UNIT 3. DOING BUSINESS INTERNATIONALLY
Lesson 1
Task 1. a)Study the following words.

| VISIBLE | VISIBLES (Plural) |
| видимий (про статті торговельного балансу, торговельні операції, доходи і т.п., пов’язані з експортом та імпортом товарів); | експорт та імпорт товарів (а не послуг); |
| TANGIBLE | TANGIBLES (Plural) |
| речовий, матеріальний, відчутний на дотик; | фізичні речі, в які можна інвестувати (а не інвестування в цінні папери); |
| MOVABLE | MOVABLES (Plural) |
| рухомий (про майно); | рухомість, рухоме майно; |
| MULTINATIONAL | |
| багатонаціональний; такий, що має підприємства, офіси в різних країнах; | мультинаціональна (багатонаціональна) компанія (корпорація); мультинаціонал. |
b) Give the English equivalents for:
· невидимі статті платіжного балансу; невидимі статті експорту або імпорту (послуги, такі як банківська справа, освіта, туризм і т.д., які країни експортують чи імпортують);
· нематеріальне майно;
· нерухомість.
Task 2.Give the opposites for:
| ----------- |
| ----------- |
| ----------- |
| ----------- |
| ----------- |
| ----------- |
| ----------- |
| ----------- |
| ----------- |
Task 3. a) Match the terms in column A with their definitions in column B:
| A | B |
| 1. tangibles 2. immovables 3. invisible trade 4. a multinational 5. intangible asset 6. invisible balance | a)services such as education, banking, tourism, etc. that countries sell to and buy from each other; b)something that a company has and that benefits it but does not exist physically, for example a brand or the company’s reputation; c)the difference in value between total exports of services plus payment of property incomes from abroad and total imports of services plus payment abroad of property incomes; d)a firm that undertakes direct investments in foreign countries; e)physical things that you can invest in, rather than financial investments; f)items of property that cannot be moved. In the United States it is also commercially and legally known as real estate and in Britain as property; |
b) Translate into Ukrainian paying special attention to the words in italics.
|
|
|
1.Tangibles are material assets. 2.There can be many problems in investing in tangibles like antiques. 3.Prices of tangibles (tangible goods) are rising faster than services. 4.Property is divided into immovables and movables. 5.Immovables include premises, and property rights, houses and land. 6.Trade in items such as financial and other services that are listed in the current account of the balance of payments is called invisible trade. 7.Services account for the vast majority of invisible trade. 8.A multinational (also known as a multinational corporation (MNC) / a transnational corporation (TNC) / a multinational enterprise (MNE)), is a corporation or enterprise that manages production or delivers services in more than one country. 9.A multinational can also be referred to as an international corporation. 10.The first modern MNC is generally thought to be the Dutch East India Company, established in 1602. 11.Very large multinationals have budgets that exceed some national GDPs. 12.Multinationals can have a powerful influence in local economies as well as the world economy and play an important role in international relations and globalization. 13.The most important intangible asset is the company’s brand. 14.Intangible assets are defined as identifiable non-monetary assets that cannot be seen, touched or physically measured. 15.Millions are spent each year by corporations to research and develop new intangible assets. 16.Employees of the company are the invisible asset which will determine future profits. 17.In many developing countries, receipts for invisibles are exceeded by payments for them. 18.The Invisible Balance or Balance of Trade on Services is that part of the balance of trade that refers to services and other products that do not result in the transfer of physical objects. 19.For countries that rely on service exports or on tourism, the invisible balance is particularly important. 20.Invisible balance is the difference between the imports and exports of services as opposed to those of goods.
|
|
|
Task 4. a)Study the etymology of the words “EXPORT” and “IMPORT”.
| Etymology: | EXPORT | |
| Latin portāre – to carry → exportāre – to carry away | ||
| Derived words: exportable; exportability; exporter; | ||
| IMPORT | ||
| Latin portāre – to carry → importāre (IM- + portāre) – to carry in | ||
| Derived words: importable; importability; importer. | ||
b) Make difference between the following compound adjectives.
| Import-Export | Export-Import |
| an import-exportcompany, business, etc. is one that buys goods from foreign suppliers to sell to local companies, as well as supplying local goods to foreign buyers; | Export-Import Bank (also Eximbank) is a bank in some countries that is created by the government to provide loans, etc. so that foreign companies and governments can buy goods and services that are exported by local businesses. |
Task 5. a)Singular or plural?
| IMPORT vs. IMPORTS | |||
| 1. a product or service that is brought into one country from another; | the amount or value of goods and services that are brought from one country into another over a period of time – імпортні товари, статті імпорту; обсяг (вартість) імпорту. | ||
| 2. the act of buying a product or service from another country and bringing it into a country; | |||
| EXPORT vs. EXPORTS | |||
| 1.a product or service that is sold and sent or supplied to another country; | the amount or value of goods and services that are sold and sent or supplied to other countries over a period of time – предмети вивозу, статті експорту; обсяг експорту.
| ||
| 2.the selling and sending of goods or services to another country; | |||
b) Translate the words in italics into English.
