Take a piece of paper. Fold it like a fan. What does it look like? Does it show the geometric parts of a fold?
2. Read the definitions and draw the corresponding folds and label them . (R.P 8.3.2.2)
1. Rock beds are folded into an arch; arch from a few feet to many miles across;
2. Downfolded sedimentary rock layers that form a basin. Immense synclines are called geosynclines.
3. Its shape and mirror image are identical; a vertical hinge surface.
4. Hinge surface is usually inclined.
5. Both limbs and the axial plane dip in the same direction
LISTENING COMPREHENSION
You will hear part of a lecture. For statements 1- 8, complete the notes, which summarize what the speaker says. You will need to write a word or short phrase in each box.
| 1. Sediments accumulate horizontals beds or _________________ . |
| 2. The old deposits can be usually found in ____________________ . |
| 3. The main forces that form mountains are tilting, breaking _______ and _______________ . |
| 4. These forces are affected by _____________ and ____________ . |
| 5. Each type of deformation depends on two factors: _________ and _____________ . |
| 6. Folding occurs at the edges of _____________ ____________ ___________ . |
| 7. High temperature and pressure ____________ brittle rocks. |
| 8. There are _______________ types of folds. |
DISCUSSION
The topic of our discussion- Faulting and Folding. There are two groups. Each group discusses the following monitoring packet. The monitoring packet- consists of 4 parts. (R.P. – 8.3.1.4, 8.3.2.3, 8.3.1.1)
Part 1- checks vocabulary by means of reading comprehension
Part 2- detail reading; questions that ask for specific details (using
Diagrams)
Part 3- main idea: checks the student's comprehension of the topic
Part 4- interpretive questions; requires the students to understand, analyze
And infer from the text.
| Part 1 Fill in the gaps | Part 1 Fill in the gaps |
| 1. Fault is ________ in the Earth's crust with visible movement. 2. Faulting often accompanies ________ . 3. The stress patterns for faulting and folding depend on the type of _______ involved. 4. ____________ is the principle deformational stress involved in normal faulting. 5. Compression is responsible for ________ . | 1. Fold is a deformation of strata formed by forces, such as and ___ . 2. Faulting precedes or follows . 3. ___________ is the locus of maximum curvature of a fold. 4. Inflection occurs where _________ changes to _____________ . 5. A fold is ___________ when its shape and mirror image are identical. |
| 6. In reverse (thrust) faults intermediate principal stress remains ______ . 7. Strike-slip faults occur when blocks slide ________________ . 8. Fault consists of two ________ . 9. The hanging wall of a fault is located the fault surface. 10. The footwall of a fault is located the fault. | 6. Limbs ________ upon the inflection line synclines and ___________ from it in anticlines. 7. Folds usually form in association with _________ . 8. _________ is a fold with upward convexity. 9. _________ is a concave upward. 10. The locus of all hinge lines is . |
| Part 2 Answer the following questions using different diagrams: | Part 2 Answer the following questions using different diagrams: |
| 1. What is the difference between the hanging wall and footwall? 2. There are two main types of faulting-normal and reverse. Draw diagrams and explain the similarity and difference between them. 3. What affects the type of strike-slip fault? 4. What are the synonyms for right\ left lateral faults? 5. What factor (s) connect(s) all the types of faults together? | 1. How are folds formed? 2. What main factors effect the classification of folds? 3. There are two main types of folds. Draw diagrams and explain the similarity and difference between them. 4. When is a fold symmetrical or asymmetrical? 5. Draw a diagram showing the principal stresses involved in a fold. |
