.to be in work; | 13.to run the risk; |
| 2.to do work; | 8.to be in business; | 14.to run a business; |
| 3.to do business; | 9.to be out of work; | 15.to cover the risk; |
| 4.to make a loss; | 10.to be out of business; | 16.to cover expenses; |
| 5.to make goods; | 11.to share profits; | 17.to incur a risk; |
| 6.to make a profit; | 12.to share expenses; | 18.to incur an expense. |
Task 23.“Odd man out.” In each line cross out a word that in its meaning differs from the others. Explain your choice.
| 1. term – definition – competition; 2. meaning – increasing – etymology; 3. a business – an enterprise – agribusiness; 4. competition – market – community; 5. profitable – relevant – overestimated; 6. challenge – success – obstacle; 7. buying – selling – supplying; | 8. apply – scope – usage; 9. issue – debate – goal; 10. sell – excel – success; 11. viable – relevant – busy; 12. brisk – risk – successful; 13. expenses – profit – surplus; 14. create – develop – re-invent; 15. giant – all-inclusive – broad. |
Task 24. Give the English equivalents for the following words and word-combinations.
1.Бути пов’язаним, стосуватися, пов’язувати; 2.виробник; 3.визначати; 4.використання; 5.створювати; 6.постачальник; 7.перевозити, рухати; 8.конкуренція; 9.розвивати; 10.втрати, збитки; 11.наймати, давати роботу; 12.продукція; 13.гарантувати; 14.процвітання; 15.робити внесок.
Task 25. Fill in the blanks with noun or verb forms. Use your dictionary if necessary.
| NOUN | VERB |
| 1.----------- | to relate |
| 2.manufacturer | ----------- |
| 3.----------- | to define |
| 4.usage | ----------- |
| 5.----------- | to create |
| 6.supplier | ----------- |
| 7.----------- | to move |
| 8.competition | ----------- |
| 9.----------- | to develop |
| 10.loss | ----------- |
| 11.----------- | to employ |
| 12.products | ----------- |
| 13.----------- | to ensure |
| 14.prosperity | ----------- |
| 15.----------- | to contribute |
Task 26. Use the correct noun or verb forms in the sentences. Change the grammatical form of the words if necessary.
Relate
a) We are only interested in figures that _____ directly to the company’s profitability.
b) International business _____ can be of different kinds.
Manufacturer
a) Faulty goods should be returned to _____.
b) The plant _____ 500 000 cars annually.
Define
a) The _____ of “business” has changed over the years.
b) A business case clearly _____ goals of the company.
Usage
a) The word “business” _____ in many different languages.
b) This term has at least three _____, depending on the scope.
Create
a) _____ of an economic surplus is a primary goal of business activities.
b) Business _____ thousands of jobs every year.
Supplier
a) We _____ Internet-based services to big businesses in Europe.
b) It is one of the world’s largest _____ of mobile phones.
Move
a) Manufactured products need to be _____ from the factory to the marketplace.
b) These laws facilitate free _____ of goods and services across national borders.
Competition
a) They were faced with fierce _____.
b) We can’t _____ with them for price.
Develop
a) Business offers great opportunities for career _____.
b) The company _____ and markets new software.
Loss
a) The business has _____ money on that deal.
b) The company reported heavy _____ for last year.
Employ
a) How many people does a company _____?
b) Graduates are finding it more and more difficult to find _____.
Products
a) The firm _____ 25 million tons of steel a year.
b) We need a new range of _____.
Ensure
a) Millions of dollars were paid out on business interruption _____ claims.
b) Our new marketing strategy _____ that we get the best possible results.
Prosperity
a) Our future _____ depends on economic growth.
b) The business has overcome its early problems and is now _____.
Contribute
a) His company made a very large _____ to the local community development.
b) We made a suggestion that each worker should _____ one day’s pay.
Task 27. a)Translate the following proverbs into Ukrainian.
