Compose sentences, using the following words and phrases
1.to creep outward 6. to plug
2. to subside 7. to be tugged apart
3. to thin away 8. to stick
4. to rise from beneath 9. to sink
5. to well up 10. to create
3.1.3. Spreading ridge evolves several stages. Put the words according to
the stages. Compose sentences to describe the process. (R.P – 8.1.2, 8.1.3)
Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4
mantle new rise through molten
upwelling blocks rock plug
melt subside molten gap
partly cracks cracks rock
oceanic crustal block pull apart
crust fresh rim old
push up appear plate tension
above bulging crust
subside
block
central
Put the facts in the correct order spreading develops.
1. Fresh cracks appear.
2. Mantle upwells.
3. It partly melts.
4. Molten rock plugs gaps.
5. Tension pulls old crust apart.
6. New crustal blocks subside.
7. Mantle pushes up the oceanic crust.
8. Molten rock rises through cracks.
9. Bulging plate splits.
10. The process is repeated.
11. A central block subsides.
4. LISTENING COMPREHENSION You will hear part of a radio report about the oceanic crust. For statements 1-12, complete the notes, which summarize what the speaker says. You will need to write a word or short phrase in each sentence. You will hear the recording twice.
1. The oceanic crust is different from ___________________ .
2. Besides aluminum and calcium, ocean crust has a high content of .
3. The combination is called _________________ .
4. The ocean crust has __________________ .
5. The first layer consists of _______________________ .
|
|
|
6. They may be ______________________ , which lie up on
______________ .
7. The next layer is mainly ____________________ , which is found at
_________________________ .
8. The third layer is made up of __________________ .
9. While the last layer is _____________________ .
10. It is made up of peridotite, chiefly _______________ .
DISCUSSION (R.P – 8.1.5)
We’ll discuss the subject: «Plate tectonics in action». Pay attention to the words and expressions and pronunciation of some of the geographical names. Read the text, which will give you some necessary information. Use the earlier communicative formulas (Unit 7). Pay special attention to the questions, which will help you to underline what facts are more important. Use the diagrams – «Plate tectonics in action», «Tectonic plates». (R.P. 8.2.10, 8.2.11)
Geographical Names
Eurasian Plate Indo-Australian Plate Nazca Plate
African Plate Pacific Plate South American Plate
Antarctic Plate North American Plate
| restless | непрекращающийся, неугомонный |
| jigsaw puzzle | картинка-головоломка, мозаика |
| abutting | примыкающий, прилегающий |
| diverging | расходящийся |
| colliding | сталкивающийся |
| slab | кусок, плита, блок |
| tectonic plate | тектоническая плита |
| coupled to | связанный / соединенный с |
| rigid | устойчивый, твердый |
| to ride upon | передвигаться / скользить по (поверхности) |
| convection current | конвективный поток |
| to shift | перемещать, сдвигать |
| margin -constructive -destructive -conservative passive -active | -граница -конструктивная -деструктивная -консервативная -пассивная -активная |
| lithosphere | литосфера |
| zone -collision -subduction | зона -столкновения -субдукции |
| spreading ridge | спрединговый хребет |
| to dive down | погружаться, нырять |
| to slide past | скользить мимо |
| to spark off | вызывать, порождать |
| boundary | граница, поверхность раздела |
| permutation | изменение |
| interlock | смыкаться |
EARTH’S CHANGING SURFACE
|
|
|
Our planet’s solid surface is a restless jigsaw of abutting, diverging and colliding slabs called plates (lithospheric plates). How plates behave forms the subject known as plate tectonics.
Each plate involves a slab of oceanic crust, continental crust, or both, coupled to a slab of rigid upper mantle. Collectively these plates make up the lithosphere. This rides upon the asthenosphere, a dense, plastic layer of the mantle. Heat rising through this layer from the Earth’s core and lower mantle seemingly produces convection currents that shift the plates above.
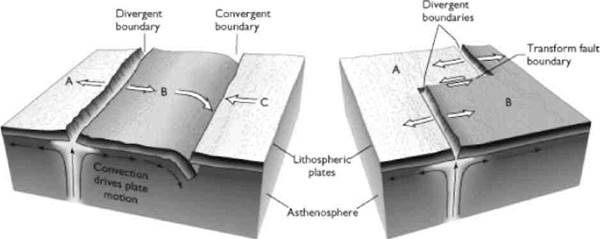
Plate activities produce three main kinds of plate margins.
• Constructive (divergent) margins are oceanic spreading ridges where new lithosphere is formed between two separating oceanic plates.
• Destructive (convergent) margins are oceanic trenches where an oceanic plate dives down below a (less dense) continental plate.
• Conservative (transform) margins are where two plates slide past each other and lithosphere is neither made nor lost.
Дата добавления: 2019-01-14; просмотров: 263; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
