Forms of Business Organization
Most countries allow you to run a business in at least three different ways:
· as a sole trader (especially in British English) or sole proprietorship (in American English);
· as a partnership;
· as a company (British English) / corporation (especially American English).
A sole trader (sole proprietorship) is a firm with a single owner – a proprietor – who has unlimited liability. Unlimited liability is the legal responsibility for all the debts of a firm. Sole proprietorships are the most numerous kind of business organization, but most are very small. They are popular because they are the easiest – and the least costly – to organize.
Partnerships are the second most common type of business organization. Most law firms and accounting firms are partnerships. A partnership is a firm with two or more owners who have unlimited liability. Partners bring additional funds to a proprietorship. They can also bring fresh ideas and talents to business organizations.
Corporations are the best known types of business organizations, though they are not the most common. A corporation is a business organization created under a government charter. Ownership of a corporation is represented by shares of stock, so corporate owners are known as stockholders. Corporate stockholders have limited liability, which means that they have legal liability only for the value of their initial investment. IBM, Exxon Mobil, and Sony are all examples of corporations. Many corporations, including these three, are multinational giants.
A scope of business activity (its turnover and the headcount) is the major criterion for distinguishing small, medium-sized and big business.
A small business is a business that is independently owned and operated, with a small number of employees and relatively low volume of sales. The legal definition of “small” often varies by country and industry, but is generally under 100 employees in the United States and under 50 employees in the European Union.
Small businesses are common in many countries, depending on the economic system in operation. Small businesses are normally partnerships, or sole proprietorships. Typical examples include: convenience stores, other small shops (such as a bakery or delicatessen), hairdressers, tradesmen, lawyers, accountants, restaurants, guest houses, photographers, small-scale manufacturing etc. Small businesses are usually not dominant in their field of operation, though they are the major job providers in most economies.
The smallest businesses, often located in private homes, are called microbusinesses (term used by international organizations such as the World Bank and the International Finance Corporation) or Soho’s. The term “mom and pop business” is a common colloquial expression for a single-family operated business with few (or no) employees other than the owners.
SMB is an abbreviation for small and medium-size business, sometimes seen as small and mid-size business. The definition of SMB by the number of employees is generally under 500 in the U.S. and 250 for the European Union.
Big Business is a term used to describe large corporations, in either an individual or collective sense. The term first came into use in a symbolic sense subsequent to the American Civil War, particularly after 1880.
Organizations that fall into the category of “big business” include Exxon Mobil, Wal-Mart, Google, Microsoft, General Motors, Citigroup, Arcelor Mittal and others.
The social consequences of the concentration of economic power in the hands of those persons controlling “Big Business” has been a constant concern both of economists and of politicians since the end of the 19th century. Various attempts have been made to investigate the effects of “bigness” upon labour, consumers and investors, as well as upon prices and competition.
Vocabulary Notes:
1. sole trader [`səul `treıdə] – індивідуальний підприємець;
2. sole proprietorship [`səul prə`praıətə∫ıp] – індивідуальне приватне підприємство; одноосібна власність;
3. partnership [`pα:tnə∫ıp] / [`pα:rtnər∫ıp] – товариство, партнерство;
4. company [`kAmpəni] – товариство, компанія, об’єднання (торговельне і т.п.);
5. corporation [ֽkO:pə`reı∫ən] / [ֽkO:rpə`reı∫ən] – корпорація; амер. акціо-нерне товариство;
6. owner [`əunə] / [`əunər] – власник, хазяїн; господар;
7. proprietor [prə`praıətə] / [prə`praıətər] – власник, володар; господар;
8. (un)limited liability [An`lımıtıd ֽlaıə`bıləti] – (не)обмежена відповідаль-ність;
9. legal responsibility [`li:gəl rıֽspOntsə`bıləti] – юридична відповідальність;
10. debt [det] – борг; заборгованість; боргове зобов’язання;
11. costly [`kOstli] / [`kO:stli] – дорогий;
12. law firm [`lO: fə:m] – адвокатська контора; юридична фірма;
13. accounting firm [ə`kauntıŋ fə:m] – бухгалтерська фірма;
14. charter [`t∫α:tə] / [`t∫α:rtər] – право, привілей, пільга; документ, який дає дозвіл на створення університету, компанії;
15. ownership [`əunə∫ıp] / [`əunər∫ıp] – власність; володіння; право власності;
16. share of stock [ֽ∫eər əv `stOk] – частка (пай) в акціонерному капіталі; пай акціонерного капіталу;