1. When pleasure interferes with business, give up business. (from American)
2. There are no old friendships in business. (from Ukrainian)
3. Do not leave the morning the business of the evening. (from Turkish)
4. The art of doing business lies more in paying than in buying. (from Spanish)
5. Let every man mind his own business. (from Spanish)
6. Nothing ventured, nothing gained. (from French)
7. Who ventures to lend, loses money and friend. (from Dutch)
8. Venture a small fish to catch a much greater one. (English proverb)
9. Profit is the brother of loss. (from Turkish)
10. Cut your losses and let your profits run. (from American)
11. Accomplishment of purpose is better than making a profit. (from Nigerian)
12. Where profit is, loss is hiding nearby. (from Japanese)
13. A wealthy man will always have followers. (from Nigerian)
14. Poverty is not a crime. (from Spanish)
15. Work is the medicine for poverty. (from Beninese)
16. True poverty does not come from God. (from Yiddish)
17. The doctor has a remedy for everything but poverty. (from Yiddish)
18. When poverty comes in the door, love flies out of the window. (English proverb)
19. Unemployment does not guarantee leisure. (English proverb)
b)Choose one of the proverbs to comment on.
Task 28. Translate into English:
1.Слово “бізнес” широко використовується в багатьох мовах. 2.Поход-ження слова “бізнес” пов’язане зі станом зайнятості. 3.Термін “бізнес” застосовується до багатьох видів підприємництва. 4.Точне визначення “бізнесу” залишається дискусійним питанням. 5.У найширшому розумінні бізнес включає в себе діяльність усієї спільноти постачальників товарів і послуг. 6.Бізнес включає в себе виробництво, торгівлю й інші види економічної діяльності окремих осіб та установ. 7.Мільйони людей займаються виробництвом, купівлею, продажем або постачанням товарів і послуг. 8.Прибуток – це гроші, які залишаються після сплати всіх витрат. 9.Створення економічного надлишку є основною метою ділової діяльності. 10.Бізнес – це серія викликів, перешкод, економічних змін. 11.Підприємство повинно постійно оновлюватися та розвиватися, щоб залишатися успішним. 12.На жаль, бізнес не завжди йде жваво. 13.Хто не ризикує, той не п’є шампанське. 14.Бізнес часто визначають як мистецтво відбирання грошей з кишені людей, не застосовуючи силу. 15.Бізнес – це сфера, де кожен може відзначитися.
Task 29. Answer the questions:
1. What is the etymology of the word “business”?
2. What does the concept of business cover?
3. What is the exact definition of business? Is it still a matter of debate? Why?
4. What are the three most common usages of the term “business”? What do they depend on?
5. Is business an increasingly important activity throughout the world today? Why?
6. What is a primary goal of business activity?
7. What is an economic surplus?
8. What makes business similar to life itself?
9. What will always remain the integral part of business?
10. Why must enterprises continually re-invent and develop themselves?
11. Is business a risk-free activity? Explain your answer.
12. What makes activities of venture capitalists risky?
13. Why is business sometimes defined as the art of removing money from a person’s pocket without using violence? Do you agree with the definition?
14. How does business contribute to the social welfare?
15. Is business important for personal prosperity? Why?
Task 30. Say what you know about:
1. The etymology of the word “business”.
2. The scope of meanings of the term “business”.
3. Major goal of business activity.
4. The cyclical nature of business.
5. Most venturesome activities in business.
6. The importance of business for social welfare.
Task 31. Comment on the following statements:
1. Business is business.
2. Business before pleasure.
3. Profit is the brother of loss.
4. Work is the medicine for poverty.
5. There are no old friendships in business.
6. A wealthy man will always have followers.
7. Everybody’s business is nobody’s business.
8. The growth of a large business is merely the survival of the fittest. (John D. Rockefeller).
9. It is difficult but not impossible to conduct strictly honest business. What is true is that honesty is incompatible with the amassing of a large fortune. (Mahatma Gandhi)
10. Business is not a game (although it has many parallels in sport), is not a club or benevolent society but should be the most noble of all human endeavour with the highest ethics, standards, diversity and above all, transparency.
