Specific features of Labor market in dual economy
Development economics
Lecture 2
Theme: Neoclassical Models of Economic Development
• Neoclassical models as the alternative to Neo-Keynesian models.
• Neo-Keynesians consider the economic growth, first of all, as quantitative changes (i. e. increase of GDP as the result of capital inflow). Qualitative changes are ignored. Rely on the foreign aid.
• Neo-classics put priority on the endogenous resources of economic development.
• Capital is scarce in developing countries.
• Developing countries are rich with cheap labor power.
• Neo-Keynesian theories focus on the relationship between S (savings)and I (investments). Neoclassical theories analyze the equilibrium between capital accumulation and population growth.
• The founders of neoclassical models:Lewis W. A., Jorgenson O., Ranis A., Fei J.
• Thereal dualismas the main characteristic of any weakly developed economy
• The Neoclassical models may by classified into two groups:
I. Models with excessive labor supply.
II. Models of dualistic economy.
I.Models with excessive labor supply
Theories of dual economy
| Authors | Economicsectors | |
| Modern | Traditional | |
| Lewis W. | Capitalist | Non-capitalist |
| Hirshman A. | Developed North | Backward South |
| Shutz S. | Commodity economy | Natural economy |
Theme: Theories of dualistic economy
• Real dualism: traditional agricultural and modern industrial sectors .
• Traditional sector (pre-capitalist forms of production): quasi-stable equilibrium based on primitive technology and local experience.
• Modern sector (capitalist form of production ): high rates of technological progress, close links with the world market.
• Isolated position of capitalist sector in the national economy.
• Lewis W.A.: the theory of real dualism is applicable to the countries that are characterized by high density of population, capital shortage and scarce natural resources (India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Egypt and others) .
• Entrepreneur as the main driver of economic modernization (while the Keynesianists put the accent on the role of the state).
• Recall J. Schumpeter’s concept of the entrepreneur as the promoter of progress.
• The differences between Schumpeter’s and Lewis’ entrepreneurs.
• Unlimited supply of labor resources and minimum subsistence wage level.
Labor market equilibrium in developed countries
|
|
|

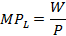
Specific features of Labor market in dual economy

• Labor supply is abundant and absolutely elastic. Average per capita wage is constant.
• An increase of labor demand does not cause any increase of real wage.
• In so doing, in dual economy in each of two sectors the distribution is determined by different economic laws: in industrial sector by the law of marginal productivity while in the agricultural sector by the law of average product of labor (institutional labor).
• Institutional labor in the agricultural sector does not exceed 70% of minimum subsistence wage in industrial sector.
• The wage in industrial sector is constant and independent of quantity of labor.
• On the next two slides there are represented two graphs: the initial Lewis’ model and Lewis’ model development prospects.
• The first slide shows the absolutely elastic labor supply in traditional (agricultural) sector and constant average per capita income.
Specific features of Labor market in dual economy

§ The labor supply exceeds labor demand. Marginal productivity of the excessive rural population is equal to zero.
Lewis’ model(the initial level of wage in industrial sector)

• In industrial sector(unlike agricultural sector) institutional wage is determined by the law of marginal production and diminishing following the increase of employment (negative D-curves slope).
Lewis’ model(the wage level dynamic in industrial sector)
• In industrial sector(unlike agricultural sector) institutional wage is determined by the law of marginal production and diminishing following the increase of employment (negative D-curves slope).
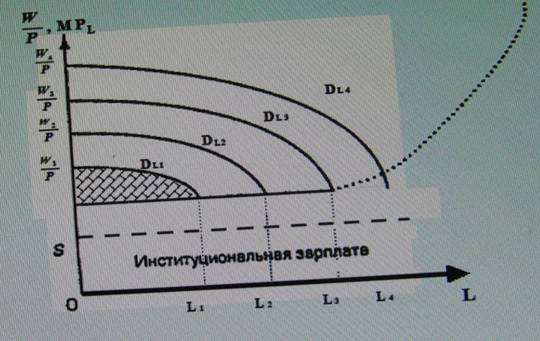
• As the industry develops, both wage and employment increase. D-curve shifts to the right until labor supply starts growing and real wage (  ) increases.
) increases.
• The profit is entirely used to hire ever new workers.
• The shadowed area on the graph shows the producer surplus
• It is received until there is surplus of labor power and labor supply is absolutely elastic.
• In future due to exhaustion of labor resources wage will start growing and surplus will be diminishing.
|
|
|
• Basing on this analysis, Lewis suggested that for the sake of economic modernization it would be necessary to redistributethe resources from agricultural sector to industrial.
Lewis’ model logic

• In accordance with the Lewis’ model, the development is understood, first of all, as an elimination of dualism of traditional (pre-industrial) and modern (industrial) economies.
Дата добавления: 2018-05-12; просмотров: 229; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