17. stockholder [`stOkֽhəuldə] – акціонер; власник пакету акцій;
18. initial investment [ı`nı∫əl ın`vestmənt] – початкові інвестиції; первісні капіталовкладення (здійснювані у перші чотири роки);
19. multinational [ֽmAlti`næ∫ənəl] – багатонаціональний; мультинаціонал, мультинаціональна (багатонаціональна) компанія (корпорація);
20. scope [skəup] – масштаб; розмах;
21. turnover [`tə:nֽəuvə] – обіг; обсяг реалізації; обсяг продажу; товарообіг;
22. headcount [`hedkaunt] – кількість штатних працівників; кількість співробітників за штатним розписом; кількість посад за штатним розписом;
23. employee [ım`plOıi:] / [emplOı`i:] – службовець, працівник, робітник;
24. volume of sales [`vOlju:m əv `seıəlz] – обсяг реалізації (продукції); обсяг продажу; масштаби збуту;
25. industry [`ındəstri] – промисловість, індустрія; галузь; галузь промисловості; галузь економіки; вид економічної діяльності; підприємство;
26. convenience store [kən`vi:niənts] – магазин самообслуговування;
27. delicatessen [ֽdelıkə`tesən] – гастрономічний магазин;
28. tradesman [`treıdzmən] – торговець, крамар; ремісник;
29. guest house [`gest haus] – пансіонат;
30. microbusiness [ֽmaıkrəu`bıznəs] – мікробізнес;
31. SoHo (small office, small house; = SoHo, = Soho) [`səu həu] – квартира-офіс (дрібного підприємця);
32. “mom and pop business” [`mOm ænd pOp `bıznəs] – амер. дрібне приватне підприємництво; родинний бізнес, приватна крамничка;
33. colloquial expression [kə`ləukwiəl ık`spre∫ən] – розмовний зворот (вираз);
34. subsequent [`sAbsıkwənt] – наступний; подальший;
35. consequence [`kOntsıkwənts] / [`kα:ntsəkwənts] – наслідок.
Task 11. Complete the sentences with the most appropriate items.
1.Most countries allow you to run a business in …
A.two ways;
B.three ways;
C.at least three ways;
D.more than three ways;
2.A sole trader is a firm owned by …
A.two or more partners;
B.a single proprietor;
C.the government;
D.stockholders;
3.Sole proprietorships are …
A.the second most common type of business organization;
B.the most numerous kind of business organization;
C.created under the government charter;
D.the most costly to organize;
4.Partnerships are owned by …
A.two or more partners;
B.at least three partners;
C.a single proprietor;
D.two partners;
5.Corporate stockholders …
A.are legally responsible for all debts of their organization;
B.bring fresh ideas and talents to business organizations;
C.risk only the value of their initial investment;
D.have unlimited liability;
6.A small business …
A.employs up to 300 workers;
B.is independently owned and operated;
C.usually boasts of huge volumes of sale;
D.is the least common type of business organization;
7.Multinational giants are usually represented by …
A.companies;
B.sole traders;
C.partnerships;
D.sole proprietors;
8.The legal definition of “small business” often varies by …
A.country;
B.industry;
C.economic system;
D.all the above;
9.Typical examples of small businesses include …
A.small-scale manufacturing;
B.convenience stores;
C.delicatessen;
D.all the above;
10.The abbreviation SMB stands for …
A.“sons and moms business”;
B.senior manager of a business;
C.Specialist – Master – Bachelor;
D.small and medium-size business;
11.Middle businesses in the USA usually employ …
A.250 employees;
B.up to 500 employees;
C.at least 500 employees;
D.fewer than 250 employees;
12.The smallest businesses, often located in private homes, are called …
A.SoHo’s;
B.microbusinesses;
C.“mom and pop businesses”;
D.all the above;
13.Big Business is a term used to describe …
A.sole proprietorships;
B.large corporations;
C.partnerships;
D.sole traders;
14.The term “big business” first came into use soon after …
A.the Gulf War;
B.World War II;
C.the Vietnam War;
D.the American Civil War;
15.Big business is likely to affect …
A.labour;
B.consumers and investors;
C.prices and competition;
D.all the above;
Task 12. a) Match the terms in column A with their definitions in column B:
| A | B |
| 1. convenience store 2. initial investment 3. delicatessen 4. headcount 5. turnover 6. liability 7. SoHo | a)the state of being legally responsible for something; the amount of money that a company or a person owes; b)the total value of goods or services sold by a company during a particular period of time; the rate at which goods are sold in a shop and replaced by others; c)a small shop that sells food, newspapers, etc. and often stays open all or most of the day and night; d)an act of counting the number of people who are employed by an organization; the number of people that have been counted in this way; e)a shop selling various foods, especially unusual or imported foods, already cooked or prepared; f)a small business, especially one that is run from somebody’s home, or a person who works at home; a room in somebody’s home that is used as an office; g)the amount of money a shareholder invests in shares of stock while joining a corporation; |
b) Translate into English:
1. Власники індивідуальних приватних підприємств і партнерств несуть необмежену відповідальність.