––––––––––
John D. Rockefeller [`rOkəfelər] (1839-1937) a US businessman and philanthropist, known for being extremely rich.
incompatible [ֽınkəm`pætəbəl] – несумісний, несполучний (з – with);
amassing [ə`mæsıŋ] – накопичення; нагромадження;
Mahatma Gandhi [mə`hætmə `gændi] (1869-1948) an Indian lawyer and politician who successfully led the fight for India’s independence from the British. Gandhi is famous especially for developing the idea of non-violent protest, and his methods have been copied in many other places;
benevolent [bə`nevələnt] – доброзичливий; милосердний;
noble [`nəubəl] – благородний; шляхетний;
endeavour [ın`devə] – намагання; зусилля;
transparency [trænts`pærəntsi] – прозорість.
Lesson 2
Task 1. a)The words below frequently occur in front of “BUSINESS”.
|
b) Which of the above word combinations can be translated as:
· одноосібне підприємство; підприємство, що перебуває в управлінні однієї людини; підприємство з одним працівником;
· комерційна діяльність;
· власна справа;
· солідна справа;
· основна діяльність; профільна діяльність; основний вид діяльності, яким займається компанія;
· малий бізнес; мале підприємство;
· великий бізнес; велике підприємство; великий капітал;
· вітчизняний бізнес; вітчизняне підприємництво; внутрішня торгівля?
Task 2.Translate into Ukrainian paying special attention to the words in italics.
1. There have always been links between politics and big business.
2. The Republican Party always had a lot of support from big business.
3. The government adopted a policy to encourage investment and promote small business.
4. Today there are more small businesses in Japan than ever before.
5. It’s time to focus on the company’s core business.
6. Selling insurance is still their core business.
7. He is involved in do-it-yourself (DIY) business.
8. Years ago my grandfather started his DIY business.
9. They were accused of illegal trade business.
10. There are a number of one-man businesses in Ukraine these days.
11. Following the global economic crisis the domestic business went into a recession.
12. He has built up sound business.
Task 3.Compare the usage of the two adjectives below.

| · Small business is a business which usually employs fewer than 50 people and has a quite small financial turnover; small businesses used collectively: малий бізнес; мале підприємство. · Little business is an issue that needs consideration, but which is usually not of paramount importance and is not likely to be time-consuming: невелика справа. |
Task 4. Translate the sentences. Divide the sentences into two groups according to the meaning of “BIG BUSINESS”:
1) Large companies which have a lot of power and influence, considered as a group;
2) Something that has become important because people are willing to spend a lot of money on it; important business activity that makes a lot of money.
1. Elections are now big business.
2. Modern world is dominated by big business.
3. Health and fitness have become big business.
4. Alternative medicine can be big business these days.
5. He has always wanted to be in big business, be a big boss.
6. Big business will never let nationalism get in the way of a good deal.
Task 5. a)Study the verbs in the box.

b)Which of the above verbs mean:
b)Which of the above verbs means:
1. Керувати (торговельним) підприємством;
2. відкрити (розпочати) свою власну справу; відкрити торговельне підприємство;
3. вести комерційну діяльність?
c) Translate into Ukrainian.
1. We are starting up a new business.
2. They are very easy to do business with.
3. Susan built up a very successful business.
4. She had the idea of starting her own business.
5. We do very good business with this company.
6. Partners have equal rights to conduct business.
7. My cousin has set up in business as a hairdresser.
8. This is most efficient way of managing a business.
9. They advertised their services to drum up business.
10. We operate the whole business from our central office.
11. They launched their business last year with 15 employees.
12. Manufacturers are getting used to transacting business online.
13. He managed the family business while his father was away ill.
14. He left the teaching profession in 1999 to set up his own business.
15. He is far too poor hand (нікудишній бізнесмен)to be able to run a business.
16. John set up in business as a property developer (забудовник; венчурний будівельник).
17. As more businesses were established, Front Street became the main business street in town.
Task 6.Think and answer.
1. Can big business overcome cultural and political differences between countries?
2. Do governments always support the interests of big business?
3. Are elections big business in this country now? Why (not)?
4. Are there many small / big businesses in your city?
5. How does big business affect our lives?
6. What can be big business nowadays?
Task 7. a)Mind the usage of verbs in the following phrases.

