Fig. 43 Ocean areas and depths
UNIT 8 THE RESTLESS CRUST
PART 1: OCEANIC CRUST 1. COMPREHENSION 1.1 Vocabulary
Pay attention to the pronunciation of the geographical terms and especially to the pronunciation of numbers
Pacific Ocean Marianas Trench
Mid-Atlantic Ridge Arctic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean Ascension Island
Mt. Everest Indian Ocean
97 per cent 7.5 per cent
71 per cent 8.5 per cent
12,400 ft. (feet) ≈ 3 700 m 650 ft. ≈ 200 m 11,500 ft. = 3 450 m 3,300 ft. ≈ 1000 m 10,000 ft. = 3000 m 37,000 mi. (miles) ≈ 60 000 km 35,840 ft. = 10 752 m 3300 ft. - 33 hundred feet
| Pay attention to the bold terms and expressions in the text | |
| continental shelf | континентальный (материковый) шельф |
| continental slope | континентальный (материковый) склон |
| submarine canyon | подводное ущелье (каньон) |
| continental rise | континентальное (материковое) подножие |
| submarine plateau | подводное плато |
| abyssal plain | абиссальная равнина |
| seamount | морская гора |
| spreading ridge | спрединговый (срединно-океанический) хребет |
| trench | желоб |
| island arc | островная дуга |
| trough | впадина, мульда |
| guyot | гайот |
| continental side | континентальная сторона, склон |
| to strip off | обнажать |
| sheath | оболочка, покров |
| plateau | плато |
| peak | вершина горы, пик |
| to submerge | погружать |
| rim | край |
| to descend | опускаться; нисходить |
| slope | склон; крыло складки |
| cleft | трещина; расселина |
| turbid | мутный |
| surroundings | окружение; среда |
| mountain chain | горная цепь |
| tableland | плоскогорье, плато |
Read the text «The Ocean Floor». Pay attention to the diagram. Fulfill the exercises after the text. (R.P – 8.1.1)
Oceans and their seas hold 97% of all surface water, and cover some 71% of
the Earth to an average depth of 12,400 ft. (3700 m). Stripping off this watery
|
|
|
sheath would reveal valleys, plateaus, peaks and plains. We show ten
features of the ocean floor.
Continental shelf- a continent’s true but submerged and gently sloping rim,
descending to an average depth of 650 ft. (200 m). Continental shelves
occupy about 7.5% of the ocean floor.
Continental slope- a relatively steep slope descending from the continental
shelf. Such slopes occupy about 8.5% of the ocean floor.
Submarine canyon- a deep cleft in the continental slope, cut by turbid river
water flowing out to the sea.
Continental rise- a gentle slope below the continental slope.
Submarine plateau- a high seafloor tableland.
Abyssal plain- a sediment-covered deep-sea plain about 11,500-18,000ft
(3450-5400 m) below sea level.
Seamount- a submarine volcano 3300ft. (1000 m) or more above its
surroundings. Guyots are flat-topped seamounts that were once volcanic
islands.
Spreading ridge- a submarine mountain chain generally 10,000 ft. (3000 m)
above the abyssal plain. A huge system of such ridges extends more than
37,000 ft. (60000 m) through the oceans. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge surfaces in
places as volcanic islands such as Iceland and Ascension Island.
Trench- a deep, steep-sided trough in an abyssal plain. At 35,840 ft. (10752
m) below sea level (deep enough to drown Mt. Everest). The Pacific’s
Marianas Trench is the deepest part of any ocean.
Island arc- a curved row of volcanic islands, usually on the continental side
of a trench.
(Lambert “The Field Guide to Geology” 1988, Cambridge University Press)
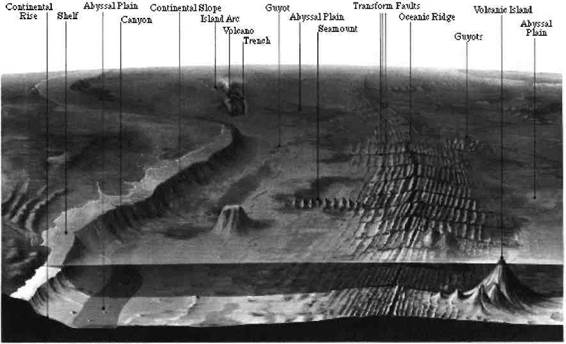
Fig. 42 Ocean floor
EXERCISES
Look at the geographical map and point out the oceans. Name them.
2.2 Look at the diagram below and answer the following questions (R.P.-8.2.1)
a) Which ocean is the deepest?
b) Which ocean is the shallowest?
c) Which ocean is the largest in area?
d) Which two oceans are the same in area?
|
|
|
|
Fig. 43 Ocean areas and depths
Дата добавления: 2019-01-14; просмотров: 177; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!