2. Компанія керує мережею магазинів самообслуговування.
3. Гастрономічні магазини є типовим прикладом малого бізнесу.
4. Кількість штатних працівників на великих підприємствах перевищує 500 осіб.
5. Юридична відповідальність акціонерів обмежується вартістю їхніх первісних капіталовкладень.
6. Квартири-офіси – це сучасна тенденція малого бізнесу.
7. Товарообіг малих підприємств незначний, але вони забезпечують основну частку робочих місць.
Task 13. Translate into Ukrainian paying special attention to the words in italics.
1. Convenience store is a shop that has long opening hours, caters to local tastes, and is conveniently situated.
2. I bought some salami from the delicatessen.
3. The company is cutting its headcount to about 45 000.
4. She made an initial investment of £1000 in the new firm.
5. We assumed full liability for our children’s debts.
6. The business has liabilities of 2 million dollars.
7. They developed new software products for the rapidly growing SoHo market.
8. SoHo is a district of central London, in the City of Westminster: a foreign quarter since the late 17th century, now chiefly known for restaurants, nightclubs, striptease clubs, etc.
9. The firm has an annual turnover of $75 million.
10. The factory has a high turnover of staff.
Task 14.“Odd man out.” In each line cross out a word or word combination that in its meaning differs from the others. Explain your choice.
1. sole proprietorship – corporation – company;
2. SoHo – SMB – Exxon Mobil;
3. sole trader – unlimited liability – government charter;
4. additional funds – single owner – partnership;
5. corporation – most numerous – shares of stock;
6. stockholders – proprietors – turnover;
7. debts – fresh ideas – liability;
8. limited liability – stockholders – sole trader;
9. partnership – multinational giant – IBM;
10. corporations – bulk of employment – small businesses;
11. convenience store – guest house – company;
12. family – big business – “mom and pop business”;
13. economic power – SMB – big business;
14. Google – Microsoft – General Motors;
15. liability – turnover – headcount.
Task 15. a)Find 10 pairs of synonyms among the words given below.
1.Corporation; 2.ownership; 3.tradesman; 4.organization; 5.sole; 6.trader; 7.company; 8.to create; 9.firm; 10.liability; 11.sole proprietorship; 12.to operate; 13.to organize; 14.owner; 15.proprietor; 16.proprietorship; 17.responsibility; 18.to run; 19.single; 20.sole trader.
b) Use the above words in the sentences of your own.
Task 16. a)Translate the following nouns. Find the paronymous (related) adjectives in the text “Forms of Business Organization” (Task 10).
| 1. Solo; | 3.limit; | 5.legacy; | 7.society; | 9.initiation; | 11.difference; |
| 2. type; | 4.symbol; | 6.privacy; | 8.variety; | 10.economy; | 12.corporation. |
b) Use the derived adjectives to make up word combinations with the following nouns. Make up as many word combinations as possible.
| _____ ways; _____ sense; _____ homes; _____ liability; | _____ attempts; _____ examples; _____ investment; _____ consequences; | _____ system / power; _____ liability / definition; _____ owners / stockholders; _____ trader / proprietorship. |
c)Which of the above word combinations were used in the text “Forms of Business Organization” (Task 10)?