1.Імпортно-експортна статистика свідчить, що експорт у вересні зріс на 18%. 2.В Об’єднаному Королівстві видимий імпорт традиційно перевищує видимий експорт. 3.Туризм у Британії є єдиною значущою статтею невидимого експорту. 4.Експорт до Малайзії може бути підтриманий Експортно-імпортним банком країни. 5.Підприємство виготовляє продукцію на експорт. 6.Сільськогосподарська продукція є найбільшою статтею експорту країни. 7.Китай намагається виробляти більше вітчизняних продуктів харчування, щоб зменшити свою залежність від імпорту. 8.Третина експорту індустріальних держав надходить до країн, що розвиваються. 9.Ринок перенасичений дешевим імпортом з Китаю. 10.Система контролю над імпортом повинна бути вдосконалена.
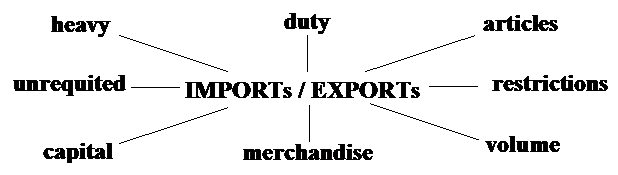
Task 6. a)The words below often occur with “IMPORTs / EXPORTs”.
|
b)Which of the above word-combinations means:
1.імпорт (завезення) капіталу (надходження капітальних засобів у дану країну з інших країн, наприклад, у вигляді фінансових та реальних інвестицій іноземних осіб, отримання іноземних кредитів і т.п.); 2.вивізне мито; мито на експорт; експортне мито; 3.несплачений експорт; значний експорт; 4.статті (предмети) імпорту; 5.обмеження експорту; 6.
|
|
|
значний імпорт; 7.експорт товарів; 8.обсяг експорту; 9.обсяг імпорту; 10.імпорт товарів; 11.значний експорт; 12.статті (предмети) експорту; 13.імпорт, несплачений грішми чи товарами; 14.обмеження на імпорт; імпортні обмеження; 15.імпортне мито; ввізне мито; мито на імпорт; ввізний збір; імпортний збір; 16.експорт (вивіз) капіталу (переведення капіталу з однієї країни в інші країни, наприклад, шляхом надання кредитів іноземним особам, інвестування в зарубіжні реальні активи і т.п.)?
Task 7. a)Pronounce the words in the table.
| NOUN | VERB | PARTICIPLE |
Verb
| NOUN | ||||
| export | to export | exporting | / exported | exporter | ||||
| [`ekspO:t] | [ık`spO:t] | [ık`spO:tıŋ] | [ık`spO:tıd] | [ık`spO:tə] | ||||
| import | to import | importing | / imported | importer | ||||
| [`ımpO:t] | [ım`pO:t] | [ım`pO:tıŋ] | [ım`pO:tıd] | [ım`pO:tə] | ||||
| transport | to transport | transporting | / transported | transporter | ||||
| [`træntspO:t] | [trænts`pO:t] | [trænts`pO:tıŋ] | [trænts`pO:tıd] | [trænts`pO:tə] | ||||
b) Read aloud the following sentences paying attention to the words in italics.
1. Exports fell while imports rose.
2. Most of our output is for export.
3. Copper is Chile’s biggest export.
4. Have you got your own transport?
5. A weaker dollar would boost exports.
6. Demand for Asian exports has grown.
7. Sales of imported cars have increased.
8. Our largest agricultural import is wheat.
9. Applicants must have their own transport.
10. China is among leading importing nations.
11. 90% of the engines are exported to Europe.
12. The goods were damaged during transport.
13. The company is the largest gas transporter.
14. What goods are imported from Japan into the US?
15. We will need a big truck to transport all the boxes.
16. The country has to import most of its raw materials.
17. There are strict controls on the export of certain chemicals.
18. The retailer has exported its marketing expertise to the US.
19. China became the second-largest importer of Japanese steel.
20. Nigeria exports around two million barrels of crude oil a day.
21. Exports account for around 40 per cent of the country’s GDP.
22. Some domestic producers had been harmed by cheap imports.
23. The chemicals are transported by road to the processing plant.
24. The extra money could be spent on improving public transport.
25. The country is a net importerof oil (= it imports more than it exports).
26. Traditionally, the country was an importer of capital to finance industrial growth.
27. Ferryboat is a vessel for transporting passengers and usually vehicles across a body of water, especially as a regular service.
Task 8. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate words from the box. Translate the passage.
| deficit | imports | tangible | Balance of Trade |
| surplus | exports | invisibles | Balance of Payments |
In many countries a useful distinction is drawn between the (1)_____ and the Balance of Payments. The “Balance of Trade” refers only to the trade of (2)_____, or physical, objects (commonly known as (3)_____ and imports) – in other words, “visibles”, while the “(4)_____” includes trade in “(5)_____” as well.
Thus a nation may have a positive (or (6)_____) “Balance of Trade” because it exports more than it (7)_____ – but a negative (or (8)_____) “Balance of Payments” because, overall, it has a much greater shortfall in “invisible” transfers.
Task 9. Think and answer.
