Read the description of the phenomenon and complete the sentences with the correct terms.
Superconductivity: it gets the current flowing Module 11 Lesson 2 18 Look at the list of Nobel Laureates in Superconductivity and match them with the photos 1________________ 2_____________________ 3___________________ 4____________________ 5______________________ 6__________________ 7___________________ 8____________________ 9_____________________ 1 Heike Kamerlingh Onnes 2 Pyotr L. Kapitsa 3 Lev Landau 4 Vitalij Ginzburg 5 Leon Cooper 6 John Schrieffer 7 John Bardeen 8 Brian David Josephson 9 Alexei Abrikosov
Complete the sentences with the proper names of the Nobel Laureates in Superconductivity.
P.Kapitsa J. Bardeen K.Onnes L. Cooper L.Landau V. Ginzburg J.Schrieffer
1 The era of low-temperature physics began in 1908 when the Dutch physicist _____________first liquefied helium which boils at 4.2 K at standard pressure.
2 The BCS theory named after_________ ___________ __________ is the first microscopic theory of superconductivity since the discovery in 1911. They received the Nobel prize in Physics for this theory in 1972.
3 In 1932, the Royal Society Mond Laboratory* was created specially for _________. By 1934 he had developed there “an ingenious device for liquefying helium in large quantities – a pre-requisite for the great progress in low- temperature physics.”
4 In 1950_________and ______published a phenomenological theory for superconductivity, wherein the order parameter introduced by ________to describe phase transitions is identified as a scalar wave function. According to this theory the properties of superconductors depend on a dimensionless material constant- now known as ________– ________ constant.
5 You have to be brilliant to win a Nobel Prize in Physics. But imagine how amazingly brilliant you need to be to scoop two of these prizes. That was the achievement of American physicist _________. He won his first prize in 1956 (with Brattan and Shockley) for inventing the transistor.
|
|
|
But he won a second prize almost three decades later, in 1972 (with Cooper and Schrieffer), for developing the best theory we currently have of how superconductors work.
*Royal Society Mond Laboratory – Laboratory for Studying Liquid Hydrogen, Cambridge, England.
Complete the sentences with the correct dates.
2003 1972 1962 1913 1973 1978
1. In … Lev Landau received the Nobel Prize in Physics “for his pioneering theories for condensed matter, specially liquid helium.
2. In … John Bardeen, Leon Cooper and John Shrieffer received the Nobel Prize in Physics “for the jointly developed theory of superconductivity, usually called the BCS theory.
3. In … Heike Kamerling Onnes received the Nobel Prize in Physics “for his investigations on the properties of matter at low temperatures, which led to the production of liquid helium and the discovery of superconductivity.
4. In … Pyotr Kapitsa received one half of the Nobel Prize in Physics “for his basic inventions and discoveries in the area of low temperature physics, which included the discovery of superfluidity in helium.”
5. In … AlexeiAbrokosov and Vitalij Ginzburg received the Nobel Prize in Physics “for pioneering contributions to the theory of superconductors and superfluids.”
6. In … Brian David Josephson received one half of the Nobel Prize in Physics “for his theoretical predictions of the properties of a current through tunnel barrier, in particular those phenomena which are generally known as the Josephson Effects.
21Choose one scientist you like most and write several sentences about their discoveries and research work. Search the Internet if necessary.
22 Work in pairs. Ask and answer the questions about Nobel Laureates in Superconductivity.
Student A: Do you remember when Onnes received the Nobel Prize in Physics?
|
|
|
Student B: I suppose it happened in 1913.
Student A; What did he get it for?
Student B: Well, I think for the discovery of superconductivity.
Read the information and prepare to talk about this important discovery. Present your talk to other students in your group. Listeners: make notes of questions to ask them at the end.
Why and how did Kamerlingh Onnes discover superconductivity?
At the beginning of the 20th century, K. Onnes wanted to measure and understand the properties of metals at very low temperatures. Until then, we only knew that the resistance in a metal progressively drops when the temperature is decreased. But what would happen if we cooled the metal to absolute zero? Would the resistance continue to slowly decrease, would it reach an absolute minimum or would it approach an infinite value?
The first measurements showed a saturation to a minimum of resistance, but this limit seemed to depend on the purity of the metal. This is the reason why Onnes decided to measure a metal he knew how to purify: mercury.
 On April 8th 1911 Onnes discovered to his own amazement that below 4.2 K the resistance of mercury suddenly dropped to zero!
On April 8th 1911 Onnes discovered to his own amazement that below 4.2 K the resistance of mercury suddenly dropped to zero!
.
These words in Dutch Kwik nagenoeg nul werefound in
Onnes’s notebook. They were written on April 8th 1911.
In English it means the resistance of mercury is zero.
|
|
|
This experiment can be repeated showing a very sudden drop which is completely unexpected. This happens as if the metal electrons suddenly started to move forward with nothing to slow them down.
K.Onnes called this phenomenon of perfect conductivity – superconductivity.
In the same experiment, he also observed the superfluid transition of helium at 2.2 K., without recognizing its significance. The precise date and the circumstances of the discovery were only reconstructed a century later, when Onnes’s notebook was found. In subsequent decades, superconductivity was observed in several other materials. In 1913 lead was found to superconduct at 7 K, in 1941 niobium nitride (нитрид ниобия) was found to superconduct at 16 K
Subsequent tests of tin and lead showed that superconductivity was a property of numerous metals if they were cooled sufficiently.
Although superconductivity remained an esoteric scientific research area during his lifetime, Onnes firmly believed that the resistance-free current would eventually allow for the creation of many practical devices.
24 Watch the video “What is a superconductor – Magic Marks” and complete these dialogues.
Student A: What is meant by the critical current densitywhen we speak about superconductors?
Student B: I suppose it is current density above which…
Student A: What does the critical current density depend on?
Student B; As far as I remember it depends on…
Student A; You know, some conditions can break the superconductivity of a material. What are they?
Student B: They mentioned three conditions: a)… b)… c)…
Student A: Could you explain the term the critical temperature for a superconductor?
StudentB I think it is the temperature at which...
25 Complete each figure with the correct term.


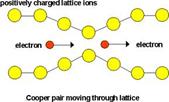 Cooper pairs The Meissner effect The Josephson effect
Cooper pairs The Meissner effect The Josephson effect
Fig. 1 __________ Fig 2 ____________ Fig.3 __________
|
|
|
Read the description of the phenomenon and complete the sentences with the correct terms.
BCS theory The Josephson effect Cooper pair The Meissner effect Josephson junction/current
1 _____ ____, the expulsion (вытеснение) of a magnetic field from the interior of a material that is in the process of becoming a superconductor, that is losing its resistance to the flow of electrical currents when cooled below a certain temperature, usually close to absolute zero.
2 The central feature of the ______ ____is that two electrons in the superconductor are able to form a bound called a _____ ________ if they somehow experience an attractive interaction.
3 ______ _____, flow of electric current between two pieces of superconducting material separated by a thin layer of insulating material. This arrangement – two superconductors linked by a non-conducting barrier- is known as a_____ ______, the current that crosses the barrier is the____ _____
Дата добавления: 2018-05-09; просмотров: 538; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
