Geodesy, Student – group, name
Information
Traverse (surveying) and Types Of Traverse
Traverse is a method in the field of surveying to establish control networks. It is also used in geodetic work. Traverse networks involved placing the survey stations along a line or path of travel, and then using the previously surveyed points as a base for observing the next point.
Traverse (surveying)
Traverse is a method in the field of surveying to establish control networks. It is also used ingeodetic work. Traverse networks involved placing the survey stations along a line or path of travel, and then using the previously surveyed points as a base for observing the next point. Traverse networks have many advantages of other systems, including:
� Less reconnaissance and organization needed;
� While in other systems, which may require the survey to be performed along a rigid polygon shape, the traverse can change to any shape and thus can accommodate a great deal of different terrains;
� Only a few observations need to be taken at each station, whereas in other survey networks a great deal of angular and linear observations need to be made and considered;
� Traverse networks are free of the strength of figure considerations that happen n triangular systems;
� Scale error does not add up as the traverse is performed. Azimuth swing errors can also be reduced by increasing the distance between stations.
The traverse is more accurate than triangulateration (a combined function of the triangulation and trilateration practice).
Types
Frequently in surveying engineering and geodetic science, control points (CP) are setting/observing distance and direction (bearings, angles, azimuths, and elevation). The CP throughout the control network may consist of monuments, benchmarks, vertical control, etc.
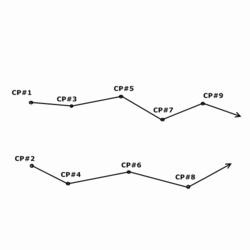
Diagram of an open traverse
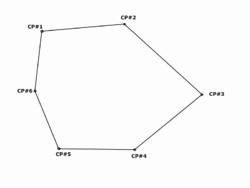
Diagram of a closed traverse
Open/Free
An open, or free traverse (link traverse) consist of known points plotted in any corresponding linear direction, but do not return to the starting point or close upon a point of equal or greater order accuracy. It allows geodetic triangulation for sub-closure of three known points; known as the "Bowditch rule" or "compass rule" in geodetic science and surveying, which is the principle that the linear error is proportional to the length of the side in relation to the perimeter of the traverse
|
|
|
� Open survey is utilised in plotting a strip of land which can then be used to plan a route in road construction. The terminal (ending) point is always listed as unknown from the observation point.
Closed
A closed traverse (polygonal, or loop traverse) is a practice of traversing when the terminal point closes at the starting point. The control points may envelop, or are set within the boundaries, of the control network. It allows geodetic triangulation for sub-closure of all known observed points.
� Closed traverse is useful in marking the boundaries of wood or lakes. Construction and civil engineers utilize this practice for preliminary surveys of proposed projects in a particular designated area. The terminal (ending) point closes at the starting point.
� Control point - the primary/base control used for preliminary measurements; it mayconsist of any known point capable of establishing accurate control of distance and direction (i.e. coordinates, elevation, bearings, etc).
1. Starting -It is the initial starting control point of the traverse.
2. Observation -All known control points that are setted or observed within thetraverse.
3. Terminal -It is the initial ending control point of the traverse; its coordinates areunknown
How to make 1 part of work?
There are different Traverse. Theodolite, total station, leveling - it depends on which machine you use.
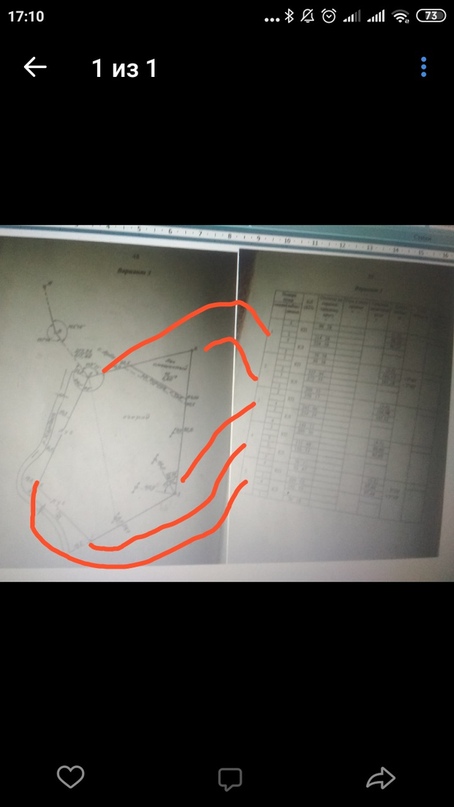
Example you need this for make plan of territory. Plan is like a little map. Imagine. Boss told you - "i need plan of this territory". You have teodolite amd nivelir. You go on the street on the territory and driving 5 stakes into the ground. So that your territory was inside of this 5 stakes. Green - is yout territory, and red is your 5 stakes. Outline is a schematic representation of a territory. On the figure you can see outline, points (red) on the territory (green) , and table log of angles measured by theodolite (results of measurements and calculations).
|
|
|
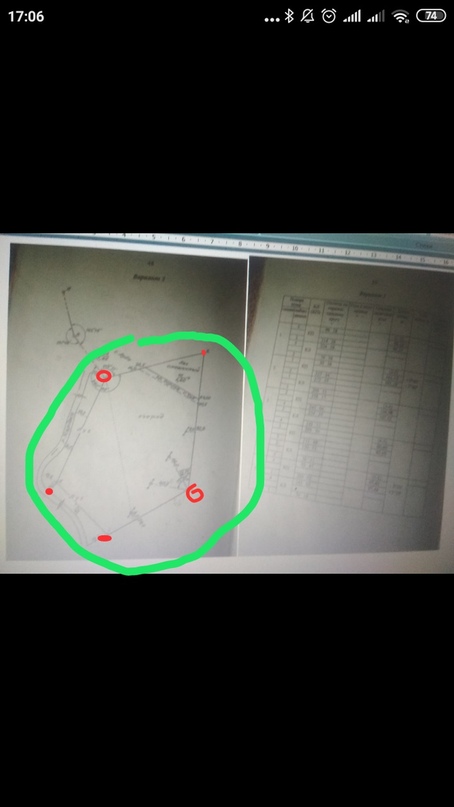
This is anchorage