1. Is it possible for nations to remain economically self-sufficient these days?
2. Does globalization have anything to do with international business?
3. Why do some countries export more than import?
4. Does a surplus Balance of Trade of a country say anything about its overall financial health?
5. Why do governments try hard to attract foreign investments?
6. Can domestic business be integrated into the world business without government assistance?
7. Why do many companies try to engage in international business activities?
8. What forms can international business activities take?
9. Is international business expansion possible without foreign ownership?
10. Is it easy for businesses to reach international markets?
11. Are there specific legal restrictions for companies with interests in multiple countries?
12. Can cultural factors interfere with a company’s attempt to sell its products in foreign countries?
13. Is politics an important factor influencing international business?
14. Is it possible for nations to achieve political objectives through international business activities?
15. Is international business affected by various trade restrictions?
16. Can international business facilitate mutual understanding between nations?
17. What companies dominate the world business these days?
Task 10. Practice reading the following words.
| 1. acumen [`ækjumən] / [ə`kju:mən] 2. advance[əd`vα:nts] / [əd`vænts] 3. the Basel Accords [`bα:zəl ə`kO:dz] 4. branch [brα:nt∫] / [brænt∫] 5. catalogue [`kætəlOg] 6. category [`kætəgəri] / [`kætəgO:ri] 7. to cause [kO:z] 8. collaborative [kə`læbərətıv] 9. commission [kə`mı∫ən] 10. conflict [`kOnflıkt] / [`kα:nflıkt] 11. consortium[kən`sO:tiəm] 12. to continue [kən`tınju:] 13. conventional[kən`vent∫ənəl] 14. determinant [dı`tə:mınənt] 15. dynamic[daı`næmık] 16. e-commerce[`i: `kOmə:s] / [`i: `kα:mərs] 17. energy[`enəGi] / [`enərGi] 18. environment [ın`vaıərənmənt] 19. expansion [ık`spænt∫ən] 20. ExxonMobil [`eksOn ] 21. franchise [`frænt∫aız] 22. General Motors[`Genərəl `məutəz] 23. globalization [ֽgləubəlaı`zeı∫ən] 24. grouped [gru:pt] 25. increasing [ın`kri:sıŋ] 26. the Kyoto Protocol [ki`əutəu `prəutəukOl] 27. legal [`li:gəl] 28. licence [`laısənts] 29. manufacturer [ֽmænju`fækt∫ərə] 30. multiple [`mAltıpəl] 31. to navigate [`nævıgeıt] | 32. to occur [ə`kə:] 33. ownership [`əunə∫ıp] / [`əunər∫ıp] 34. patent [`peıtənt] / [`pætənt] 35. pathway [`pα:θweı] / [`pæθweı] 36. perspective [pə`spektıv] / [pər`spektıv] 37. physical[`fızıkəl] 38. primary [`praıməri] 39. to prove [pru:v] 40. purchaser [`pə:t∫əsə] 41. religious [rı`lıGəs] 42. representative [ֽreprı`zentətıv] 43. to require [rı`kwaıə] / [rı`kwaıər] 44. respective [rı`spektıv] 45. to respond [rı`spOnd] / [rı`spα:nd] 46. Samsung [`sæmsAŋ] 47. signatory [`sıgnətəri] / [`sıgnətO:ri] 48. socio-cultural[`səu∫iəu `kAlt∫ərəl] / [`sousiou `kAlt∫ərəl] 49. sole [səul] / [soul] 50. Sony [`səuni] / [`souni] 51. subsidiary [səb`sıdiəri] / [səb`sıdieri] 52. success [sək`ses] 53. technological[ֽteknə`lOGıkəl] 54. therefore [`ðeəfO:] / [`ðerfO:r] 55. through [θru:] 56. Toyota [tOı`əutə] / [tOı`outə] 57. transaction [] 58. treaty [`tri:ti] 59. typically [`tıpıkəli] 60. uniform [`ju:nıfO:m] / [`ju:nıfO:rm] 61. various [`veəriəs] 62. vehicle [`vi:ıkəl] / [`vi:əkəl] 63. wholly-owned [`həuli `əund] / [`houli `ound] |
Task 11. Read the text.
International Business
With new technological advances in telecommunications, the business world continues to get smaller. Such modern phenomena as globalization, worldwide communication networks, multinational corporations, the global marketplace prove that, in one way or another, we are all interconnected in today’s world. Globalization is a result of the increasing success of international business ventures.
International business is a term used to collectively describe topics relating to the operations of firms with interests in multiple countries. It is a dynamic activity which changes, adapts and responds according to respective conditions.
In its simplest form, international business occurs when a business sells its product or service to a purchaser who lives in a different country, such as, through a mail-order catalogue or by way of an e-commerce transaction.
Apart from conventional trade it takes various forms such as transactions in patents, licences, know-how, joint-ventures, mixed commissions and many other forms.
There are many different pathways to international expansion. Such pathways are typically grouped into three categories:
1. Expansion without foreign ownership, for example, exports, franchises and licensing;
2. Collaborative ventures, such as, joint-ventures, partnerships and consortiums; and
3. Sole foreign ownership, consisting of representative, branch offices and wholly-owned subsidiaries.
Multinational corporations (MNCs) – large firms with physical presence in various countries – are important players in international markets. Well known MNCs include fast food companies Mc Donald’s and Yum Brands, vehicle manufacturers such as General Motors and Toyota, consumer electronics companies like Samsung, LG and Sony, and energy companies such as ExxonMobil and BP.
MNCs typically have subsidiaries or joint-ventures in a number of national markets. How these companies are organized and operate, and their lines of business are heavily influenced by socio-cultural, political, global, economic and legal environments of each country a firm does business in.