Task 17. Complete the following table with the appropriate Ukrainian noun / verb, noun / adjective forms. Use your dictionary if necessary.
| WORD | TRANSLATION | |
| Noun | Verb | |
| run | _______ | _______ |
| end | _______ | _______ |
| fund | _______ | _______ |
| stock | _______ | _______ |
| value | _______ | _______ |
| attempt | _______ | _______ |
| concern | _______ | _______ |
| Noun | Adjective | |
| firm | _______ | _______ |
| kind | _______ | _______ |
| single | _______ | _______ |
| collective | _______ | _______ |
| individual | _______ | _______ |
Task 18. Fill in the blanks with the most appropriate terms from the box.
| abbreviation | corporations | partnerships | stockholders |
| advantages | debts | shares of stock | success |
| corporate | loss | sole proprietors | unlimited liability |
(1)_____ own all the profits of their enterprises, and they are their own bosses, free to make whatever changes they please. They also have the opportunity to achieve (2)_____ and recognition through their individual efforts.
All (3)_____ and problems associated with the business belong to the sole proprietor. If a business fails, he must personally assume the debts. This could mean the (4)_____ of personal property such as automobiles, homes, and savings.
Like the sole proprietorship, (5)_____ are relatively easy to form and are not subject to special taxes. In many cases, each of the partners is subject to (6)_____ . Partners are individually responsible for all business debts.
A corporation is a business organization created under a government charter. A corporation may have many (7)_____ or only a limited few, such as the members of a family or a group of business associates.
Although (8)_____ are outnumbered by about four to one by sole proprietorships, they dominate the world business. They are so important because of the (9)_____ they offer.
Unlike the owners of proprietorships and partnerships, who can be held personally liable for the debts of their firms, the most that (10)_____ shareholders can lose is limited to whatever they paid for their (11)_____.
Limited liability is so important that corporations in most English-speaking countries outside of the United States add the (12)_____ “Ltd.” (for Limited) to their company name.
Task 19. Translate into English.
1.Одноосібні власники несуть необмежену відповідальність. 2.Більшість адвокатських фірм організовані як партнерства. 3.Акціонери несуть обмежену відповідальність за борги компанії. 4.Більшість корпорацій є багатонаціональними гігантами. 5.Обсяг ділової діяльності є основним критерієм для визначення малого, середнього та великого бізнесу. 6.Мале підприємство має порівняно невеликі обсяги продажу. 7.Підприємство, на якому працює менше 50 співробітників, у Європейському Союзі вважається малим. 8.У більшості економік світу малий бізнес забезпечує основну частку робочих місць. 9.Термін “великий бізнес” став вперше ви-користовуватися в символічному значенні після 1880 року. 10.Соціальні наслідки концентрації економічної влади в руках великого бізнесу традиційно турбують економістів і політиків.
Task 20.Tick the correct box: match major forms of business organizations with their relevant features.
| Characteristic features | Sole Proprietorship | Partnership | Corporation |
| 1. Has many owners | |||
| 2. has a single owner | |||
| 3. is very small as a rule | |||
| 4. is the easiest to organize | |||
| 5. dominate the world business | |||
| 6. is not subject to special taxes | |||
| 7. is the least costly to organize | |||
| 8. is owned by two or more persons | |||
| 9. is created under a govern-ment charter | |||
| 10. is represented by multina-tional giants | |||
| 11. is represented by law firms and accounting firms | |||
| 12. is the least common type of business organization | |||
| 13. is the most numerous kind of business organization | |||
| 14. is the second most common type of business organization |
Task 21. Answer the questions.
