Major ocean surface currents. NOAA map.
I. Learn active vocabulary:
contour – очертание, контур, характер
volume flow rate – объемная скорость течения, объемный расход
swift - быстрый
to empty - вливаться
brine – морская вода
exclusion – за исключением
ocean current – океанское течение
II. Read and translate the text:
An oceancurrent is continuous, directed movement of ocean water. Ocean currents are rivers of hot or cold water within the ocean. The currents are generated from the forces acting upon the water like the planet rotation, the wind, the temperature and salinity differences and the gravitation of the moon. The depth contours, the shoreline and other currents influence the current’s direction and strength.
Important currents
Ocean currents can flow for thousands of kilometers. They are very important in determining the climates of the continents, especially those regions bordering on the ocean. Perhaps the most striking example is the Gulf Stream, which makes northwest Europe much more temperate than any other region at the same latitude. Another example is the Hawaiian Islands, where the climate is cooler (sub-tropical) than the tropical latitudes in which they are located because of the California Current.
Background
Surface ocean currents are generally wind driven and develop their typical clockwise spirals in the northern hemisphere and counter-clockwise rotation in the southern hemisphere because of the imposed wind stresses. In wind driven currents, the Ekman spiral effect results in the currents flowing at an angle to the driving winds. The areas of surface ocean currents move somewhat with the seasons; this is most notable in equatorial currents.
Deep ocean currents are driven by density and temperature gradients. Thermohaline circulation, also known as the ocean’s conveyor belt, refers to the deep ocean density-driven ocean basin currents. These currents, which flow under the surface of the ocean and are thus hidden from immediate detection, are called submarine rivers. These are currently being researched by a fleet of underwater robots called Argo. Upwelling and downwelling areas in the oceans are areas where significant vertical movement of ocean water is observed.
Surface currents make up about 10% of all the water in the ocean. Surface currents are generally restricted to the upper 400 meters of the ocean. The movement of deep water in the ocean basins is by density driven forces and gravity. The density difference is a function of different temperatures and salinity. Deep waters sink into the deep ocean basins at high latitudes where the temperatures are cold enough to cause the density to increase. The main causes of currents are: solar heating, winds and gravity.
|
|
|
Ocean currents are measured in Sverdrup with the symbol Sv, where 1 Sv is equivalent to a volume flow rate of 106 cubic meters per second.
Gulf Stream
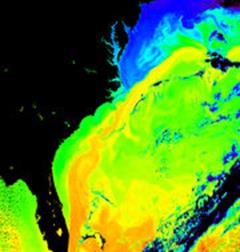
The Gulf Stream is orange and yellow in this representation
of water temperatures of the Atlantic. Source: NASA.
The GulfStream, together with its northern extension towards Europe, the North Atlantic Drift, is a powerful, warm, and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico, exits through the Strait of Florida, and follows the eastern coastlines of the United States and Newfoundland before crossing the Atlantic Ocean. At about 30°W, 40°N, it splits in two, with the northern stream crossing to northern Europe and the southern stream recirculating off West Africa. The Gulf Stream influences the climate of the east coast of North America from Florida to Newfoundland, and the west coast of Europe. It is part of the North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre.
Дата добавления: 2015-12-21; просмотров: 114; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