International business success requires more business acumen than managing a domestic enterprise. Experts in international business do not only deal with traditional business functions and values, but also must understand and work from a global perspective. They should learn how to navigate foreign business markets, as well as foreign cultural, social, and political environments.
From international trade to direct investment, business is conducted at different levels in different ways in different countries. Economic, political, social, religious and other conditions sometimes cause these differences. International treaties, such as the Basel Accords, the World Trade Organization, and the Kyoto Protocol often seek to provide a uniform framework for how business should be influenced between signatory states.
International business by its nature is a primary determinant of international trade. As is known, trade helps to prevent conflict. When countries begin to interact through trade, they are less likely to fight. International business, therefore, helps people understand cultural differences and thus, better understand the global work environment.
Vocabulary Notes:
1. advance [əd`vα:nts] / [əd`vænts] – просування; успіх; поліпшення; прогрес;
2. communication network [kə`mju:nı`keı∫ən `netwə:k] – система зв’язку;
3. multinational corporation [mAlti`næ∫ənəl ֽkO:pə`reı∫ən] – багато-національна корпорація;
4. global marketplace [`gləubəl `mα:kıtpleıs] / [`gloubəl `mα:kıtpleıs] – глобальний ринок;
5. in one way or another – так чи інакше;
6. interconnected [ֽıntəkə`nektıd] / [ֽıntəkər`nektıd] – взаємозв’язаний; взаємопов’язаний; поєднаний;
7. collectively [kə`lektıvli] – у збірному значенні; колективно; разом;
8. multiple [`mAltıpəl] – численний; багаторазовий; багатократний;
9. respective [rı`spektıv] – відповідний;
10. to occur [ə`kə:] – траплятися; відбуватися;
11. mail-order catalogue [`kætəlOg] – каталог посилочної торгівлі; каталог посилторгу (каталог товарів, які можна замовити поштою);
12. e-commerce [`i: `kOmə:s] / [`i: `kα:mərs] – торгівля за Інтернетом; електронний бізнес; результат угод за мережею Інтернет; здійснення комерційних операцій за допомогою мережі Інтернет
13. transaction [træn`zæk∫ən] / [træn`sæk∫ən] – ведення (ділових операцій); виконання (справи); справа; угода;
14. apart from [ə`pα:t] / [ə`pα:rt] – окрім; не враховуючи;
15. conventional trade [kən`vent∫ənəl] – традиційна (звична) торгівля;
16. to take(various)forms – набувати (різноманітних) форм;
17. licence [`laısənts] – ліцензія; свідоцтво; патент; дозвіл;
18. know-how [`nəu hau] / [`nou hau] – вміння, досвід, знання справи; секрети виробництва; ноу-хау;
19. joint venture [`GOınt `vent∫ə] / [`GOınt `vent∫ər] – спільне підприємство (СП); спільна діяльність;
20. mixed commission [mıkst kə`mı∫ən] – змішана (спільна) комісія;
21. pathway [`pα:θweı] / [`pæθweı] – стежина, стежка, доріжка; дорога, шлях;
22. international expansion [ık`spænt∫ən] – міжнародна експансія (розширення);
23. foreign ownership [`əunə∫ıp] / [`əunər∫ıp] – іноземна власність; власність за кордоном;
24. franchise [`frænt∫aız] – франшиза; ліцензія; комерційна концесія;
25. licensing[`laısəntsıŋ] – передача права користування; ліцензування;
26. collaborative venture [kə`læbərətıv] – спільна справа; спільне підприємство;
27. consortium [kən`sO:tiəm] – консорціум;
28. sole foreign ownership [`səul `fOrən `əunə∫ıp] – одноосібна власність за кордоном;
29. representative office [ֽreprı`zentətıv] – представництво (компанії в іншій країні);
30. branch office [brα:nt∫] – філія компанії, офіс відділення, контора відділення;
31. wholly-owned subsidiary [`həuli `əund] / [`houli `ound] – дочірня (підконтрольна) компанія, що перебуває у повній власності;
32. multinational corporation (MNC) – багатонаціональна корпорація;
33. vehicle manufacturer [`vi:ıkəl] / [`vi:əkəl] – автовиробник;
34. consumer electronics company [kən`sju:mə] / [kən`su:mər] – компанія з виробництва побутової електроніки;
35. energy company [`enəGi] / [`enərGi] – енергетична компанія;
36. subsidiary [səb`sıdiəri] / [səb`sıdieri] – дочірнє підприємство; підконтрольне підприємство; підприємство, яке контролюється материнською компанією; дочірня компанія; філіал; афілійована (споріднена) компанія;
37. line of business – галузь промисловості, галузь торгівлі, сфера діяльності, торговельна спеціальність або спеціалізація;
38. legal [`li:gəl] – юридичний; правовий; законний; узаконений; легальний;
39. business acumen [`ækjumən] / [ə`kju:mən] – ділова хватка, підприємливість;
40. domestic enterprise [də`mestık `entəpraız] – вітчизняне підприємство;
41. global perspective [`gləubəl pə`spektıv] – глобальна перспектива;
42. to navigate [`nævıgeıt] – проводити (заходи); спрямовувати (переговори);
43. international treaty [`tri:ti] – міжнародний договір;
44. the Basel Accords [`bα:zəl ə`kO:dz] – Базельські домовленості – торкаються регулювання банківської діяльності; (Базель – друге за величиною місто у Швейцарії).