1. What is the least numerous kind of business organization?
2. What is unlimited liability?
3. Why are sole proprietorships the most numerous kind of business organization?
4. Who undertakes legal responsibility for all the debts of a sole proprietorship?
5. Are corporations the easiest and least costly to organize?
6. How are most law firms and accounting firms organized?
7. What are advantages of partnerships over sole proprietorships?
8. Do partners have unlimited liability?
9. What is the best known type of business organization?
10. What is a corporation?
11. In what way is ownership of a corporation represented?
12. Do corporate stockholders have unlimited liability?
13. What does limited liability mean?
14. What is a small business?
15. How many people does a small business generally employ?
16. Is there one legal definition of “small business”?
17. What are the most typical examples of small businesses?
18. What businesses are major job providers in most economies?
19. How are the smallest businesses called? What is the origin of the term?
20. What does the term “mom and pop business” denote?
21. What does the abbreviation SMB stand for?
22. What business is considered medium-sized?
23. When did the term “big business” first come into use?
24. Why has the issue of “Big business” been a constant concern of economists and politicians?
25. Does “bigness” affect labour, consumers and investors, as well as prices and competition? In which way?
Task 22. Say what you know about:
1. The most common ways of doing business worldwide.
2. Limited / unlimited liability.
3. Advantages and disadvantages of sole proprietorships / partnerships / corporations.
4. The importance of small / medium-sized / big business for the social welfare.
5. Modern forms of microbusiness.
Task 23. Comment on the following statements:
1. Modern world is dominated by big business.
2. Elections are now big business in this country.
3. There have always been links between politics and big business.
4. Big business will never let nationalism get in the way of a good deal.
5. Big business can overcome cultural and political differences between countries.
6. “Well, you know, I was a human being before I became a businessman.” (George Soros – Investor & Philanthropist).
7. “The first rule of business is … do other men for they would do you.” (Charles Dickens – United States President).
UNIT 2. ENTREPRENEURSHIP
Lesson 1
Task 1.Study the following words.

| · Businessman [`bıznəsmæn] – комерсант; ділок, ділова людина, бізнесмен; · businesswoman [`bıznəsֽwumən] – бізнес-леді; · businessperson [`bıznəsֽpə:sən] – комерсант; · entrepreneur[ֽOntrəprə`nə:] / [ֽα:ntrəprə`nə:] –підприємець, ділок, бізнесмен;театр. антрепренер; власник приватного цирку, театру; · freelancer[`fri:lα:ntsə]/[`fri:læntsə] – позаштатний працівник; вільний художник; · tradesman [`treıdzmən] – торговець, крамар; ремісник; · merchant [`mə:t∫ənt] – купець, торговець; · trader [`treıdə] – трейдер; торговець, крамар (оптовий); біржовий маклер; спекулянт; торговельне судно; · dealer [`di:ələ] / [`di:ələr] – торговець; дилер; торговельний посередник; агент з продажу; · magnate [`mægneıt] – магнат; · tycoon [ֽtaı`ku:n] – промисловий (фінансовий) магнат; сьогун (у Японії); · wheeler-dealer [ֽwi:lə`di:lə] – ділок; воротила; махінатор; пронира; · mogul[`məugəl]– магнат (зазвичай вживається стосовно власників і керівників перших голлівудських кінокомпаній – кіномагнатів, а також власників видавничих “імперій” – медіамагнатів). |
Task 2. Translate into Ukrainian paying special attention to the words in italics.
1. He is a member of the association of small businessmen.
2. Jane works as a freelancer from home.
3. This is a job for a skilled tradesman.
4. China is now one of the largest traders in the world.
5. It is always a good idea to sell through a licensed dealer.
6. The word tycoon entered the English language in the nineteenth century.
7. U.S. President Abraham Lincoln was humorously referred to as the Tycoon by his aides John Nicolay and John Hay.
8. The word mogul originally meant Mongol, or person of Mongolian descent.
9. Many wheeler-dealers have become respectable businessmen.
10. His father was a tea merchant.
Task 3.Match the terms in column A with their definitions in column Bpaying attention to the underlined words.
