Table 10 Transactions of Interest-Rate Swaps in H1 2017
| Transactions (lots) | Amount of the notional principal (RMB 100 million) | |
| H1 2017 | 61,192 | 55,343.8 |
| H1 2016 | 40,795 | 43,693.5 |
Source: China Foreign Exchange Trade System
Growth of the inter-bank CD market leveled off and the CD business made further progress. By end-June, 527 financial institutions had disclosed their annual CD issuance plans for 2017, among which 377 had already completed their issuances on the inter-bank market. In H1, a total of 12,600 inter-bank CDs were issued on the inter-bank market, raising RMB 9.52 trillion. Trading volume on the secondary market totaled RMB 47.17 trillion. In Q2, CD issuances registered a total of RMB 4.53 trillion, a decline of RMB 0.46 trillion from Q1. Both the issuances and trading of CDs were priced based on the Shibor, and the correlation between the issuance interest rates and the medium- and long-end Shibor remained strong. In June, the average weighted issuance interest rate of 3-month inter-bank CDs was 4.88 percent, 21 basis points higher than that of the 3-month Shibor. In H1, a total of 11,400 CDs was issued by financial institutions, raising RMB 3.12 trillion, an increase of RMB 0.43 trillion year on year.
Money-market interest rates moved up. As financial institutions took an initiative to adjust assets and liabilities, in late March activities in the inter-bank market began to decline, pushing up the interest rates. In May, market interest rates declined as expectations stabilized. In June, the weighted average interest rate of inter-bank lending was 2.94 percent, up 32 and 50 basis points respectively from March 2017 and December 2016; the weighted average interest rate of pledged repos reached 3.03 percent, up 19 and 47 basis points respectively from March 2017 and December 2016. In June, the weighted average interest rate of repos among deposit-taking institutions with rate securities as pledges was 2.83 percent, 20 basis points lower than the weighted average interest rate of pledged repos in the inter-bank market. Shibor rates were up. At end-June, the overnight and 7-day Shibor posted 2.62 percent and 2.85 percent respectively, up 39 and 30 basis points from end-2016. The 3-month and 1-year Shibor posted 4.5 percent and 4.42 percent respectively, up 123 and 105 basis points from end-2016.
The bond market yield curve flattened and shifted upward, and the trading volume and issuance of spot bonds declined
In H1, institutions tended to issue and trade more cautiously. The volume of spot bond trading on the inter-bank market posted RMB 44.6 trillion, representing an average daily turnover of RMB 362.3 billion and a decrease of 21.9 percent year on year. With respect to the trading entities, Chinese-funded small- and medium-sized banks and securities institutions were net bond sellers, with their net sales totaling RMB 2.2 trillion; other financial institutions and vehicles were net bond buyers, with their net purchases totaling RMB 1.7 trillion. In terms of products, a total of RMB 4.8 trillion of spot government bonds was traded, accounting for 10.9 percent of the total spot bond transactions on the inter-bank market; turnovers of spot financial bonds and corporate debenture bonds were RMB 30.6 trillion and RMB 8.7 trillion, respectively, accounting for 68.6 percent and 19.4 percent, respectively, of the total spot bond transactions on the inter-bank market. Separately, the volume of spot bond trading on the stock exchanges totaled RMB 2.6 trillion, an increase of 19.7 percent year on year.
Figure 4 Yield Curve of Government Securities on the Inter-bank Market
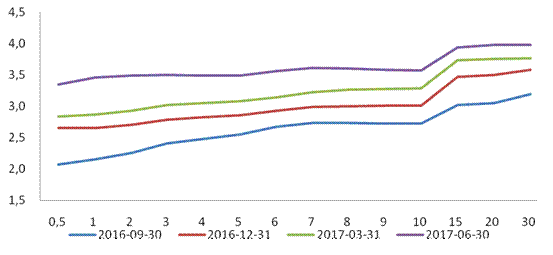
Source: China Central Depository & Clearing Co., Ltd.
The bond market yield curve flattened and shifted upward. Since April, with strengthened financial regulation, steady and improved domestic economic performance, and stronger expectations of normalization by the US Federal Reserve, there was a remarkable rise in the yield of government securities and the yield curve flattened further. Starting from late May, expectations of stronger regulation weakened and liquidity tended to stabilize, causing the yield of government securities to fall. At end-June, the yields of 1-year, 3-year, 5-year, 7-year, and 10-year government bonds were up 60 basis points, 48 basis points, 41 basis points, 39 basis points, and 29 basis points from end-March. At end-June, the spread between 1-year and 10-year government bonds narrowed by 31 basis points to 11 basis points.
Inter-bank market bond indices declined slightly. The China Bond Composite Index (net price) declined from 100.73 points at end-March to 99.77 points at end-June, representing a decrease of 0.95 percent. The China Bond Composite Index (full price) declined from 115.89 points at end-March to 114.87 points at end-June, a decrease of 0.88 percent. The Shanghai Securities Exchange T-Bond Index increased from 160.18 points at end-March to 160.41 points at end-June, an increase of 0.14 percent.
The volume of bond issuances declined significantly. In H1, a total of RMB 17.6 trillion of bonds was issued, a decrease of 2 percent year on year, among which issuances of inter-bank CDs grew rapidly whereas issuances of local government bonds and corporate bonds dropped notably year on year. At end-June, outstanding bonds posted RMB 68.6 trillion, an increase of 19.4 percent year on year.
Дата добавления: 2018-02-28; просмотров: 311; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