Points in table is here:
And how to calculate distance and horizontal lines (red color)?

Example how to find this distance for point 1 : (101.1+101.1)/2 = 101.1 :
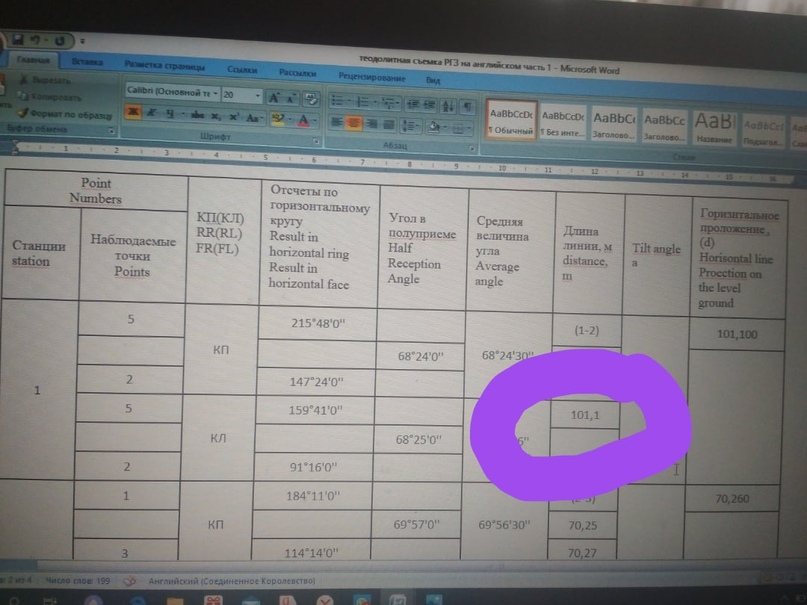
You determine in one detection next in other next determine middle.
And how to determine this??:
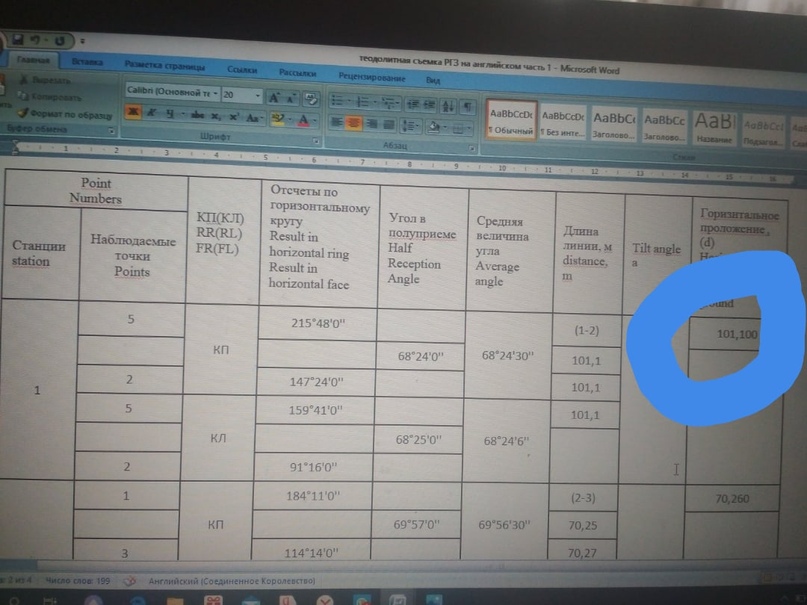
You have formula d= АВ*cos а
AB is distance ( middle distance) this:

And a - is tilt angle. If you have not title angle - title angle is 0:

PART 1
EXAMPLE
Geodesy, Student – group, name
Дата добавления: 2021-06-02; просмотров: 38; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