| A | B |
| 1. Businessman 2. businesswoman 3. businessperson 4. entrepreneur 5. freelancer 6. tradesman 7. merchant 8. trader 9. dealer 10. magnate 11. tycoon 12. wheeler-dealer | a)a businessman or industrialist with great wealth and power; a rich and powerful person who is involved in business or industry; an archaic name for a shogun; b)a man engaged in trade, especially a retail dealer; a person who buys and sells goods, especially on a small scale; a skilled person, especially one who makes or repairs something; c)a person engaged in the purchase and sale of commodities for profit, especially on international markets; trader; (AmE) a business or person who sells goods directly to the public; an old word meaning “someone who buys and sells goods”; d)a person or shop whose business is buying and selling a particular product; someone who sells illegaldrugs, especially on the streets; e)a person who earns money by selling his / her work or services to several different organizations rather than being employed by one particular organization; f)a person who engages in trade; dealer; merchant; a vessel regularly employed in foreign or coastal trade; g)a person who wheels and deals; someone who is skilled at making profitable or successful deals (perhaps, sometimes dishonest) in business or politics; h)a person who works in business, especially at a high level; a person who is skillful in business and financial matters (a gender-neutral form); i)a person, especially a man, engaged in commercial or industrial business, especially as an owner or executive; j)a wealthy and powerful man; a person of power and rank in any sphere, especially in business or industry; a great nobleman; k)a woman engaged in commercial or industrial business, especially as an owner or executive; l)the owner or manager of a business enterprise who, by risk and initiative, attempts to make profits; a person who makes money by starting or running businesses, especially when this involves taking financial risks; |
Task 4. a)Study the following words.
| · Magnate tends to have more positive associations of strength and power; · tycoon sometimes suggests a dishonest type of person who is likely to lose people’s respect at some point: the disgraced / fallen / discredited media tycoon. |
b) In which contexts are the words “магнат” and “олігарх” used in the Ukrainian language? Find (make up) sentences that exemplify the usage of the above words.
Task 5. a) Read and translate the passage.
| ENTREPRENEUR or SMALL BUSINESS OWNER? Many people use the term “entrepreneur” and “small business owner” synonymously. While they may have much in common, there are significant differences between the entrepreneurial venture and the small business. Entrepreneurial ventures differ from small businesses in these ways: 1. Amount of wealth creation– rather than simply generating an income stream (e.g. regular payments that one receives from an investment or a property, especially over a long period of time) that replaces traditional employment, a successful entrepreneurial venture creates substantial wealth, typically in excess of several million dollars of profit. 2. Speed of wealth creation– while a successful small business can generate several million dollars of profit over a lifetime, entrepreneurial wealth creation often is rapid: for example within 5 years. 3. Risk – the risk of an entrepreneurial venture must be high; otherwise, with the incentive of sure profits many entrepreneurs would be pursuing the idea and the opportunity no longer would exist. 4. Innovation– entrepreneurship often involves substantial innovation beyond what a small business might exhibit. This innovation may be in the product or service itself, or in the business processes used to deliver it. |
b) Agree or disagree with the following statements. Correct false statements.
1. There are some insignificant differences between the entrepreneurial venture and the small business.
2. Unlike entrepreneurs small business owners cannot create multimillion profits.
3. Few entrepreneurs can generate several million dollars of profit over a lifetime.
4. There are not sure profits in business.
5. High risk is an indispensable part of entrepreneurship.
6. Entrepreneurs seem to be more innovative than small business owners.
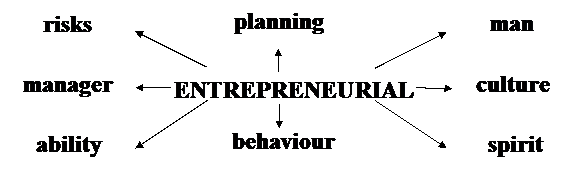
Task 6. a)The words below often occur after “ENTREPRENEURIAL”:
|
b)Which of the above word-combinations means:
1. підприємницькі ризики;
2. підприємницька здібність (здатність);
3. заповзятлива людина;
4. планування для прийняття стратегічних рішень;
5. дух підприємництва (притаманна індивіду або нації якість, що полягає в прагненні до активної економічної діяльності з метою отримання прибутку);
6. підприємницька культура (набір цінностей, символів та зразків поведінки, характерних для підприємницької діяльності: ініціатива, креативність, конкуренція і т.д.);
7. підприємницька поведінка (поведінка, пов’язана з пошуком нових можливостей: нових продуктів, нових ресурсів, нових технологій і т.д., а також прагненням ефективно використовувати ресурси, необхідні для досягнення поставлених цілей);
8. заповзятливий керівник (знаходить нові можливості й готовий йти на ризик, здійснюючи зміни та запроваджуючи удосконалення на своєму підприємстві)?
c)In which of the word-combinations “entrepreneurial” means:
· підприємницький (такий, що стосується підприємництва);
· заповзятливий; енергійний; практичний; винахідливий (готовий піти на ризик для отримання прибутку)?
d)Use the following word-combinations in the sentences of your own.