45. the World Trade Organization–світова організація торгівлі (утворена в 1995 році);
46. the Kyoto Protocol [ki`əutəu `prəutəukOl] – Кіотський протокол (угода, прийнята 11 грудня 1997 року, набула чинності 16 лютого 2005 року; станом на січень 2009 року угода підписана 183 учасниками);
47. uniform framework [`ju:nıfO:m] / [`ju:nıfO:rm] – єдина база;
48. signatory state [`sıgnətəri] / [`sıgnətO:ri] – держава-сигнатарій, держава, яка підписала договір;
49. determinant[dı`tə:mınənt] – вирішальний (визначальний) фактор.
Task 12. Agree or disagree with the following statements. Correct false statements.
1. The business world continues to get larger.
2. Despite globalization citizens remain independent in today’s world.
3. Globalization is a result of the failure of international business ventures.
4. International business is a rigid activity.
5. International business tends to change, adapt and respond according to respective conditions.
6. Patents, licences, know-how, joint ventures, mixed commissions are forms of international business.
7. International expansion is impossible without foreign ownership.
8. Multinational corporations (MNCs) typically have subsidiaries or joint ventures in a number of national markets.
9. Socio-cultural, political, global, economic and legal environments influence the way multinational companies operate.
10. International business success requires more business acumen than managing a domestic enterprise.
11. Experts in international business should be able to navigate foreign business markets, as well as foreign cultural, social, and political environments.
12. International treaties are signed to provide a uniform framework for how business should be influenced between signatory states.
13. International business is a primary determinant of international trade.
14. Trade causes conflict.
15. When countries begin to interact through trade, they are more likely to compete.
Task 13. a) Match the terms in column A with their definitions in column B:
| A | B |
| 1. licence 2. signatory 3. know-how 4. subsidiary 5. mail order 6. joint venture 7. multinational | a)a company that is owned or controlled by another company; b)a company that operates in several different countries, especially a large and powerful company; c)a new business that is started by two or more companies, often in the form of an independent company whose shares they own; the product or service that the business sells or provides; d)a person, a country or an organization that has signed an official agreement; e)a system of buying and selling goods through the mail; f)an official document that shows that permission has been given to do, own or use something; g)knowledge of how to do something and experience in doing it; |
b) Translate into Ukrainian paying special attention to the words in italics.
1.The country is not among the signatories to the Kyoto Protocol. 2.The company is selling off its subsidiary businesses. 3.Exis Power is a 58%-owned subsidiary of Exis Corp. 4.The French company has a joint venture with Dongfeng Motor in China. 5.The two firms plan to launch a 50-50 joint venture. 6.We do not have the technical know-how to design this type of structure. 7.The company won a licence to operate a mobile phone network. 8.The vehicles are manufactured under licence from Toyota. 9.We sell clothing by mail order. 10.The country’s industry is largely controlled by multinationals.
Task 14. a) Translate the words in column A and their derivatives in columns B and C. Use your dictionary if necessary.
| A | B | C |
| patent | ----------- | patentee |
| franchise | franchiser | franchisee |
| licence (BrE) / license (AmE) | licensor / licenser | licensee |
b) Which word from column A is being defined?
· The right to vote in an election, especially one in which people elect a parliament; an authority that is given by a company to someone, allowing him / her to sell its goods and services;
· an official document that shows that permission has been given to do, own or use something;
· a legal right to be the only person to make, use or sell a product or an invention; a document that proves this.
c) Fill in the blanks in the sentences below using the words from the table in a).
1. Anyone caught driving dangerously will automatically lose his _____ .
2. The company won a _____ to operate a mobile phone network.
3. The first English _____ for a typewriter was issued in 1714.
4. The traffic officer asked me to show my driving _____ .
5. In 1878, Edison received a _____ for his phonograph.
6. The restaurant chain has 257 _____ across Europe.
7. They won the _____ to operate outlets in the UK.
8. They operate a business under _____ .
9. Have you got your driving _____ yet?
10. The device was protected by _____ .
Task 15. Match items in column A with their synonyms in column B.
| A | B |
| 1.modern | a)operations; |
| 2.marketplace | b)through; |
| 3.a number of | c)traditional; |
| 4.multinational corporations | d)national; |
| 5.global | e)treaty, protocol; |
| 6.subsidiary | f)multiple; |
| 7.large firm | g)branch; |
| 8.activity | h)worldwide; |
| 9.to conduct | i)market; |
| 10.a business | j)to do; |
| 11.accords | k)international business ventures; |
| 12.domestic | l)corporation; company; |
| 13.conventional | m)a firm; an enterprise; |
| 14.by way of | n)today’s; |
Task 16. In the text “International Business” (Task 11) find antonyms of the following words.
| 1.Few; | 9.exclude; | 17.slow, rigid; |
| 2.local; | 10.absence; | 18.similarities; |
| 3.cause; | 11.national; | 19.unimportant; |
| 4.failure; | 12.outdated; | 20.unconventional; |
| 5.to stop; | 13.different; | 21.separately; solely; |
| 6.barely; | 14.reduction; | 22.isolated, independent; |
| 7.imports; | 15.to regress; | 23.international; multinational. |
| 8.indirect; | 16.decreasing; |
Task 17. Fill in the blanks with corresponding noun or verb forms. Use your dictionary if necessary.