| Part 3 Give a short explanation. | Part 3 Give a short explanation. |
| Deformation is a structural term, explaining such things as faulting and folding. | Deformation is a structural term, explaining such things as faulting and folding. |
| Part 4 Discuss and try to prove this statement: | Part 4 Discuss and try to prove this statement: |
| Deformation (faulting / folding) is an important process in oil exploration | Deformation (faulting / folding) is an important process in oil exploration. |
|
|
WORDLIST
|
|
|
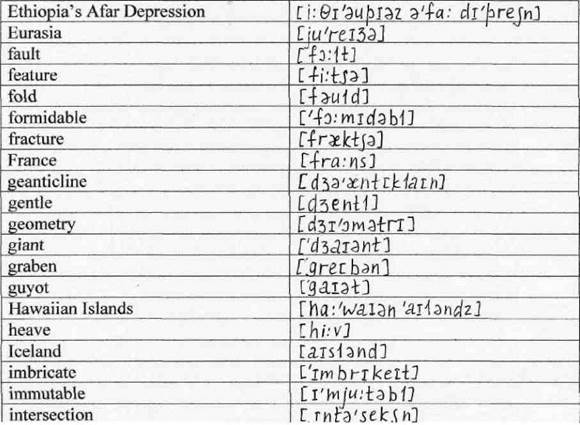
PRONUNCIATION






TERMS
| abyssal plane | абиссальная равнина |
| axial plane | осевая плоскость (складки) |
| basement block | основание |
| bearing | простирание |
| belt | зона, пояс |
| block-faulting | глыбовые дислокации |
| brittle | хрупкий |
| coalescing | объединение, слияние |
| compression | сжатие |
| concave (concavity) | вогнутый (вогнутость) |
| continental crust | континентальная кора |
| continental drift | дрейф континентов |
| continental plateau | континентальное плато |
| continental rise | континентальная подножие |
| continental shelf | континентальный шельф |
| continental slope | континентальный склон |
| convergent boundary | граница схождения |
| convex (convexity) | выпуклый (выпуклость) |
| curvature | кривизна, линия изгиба |
| dip | наклон, падение |
| divergent boundary | дивергентная граница |
| dome | купол, свод |
| downthrow | сброс |
| drape | собирать в складки |
| fault | разрывное нарушение, дизъюнктивная дислокация, разрыв, сброс |
| fault plane | плоскость разрывного нарушения, сместитель |
| feature | особенность |
| fold | складка |
| folding | складчатость, складкообразование |
| footwall | лежачий блок (бок, крыло) |
| fracture | трещина, разлом |
| graben | грабен |
| hade | угол, образуемый плоскостью разрыва с вертикалью |
| hanging wall | висячий блок (бок, крыло) |
| heave | горизонтальная амплитуда смещения |
| hinge point | шарнирная точка |
| hinge surface | осевая плоскость |
| horst | горст |
| inflection point | точка перегиба |
| intersection | пересечение |
| island arc | островная дуга |
| joint | трещина отдельности |
| left-lateral strike-slip fault (sinistral) | левосторонний сдвиг |
| limb (flank) | крыло складки |
| locus | местоположение |
| marginal sediment | прибрежный осадок |
| mobile belt | подвижный пояс |
| monocline | моноклиналь |
| mountain chain | горная цепь |
| nappe | тектонический покров |
| normal fault | сброс |
| oblique slip | диагональное смещение |
| obliquity | скос, наклон |
| oceanic crust | океаническая кора |
| orogen | ороген, горно-складчатое сооружение |
| orogenesis | орогенез, горообразование |
| overfold | опрокинутая складка |
| peak | пик |
| pericline | периклиналь |
| plain | равнина |
| plate tectonics | тектоника литосферных плит |
| pressure | давление |
| reverse fault | взброс |
| right-lateral strike-slip fault (dextral) | правосторонний сдвиг |
| rim | край |
| seal | закупорка |
| seamount | подводная гора |
| sheath | оболочка, покров |
| spreading ridge | спрединговый (срединно-океанический) хребет |
| strain | деформация, механическое напряжение |
| strain rate | интенсивность деформации |
| stress | давление, напряжение |
| stress point | точка нагрузки |
| strike | простирание |
| strike-slip(fault) | сдвиг |
| subduction zone | зона субдукции |
| submarine canyon | подводное ущелье |
| submarine plateau | подводное плато |
| supercontinent Pangea | суперконтинент Пангея |
| surroundings | окружение, среда |