| · To do business with somebody is to deal, trade or have common business with somebody. · To make it your own business to do something is to make an effort to do something because you think it is important. |
b)Read the example sentences. Make up similar sentences of your own.
1. I found them very easy to do business with. – Я з’ясував, що з ними надзвичайно легко вести справи.
2. It’s been a pleasure to do business with you. – З вами приємно мати справу.
3. You can’t do business with Uncle Whiskers!–З дядечком Семом жодних справ!
4. Don’t do business with fly-by-night people. – Не май справ з підозрілими людьми.
5. I am not used to being deceived by those I do business with. – Я не звик до того, щоб мене обманювали мої партнери по бізнесу.
6. He’s someone I can do business with. – Він той, з ким можна вести справи.
7. She makes it her own business to get to know all her staff. – Вона взяла на себе відповідальність познайомитися з усім своїм персоналом.
8. I shall make it my business to find out who is responsible. – Я вважатиму за обов’язок з’ясувати, хто винен.
Task 8. a)Revise the word-building rules.
Nouns ending in -or / -er often refer to a person who gives or sends something to somebody.
Nouns ending in -ee refer to the person who receives the thing.
For example:
· an employer gives a job to an employee;
· a payer pays money to a payee;
· a franchiser gives the right to operate a business to a franchisee;
· a lessor gives a lessee the use of a building;
· a licensor gives a licensee the right to use something.
| Some productive word-building suffixes are: -ship; -er; -ility; -ee; |
| E.g. | Friend + -SHIP= FRIENDSHIP work + -ER = WORKER able + -ILITY = ABILITY train + -EE = TRAINEE |
b) Use the above suffixes to form derivatives of the given words. Translate the words into Ukrainian.
1.Consume; 2.dealer; 3.employ; 4.entrepreneur; 5.law; 6.liable; 7.own; 8.owner; 9.partner; 10.photograph; 11.possible; 12.proprietor; 13.provide; 14.responsible; 15.trade.
Task 9. Practice reading the following words:
| 1. to allow [ə`lau] 2. category [`kætəgəri] / [`kætəgO:ri] 3. charter [`t∫α:tə] / [`t∫α:rtər] 4. civil [`sıvəl] 5. colloquial [kə`ləukwiəl] 6. consequence [`kOntsıkwənts] / [`kα:ntsəkwənts] 7. convenience [kən`vi:niənts] 8. corporate [`kO:pərət] / [`kO:rpərət] 9. criterion [kra`tıəriən] 10. debt [det] 11. delicatessen [ֽdelıkə`tesən] 12. distinguish [dı`stıŋgwı∫] 13. dominant [`dOmınənt] 14. effect [ı`fekt] 15. especially [ı`spe∫əli] 16. giant [`Gaıənt] 17. guest houses [`gest hauzız] 18. headcount [`hedkaunt] 19. initial [ı`nı∫əl] 20. kind [kaınd] 21. lawyer[`lO:jə] / [`lO:jər] | 22. legal [`li:gəl] 23. liability [ֽlaıə`bıləti] 24. limited [`lımıtıd] / [`lımətəd] 25. medium-sized [`mi:diəm `saızd] 26. multinational [ֽmAlti`næ∫ənəl] 27. numerous [`nju:mərəs] 28. ownership [`əunə∫ıp] / [`əunər∫ıp] 29. photographer [fə`tOgrəfə] / [fə`tα:grəfər] 30. politician[ֽpOlə`tı∫ən] / [ֽpα:lə`tı∫ən] 31. private [`praıvət] 32. proprietor [prə`praıətə] / [prə`praıətər] 33. proprietorship [prə`praıətə∫ıp] / [prə`praıətər∫ıp] 34. restaurant [`restərOnt] / [`restərənt] 35. sole [səul] 36. subsequent [`sAbsıkwənt] 37. symbolic [sım`bOlık] / [sım`bα:lık] 38. talent [`tælənt] 39. tradesmen [`treıdzmən] 40. vary [`veəri] / [`veri] |
Task 10.Read the text.
Дата добавления: 2018-06-27; просмотров: 874; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!