| NOUN | VERB |
| 1.----------- | to operate |
| 2.relation | ----------- |
| 3.----------- | to determine |
| 4.description | ----------- |
| 5.----------- | to transact |
| 6.occurrence | ----------- |
| 7.----------- | to succeed |
| 8.navigation | ----------- |
| 9.----------- | to expand |
| 10.response | ----------- |
| 11.----------- | to own |
| 12.requirement | ----------- |
| 13.----------- | to produce |
| 14.collaboration | ----------- |
| 15.----------- | to represent |
Task 18. a)Translate the following nouns. Find the paronymous (related) adjectives in the text “International Business” (Task 11).
| 1.Type; | 5.society; | 9.tradition; | 13.signature; | 17.technology; |
| 2.prime; | 6.variety; | 10.presence; | 14.simplicity; | 18.convention; |
| 3.nation; | 7.politics; | 11.foreigner; | 15.difference; | 19.globalization; |
| 4.culture; | 8.religion; | 12.direction; | 16.economics; | 20.collaboration. |
b) Use the derived adjectives in front of the following nouns:
| _____ form; | _____ determinant; |
| _____ trade; | _____ functions / values; |
| _____ states; | _____ conditions / environment; |
| _____ markets; | _____ differences / environment; |
| _____ ventures; | _____ environment / markets / ownership; |
| _____ advances; | _____ countries / levels / pathways / ways; |
| _____ conditions; | _____ (work) environment / marketplace / perspective. |
| _____ investment; |
Task 19. a)Translate the following word combinations into English and use them in the sentences of your own.
1.Технічний прогрес (успіхи; досягнення); 2.глобальний (світовий) ри-нок; 3.спільна справа / спільне підприємство; 4.інша країна; 5.традиційна торгівля; 6.різні шляхи (напрямки); 7.соціокультурне середовище; 8.глобальна перспектива; 9.основний чинник (детермінанта); 10.культур-ні відмінності; 11.прямі інвестиції; 12.економічні умови; 13.національні ринки; 14.держава-сигнатарій; 15. іноземна власність.
Task 20. a)“Odd man out.” In each line cross out a word (word combination) that in its meaning differs from the others. Explain your choice.
1. advances – to succeed – determinant;
2. accords – signatory state – economic conditions;
3. various pathways – direct investment – joint venture;
4. global market – MNCs – socio-cultural environment;
5. conventional trade – stereotype – cultural differences;
6. international scale – global perspective – domestic markets;
7. foreign ownership – religious conditions – a different country.
b)Use some of the items in a) to fill in the blanks in the sentences below.
1. The _____ is greatly affected by technology and commerce.
2. There are _____ for firms to engage in international business.
3. In today’s multicultural business world it is both useful and necessary to be aware of _____.
4. It is an age of enormous and unprecedented expansion in scientific, technical and economic activity on an _____.
5. When two or more organizations share in the ownership of a direct investment, the operation is known as a _____.
Task 21. Some words can be used both as a noun and a verb. Complete the table with the appropriate words from the text “International Business”.
| № | ІМЕННИК | ДІЄСЛОВО | ПЕРЕКЛАД |
| 1. | Вплив; особа / фактор, що впливає; | впливати; виявляти вплив; | ----------- |
| 2. | франшиза; ліцензія; комерційна концесія; | надавати фірмі / особі франшизу; | ----------- |
| 3. | закупівля; покупка; | купувати; закуповувати; придбавати; | ----------- |
| 4. | функція; призначення; | функціонувати; діяти; | ----------- |
| 5. | просування; успіх; поліпшення; прогрес; | просуватися вперед; удосконалюватися; робити успіхи; | ----------- |
| 6. | ризикована справа; авантюра; підприємство; | ризикувати (чимось), ставити на карту; | ----------- |
| 7. | служба, обслуговування; сервіс; | обслуговувати; проводити огляд і поточний ремонт (автомобіля тощо); | ----------- |
| 8. | зміна; переміна; заміна; | змінювати(ся); міняти(ся); обмінювати(ся); | ----------- |
| 9. | ринок; базар; торгівля; збут; | торгувати; купувати / продавати на ринку; реалізувати, збувати; знаходити ринок збуту; | ----------- |
| 10. | патент; диплом; запатенто-ваний предмет / винахід; | патентувати; брати патент (на щось); | ----------- |
| 11. | група; угруповання; фракція; | групувати(ся); розподіляти по групах, класифікувати; | ----------- |
| 12. | цінність; важливість; вартість; валюта; ціна; | оцінювати; цінити, цінувати; | ----------- |
| 13. | робота; труд; справа, діло; заняття; твір, праця; | працювати, трудитися; примушувати працювати; діяти, бути в дії; | ----------- |
| 14. | причина; підстава; привід, мотив; справа; | спричиняти, завдавати, викликати; змушувати; | ----------- |
| 15. | торгівля, заняття; ремесло; професія; | торгувати; постійно купувати, бути постійним покупцем; | ----------- |
| 16. | наказ, розпорядження; інструкція; | наказувати; розпоряджатися; | ----------- |
| 17. | форма; обриси; зовнішній вигляд; | надавати форми; набувати форми; формувати(ся), складати; утворювати(ся); | ----------- |
| 18. | кількість, частка; розм. угода; | торгувати; спілкуватися; мати справу; | ----------- |
Task 22. Translate into English.