| syncline | синклиналь |
| tableland | плоскогорье, плато |
| tear fault | поперечный сдвиг |
| temperature | температура |
| tension | напряжение, растяжение |
| throw | вертикальная амплитуда смещения |
| thrusting | образование надвигов |
| tilt block | наклонный блок |
| transform boundary | трансформная граница |
| trench | желоб, впадина |
| triaxial stress field | пространственное (трехмерное) поле напряжений |
| trough | впадина, мульда |
| upthrow | взброс |
| valley | долина |
WORDS AND PHRASES
|
|
|
|
|
|
| abandoned | покинутый, оставленный |
| accretion | аккреция, разрастание, приращение |
| alien | внешний, чуждый |
| belt | пояс, зона |
| bit | кусочек, частица |
| cleft | расселина, трещина |
| core | центр, ядро, внутренняя часть |
| current | поток |
| curved | изогнутый, кривой |
| descending | нисходящий, спускающийся, падающий |
| flat-topped | с плоской вершиной |
| full-blown | развитой, созревший, распустившийся |
| gentle | пологий (о склоне), слабый |
| immutable | неизменный, постоянный |
| intervening | промежуточный, переходный |
| junction | соединение, объединение |
| liable | подверженный, склонный к чему-либо, вероятный |
| notably | исключительно, особенно, заметно |
| patch | очаг, небольшой участок земли, обломок |
| plume | столб магмы, плюм |
| range | ряд, линия, цепь, область распространения |
| rigid | твердый, жесткий, неподвижный |
| row | ряд, последовательность |
| ruck | масса, множество, груда, кипа |
| scrap | остаток, обломок |
| shrink | уменьшение, сокращение |
| slab | плита, пластина |
| steep | крутой |
| terrane | террейн |
| to buckle | уступать давлению |
| to bulge down | провисать, выдаваться вниз |
| to converge | сходиться, встречаться |
| to disrupt | раздробить, разбить, разрушить |
| to diverge | расходиться |
| to grow outward | выходить наружу |
| to hold | держать, содержать в себе, вмещать |
| to make up | составлять, собирать |
| to occupy | занимать |
| to punch through | пробиваться сквозь |
| to punch up | пробиваться из глубины на поверхность |
| to resort | прибегнуть к помощи, силе |
| to rotate | вращать(ся) |
| to slope | клониться, иметь наклон, опускаться или подниматься наклонно |
| to split apart | разбиваться, раскалываться |
| to split open | открываться, раскрываться |
| to squeeze | сжимать, сдавливать, стискивать |
| to strip off | сдирать, соскабливать |
| to suspect | подозревать, не внушать доверия |
| to sweep | сметать, сносить |
| to tack on | добавлять, присоединять |
| to tug on | натягивать |
| to weld | cваривать(ся), спаивать(ся) |
| tract | полоса, участок, пространство, период времени |
| triple | тройное соединение |
| to drape over | ниспадать складками |
| to precede | предшествовать |
| to manifest | проявляться, становиться явным |
| adjacent to | смежный, расположенный рядом |
| to converge upon | стремиться к пределу |
| to associate with | связывать с, ассоциировать с |
| to move up | двигаться вверх |
| to move down | двигаться вниз |
| to move laterally over | двигаться по (направлению) |
| to move to | переходить к |
| to slide by | скользить |
| to observe in | замечать, наблюдать |
| to be measured by | измеряться |
| regardless of | независимо от |
| to facilitate | способствовать |
| at an angle | под углом |
| perpendicular to | перпендикулярно |
| to bear upon | опираться |
| to emerge | возникать, выясняться |
| to result from | являться результатом чего-либо |
| to result in | приводить к |
| to involve | включать в себя, вызывать |
| to be responsible for | быть ответственным за |
| to orient along | ориентироваться по, располагаться вдоль |
Дата добавления: 2019-01-14; просмотров: 230; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!