1.Entrepreneurial risks; 2.entrepreneurial man; 3.entrepreneurial culture; 4.entrepreneurial spirit; 5.entrepreneurial behaviour; 6.entrepreneurial ability; 7.entrepreneurial man; 8.entrepreneurial planning.
Task 7. Translate into Ukrainian the verbs below which are closely associated with entrepreneurial activities. Use the definitions as clues.
| 1. Develop 2. pioneer 3. evolve 4. innovate 5. design 6. create 7. invent 8. engineer | – to think of or produce a new idea / product and make it successful; – to be one of the first people to do, discover or use something new; – (rather formal) to develop something gradually, especially from a simple to a more complicated form; – to invent or begin using new ideas, methods, equipment etc.; – to decide how something will look or work, especially by drawing plans or making models; – to cause something new to happen or exist; to make something new or original that did not exist before; – to produce or design something that has not existed before; – to design and build a vehicle, machine or structure. |
Task 8. a)Study the following words.

· When you invent something, it is completely new and noting of the kind has existed before:
 Who invented the motor car? Who designed / engineered the motor car?
· You can design or engineer a new version of something that already exists:
They’ve designed / engineered a new car.
You would not use invent in this context, unless the car really is very new and different:
They’ve invented / designed / engineered a revolutionary new car.
They’ve invented / designed / engineered a whole new type of car. Who invented the motor car? Who designed / engineered the motor car?
· You can design or engineer a new version of something that already exists:
They’ve designed / engineered a new car.
You would not use invent in this context, unless the car really is very new and different:
They’ve invented / designed / engineered a revolutionary new car.
They’ve invented / designed / engineered a whole new type of car.
|
b) Explain the usage of the above verbs in the following sentences.
1.Esperanto [ֽespə`ræntəu] / [ֽespə`rα:ntəu] – an international artificial language based on words common to the chief European languages – was invented in 1887. 2.Caesar [`si:zə] Cardini (1896-1956), a Mexican restaurateur [ֽrestərə`tə:] invented Caesar salad. 3. Coffee-table book is a book designed to be looked at rather than read. 4.Euro-ad is an advertisement designed to be suitable for all countries in the European Union. 5.This new jet engine is superbly [su`pə:bli] engineered. 6.The car is beautifully engineered and a pleasure to drive.
Task 9. Fill in the blanks with adjective or verb forms. Use your dictionary if necessary.
| ADJECTIVE | VERB |
| 1. ----------- | to innovate |
| 2. inventive | ----------- |
| 3. ----------- | to imagine |
| 4. creative | ----------- |
| 5. ----------- | to originate |
| 6. risky | ----------- |
| 7. ----------- | to venture |
Task 10. Use the correct adjective or verb forms in the sentences. Change the grammatical form of the words if necessary.
Innovate
a) We must constantly adapt and _____ to ensure success in a growing market.
b) Their _____ use of existing technology provided for substantial economy.
Invent
a) A creative business person has the ability to _____ and develop original ideas.
b) He is one of the most _____ of modern business leaders.
Imagine
a) It’ the most _____ solution to a long-standing problem.
b) It was hard to _____ how the system could be improved or made more convenient.
Create
a) Municipal administration drew up a plan to _____ new jobs in the area.
b) The company’s _____ team is its major asset.
Originate
a) This work is the product of a highly _____ mind.
b) The business _____ as a shoe shop, but now offers a full range of clothing.
Risk
a) Many analysts believe the shares are still a _____ investment.
b) He would not _____ his reputation if he did not think he could get the deal.
Venture
a) The directors of the company refused to undertake such a risky _____.
b) If you describe someone as _____, you mean that they are willing to take risks and try out new things.
Task 11. a)Study the following words.