1.Світ бізнесу продовжує зменшуватися. 2.Так чи інакше ми всі взаємопов’язані в сучасному світі. 3.Глобалізація – це результат успіху підприємств у царині міжнародного бізнесу. 4.Міжнародний бізнес є динамічною діяльністю, яка змінюється, пристосовується відповідно до наявних умов. 5.Окрім класичної торгівлі, міжнародний бізнес може набувати різноманітних форм. 6.Спільні підприємства, змішані комісії, угоди щодо патентів, ліцензій, ноу-хау є формами міжнародного бізнесу. 7.Експорт, франшизи та ліцензування дозволяють компанії здійснювати міжнародну ділову експансію, не володіючи майном за кордоном. 8.Багатонаціональні корпорації є важливими гравцями на міжнародних ринках. 9.Мультинаціонали зазвичай мають філії та спільні підприємства на багатьох національних ринках. 10.Спосіб ведення бізнесу зазнає суттєвого впливу соціокультурного, політичного, економічного та законодавчого середовищ у кожній країні, в якій компанія веде бізнес. 11.Успіх у міжнародному бізнесі в більшій мірі вимагає ділової жилки, аніж керування вітчизняним підприємством. 12.Починаючи з міжнародної торгівлі, і закінчуючи прямими інвестиціями, бізнес ведеться по-різному на різних рівнях у різних країнах. 13.Міжнародні угоди передбачають відповідні стандарти у веденні міжнародного бізнесу. 14.По своїй суті міжнародний бізнес є головною детермінантою міжнародної торгівлі. 15.Торгівля допомагає запобігати конфліктам.
Task 23. Answer the questions.
1. Why does the business world continue to get smaller?
2. Which modern phenomena prove that we are all interconnected in today’s world?
3. What is one result of the increasing success of international business ventures?
4. What dynamic activity changes, adapts and responds according to respective conditions?
5. What does the term “international business” denote?
6. What is the simplest form of international business?
7. Apart from conventional trade international business takes various forms, doesn’t it?
8. Can international business take such forms as transactions in patents, licences, know-how, joint ventures, and mixed commissions?
9. Into what categories are different pathways to international expansion typically grouped?
10. What are multinational corporations?
11. What are well known examples of MNCs?
12. Is international expansion possible without foreign ownership? Explain your answer.
13. MNCs typically have subsidiaries or joint ventures in a number of national markets, don’t they?
14. What does international business success require?
15. What requirements are placed on skills and qualifications of international business experts?
16. Which conditions (environments) cause the differences in doing international business?
17. What treaties provide a uniform framework for how business should be influenced between signatory states?
18. International business by its nature is a primary determinant of international trade, isn’t it?
19. How can trade help to prevent conflict?
20. Can international business help people understand cultural differences as well as the global work environment?
Task 24. Say what you know about:
1. The simplest form of international business.
2. Different pathways to international expansion.
3. Major players in international markets.
4. Challenges experts in international business deal with.
5. Economic, political, social, religious diversity of the international business environment.
6. Major treaties in the field of international business.
7. The importance of international business for promoting cross-cultural tolerance.
Task 25.Comment on the following statements.
1. The business world continues to get smaller.
2. “Nokia mobile phones are designed in Sweden, the chips are made in Taiwan [ˏtaı`wa:n] by a group of engineers in India, and assembled in Texas [`teksəs].”
3. We are part of the “global marketplace.”
4. Trade helps to prevent conflict.
Lesson 2
Task 1. Read the passage. Substitute the words in italics for their synonyms from the box.
| get | funds | unions | visibles | fulfilment |
| vary | goods | enlarge | material | participate |
Companies seek to do international business for several reasons: to (1) expand sales, to (2) acquire resources, and to (3) diversify sources of sales and supplies.
A company can (4) engage in international business through various means, including exporting and importing of (5) merchandise and services, direct and portfolio investments, and strategic (6) alliances with other companies.
Merchandise exports are (7) tangible goods sent out of a country; merchandise imports are tangible goods brought in. Since these goods visibly leave and enter they are sometimes referred to as (8) visible exports and imports.
International business comprises many different types of services: travel, tourism, and transportation; (9) performance of activities abroad; use of (10) assets from abroad.
Task 2. Distribute the following companies into five groups according to their core business.
| 1. energy companies; | 2. fast food companies; | |
| 3. consumer electronics companies; | ||
| 4. vehicle manufacturers; | 5. consumer-goods giants. | |
| BP; | Unilever; | Burger King; | General Motors (GM); |
| LG; | Citigroup; | McDonald’s; | Microsoft Corporation; |
| IBM; | Wal-Mart; | TNK-BP Ltd.; | Royal Dutch Shell plc.; |
| Lukoil; | Pizza Hut; | Arcelor Mittal; | Hewlett-Packard Company; |
| Google; | Apple Inc.; | OAO Gazprom; | Siemens Aktiengesellschaft; |
| Toyota; | Canon Inc.; | Sony Corporation; | Nissan Motor Company, Ltd.; |
| Gillette; | Daimler AG; | Procter & Gamble; | Royal Philips Electronics N.V.; |
| Wendy’s; | ExxonMobil; | Nintendo Co., Ltd.; | Mitsubishi Motors Corporation; |
| Samsung; | Yum Brands; | Volkswagen Group; | Hyundai Kia Automotive Group. |
Task 3. Translate into Ukrainian paying attention to the words in italics.
1.British Petroleum plc is the third largest global energy company, the 5th largest company in the world, Britain’s largest company, a multinational oil company (“oil major”) with headquarters in London. 2.The LG Group – South Korea’s third largest conglomerate that produces electronics, chemicals, and telecommunications products – was renamed “LG” (the abbreviation of “Lucky GoldStar”) in 1995, so as to better compete in the western market. More recently, the company associates its tagline “Life’s Good,” with the letters. 3.International Business Machines Corporation, abbreviated IBM and nicknamed “Big Blue” (for its official corporate colour), is a multinational computer technology and IT consulting corporation. 4.The company which became IBM was founded in 1896 and took this name in 1924. 5.Lukoil was formed in 1991, when three state-run, western Siberian companies, Langepasneftegaz, Uralneftegaz, and Kogalymneftegaz, merged. The initials of the three companies are preserved in the name Lukoil. 6. Google Inc. is an American public corporation, earning revenue from advertising related to its Internet search, e-mail, online mapping, office productivity, social networking, and video sharing services as well as selling advertising-free versions of the same technologies. 7.Google was founded by Larty Page and Sergey Brin (a Russian-American computer scientist born on August 21, 1973, in Moscow, Soviet Union) while they were students at Stanford University and the company was first incorporated as a privately held company on September 4, 1998. 8.Toyota Motor Corporation is a multinational corporation headquartered in Japan, and is currently the world’s largest automaker. 9.Toyota vehicles were originally sold under the name “Toyoda” from the family name of the company’s founder, Kiichiro Toyoda. Since “Toyoda” literally means “fertile rice paddies” (“родючі рисові поля”), changing the name also helped to distance the company from associations with old fashioned farming. The newly formed word was trademarked and the company was registered in August 1937 as the “Toyota Motor Company.” 10.The Gillette Company is a leading global supplier of products under various brands, which was acquired by P&G in 2005. The original Gillette Company was founded by King C. Gillette in 1901 as a safety razor manufacturer. 11.Wendy’s is an international chain of fast food restaurants founded by Dave Thomas on November 15, 1969, in Columbus, Ohio. 12.As of December 2006, Wendy’s was the world’s third largest hamburger fast food chain following McDonald’s and Burger King’s. 13.Samsung has been the world’s most popular consumer electronics brand since 2005 and is the best known South Korean brand in the world. 14.Unilever is a multinational, formed of British and Dutch parentage, that owns many of the world’s consumer product brands in foods, beverages, cleaning agents and personal care products. 15.Unilever’s main competitors include Procter & Gamble, Nestlé, Kraft Foods, Mars, Henkel and Spotless Group. 16.Unilever was created in 1930 by the amalgamation (злиття; об’єднання) of the operations of British soap maker Lever Brothers and Dutch margarine producer Margarine Unie. 17.Citigroup Inc. (branded Citi), is a major American financial services company based in New York. 18.Citigroup Inc. has the world’s largest financial services network, spanning 140 countries with approximately 12,000 offices worldwide. 19.Wal-Mart Stores, Inc. (frequently branded as Walmart) is an American public corporation that runs a chain of large, discount department stores. 20.Pizza Hut is an American restaurant chain and international franchise based in Addison, Texas (a northern suburb of Dallas). 21.Pizza Hut is a subsidiary of Yum Brands, Inc., the world’s largest restaurant company. 22.Apple Inc. is an American multinational corporation that designs and manufactures consumer electronics and computer software products. The company’s best-known hardware products include Macintosh computers, the iPod and the iPhone. 23.Canon Inc. is a multinational corporation that specialises in the manufacture of imaging and optical products, including cameras, photocopiers, steppers (проекційні установки) and computer printers. 24.The name Canon began in 1934 with a prototype for Japan’s first-ever 35 mm camera with a focal plane shutter (із затвором бокової дії). It was named “Kwanon” after the Buddhist bodhisattva Guan Yin. 25.Daimler AG is a German manufacturer of automobiles, motor vehicles, and engines, which dates back more than a century. An Agreement of Mutual Interest was signed on May 1, 1924 between Benz & Cie (founded 1883) of Karl Benz and Daimler Motoren (founded 1890) of Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach. 26.The Exxon Mobil Corporation (or ExxonMobil) is an American oil and gas corporation. It is a direct descendant of John D. Rockfeller’s Standard Oil Company, and was formed on November 30, 1999, by the merger of Exxon and Mobil. 27.Yum! Brands, Inc. (or Yum!) is a corporation that operates or licenses Taco Bell, KFC, Pizza Hut, and Long John Silver’s restaurants worldwide.
Task 4.Think and answer.
1. Which of the above mentioned companies dominate the world economy?
2. Which of them do business in Ukraine? What is their respective market share in this country?
3. Which domestic enterprises do the above multinationals compete with?
4. Which multinationals have their service offices / branch offices in your native city?
5. How do the activities of the above multinationals affect your life? Have you ever consumed their products (goods or services)?
Task 5. Read and translate the passage.
Дата добавления: 2018-06-27; просмотров: 698; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!


 +
+ ER
ER