| · Creative [kri`eıtıv] – involving the use of skill and the imagination to produce something new or a work of art; having or showing an ability to do this; · artistic [α:`tıstık] / [α:r`tıstık] – showing a natural skill in or enjoyment of art, especially being able to paint or draw well; done with skill and imagination; · innovative [`ınəuveıtıv] / [`ınəveıtıv] – (approving) introducing or using new ideas or ways of doing something; · original [ə`rıGənəl] – (usually approving) having or showing new, different and interesting ideas; · imaginative [ı`mæGınətıv] / [ı`mæGənətıv] – (usually approving) having or showing new, different and interesting ideas; · ingenious [ın`Gi:niəs] – (often approving) having or showing new, different and interesting ideas; good at inventing things; · inventive [ın`ventıv] – (often approving) having or showing new, different and interesting ideas; good at inventing things. Innovativeis often used in practical and business contexts and is as much about using new ideas as having them. Original, imaginativeand inventive are often used in more artistic contexts. Original / imaginative ideas are interesting whether they work in practice or not. Things that are ingenious are clever and must work, or they are not ingenious; however, they may not be as big or important as things that are innovative or original. |
b) Translate into English.
1. Винахідливий;
2. творчий, креативний;
3. артистичний; художній, мистецький;
4. винахідливий; майстерний; дотепний;
5. новаторський, передовий, раціоналізаторський, інноваційний;
6. наділений багатою уявою; образний, багатий на поетичні образи;
7. самобутній, своєрідний; справжній; оригінальний; новий, свіжий.
Task 12. Translate into Ukrainian paying attention to the words in italics.
1.She has considerable artistic ability. 2.You don’t need to be very artistic to produce great designs. 3.He comes from a very artistic family. 4.Painting is a creative process. 5.The creative use of tax and incentives (стимули; засоби заохочення) let municipal authorities achieve economic goals. 6.He was a creative genius. 7.We offer people the opportunity to be creative. 8.She’s very creative – she writes poetry and paints. 9.Their success is due to innovative use of existing technology. 10.These designs are full of innovative ideas. 11.He produced stylistically innovative works. 12.How innovative is British industry? 13.The film is challenging and highly original. 14.They presented a highly original design. 15.You must take an imaginative and aggressive approach to management. 16.They suggested some very imaginative ways of reducing costs. 17.He was more imaginative than most other employees. 18.The idea was an ingenious one. 19.They thought of an ingenious plan for making lots of money. 20.The researchers conducted an ingenious experiment. 21.She’s very ingenious when it comes to finding excuses. 22.This is a courageous [kə`reıGəs] and inventive piece of film-making. 23.Does inventive activity need legal [`li:gəl] regulation? 24.He is an inventive soul. 25.We need a clever and inventive designer.
Task 13.Practice reading the following words.
| 1. to accept [ək`sept] 2. to allow [ə`lau] 3. although [O:l`ðəu] / [O:l`ðou] 4. aptitude [`æptıtju:d] / [`æptıtu:d] 5. behaviour [bı`heıvjə] 6. career[kə`rıə] / [kə`rıər] 7. characteristics [ֽkærəktə`rıstıks] 8. considered [kən`sıdəd] / [kən`sıdərd] 9. earning [`ə:nıŋ] 10. efficient [ı`fı∫ənt] 11. engine [`enGın] 12. enthusiastic [ınֽθju:zi`æstık] / [ınֽθu:zi`æstık] 13. essence [`esənts] 14. to exhibit [ıg`zıbıt] 15. extreme [ık`stri:m] | 16. to guarantee [ֽgærən`ti:] 17. inspiration [ֽınspə`reı∫ən] 18. to originate [ə`rıGəneıt] 19. overconfidence [ֽəuvə`kOnfıdənts] 20. overgeneralization [ֽəuvəֽGenərəlaı`zeı∫ən] 21. to pioneer [ֽpaıə`nıə] / [ֽpaıə`nıər] 22. possessing [pə`zesıŋ] 23. security [sı`kjuərəti] / [sı`kjurəti] 24. simultaneously [ֽsıməl`teıniəsli] 25. solo [`səuləu] / [`soulou] 26. specific [spə`sıfık] 27. substantially [səb`stænt∫əli] 28. successful [sək`sesfəl] 29. uncertain [An`sə:tən] 30. vision [`vıჳən] |
Task 14.Read the text.
Дата добавления: 2018-06-27; просмотров: 742; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!