Economic costs of unemployment.
GDP gap is the difference between potential(max возможный) and actual GDP(реальный)
For every 1 percent of unemployment above the natural rate, a 2 percent GDP gap ocurs(Okun's Law) – сколько мы теряем от процента безработицы
Inflation: meaning and measurement. Rule of 70.
Inflation - Is defined as a persistent increase in the average price level in the economy, usualy measured trough the calculation of a consumer price index (CPI) – процесс обесценения ден. cредств, кот. может выражаться в повышении ур-ня цен)
«The Rule of 70»: 70 / inflation rate = years for the price level to double
Types of inflation
· Demand-pull inflation(спроса): an excess of total spending beyond the economy's capacity to produce. When resources are already fuly employed, firms can't respond to increase in demand.
· Cost-push or suply side inflation(предложения, издержек): prices rise because of rise in per-unit prodaction costs
12.Effects of inflation
.» wage-push(рост зароб.пл):can occur as result of union strength and supply shocks may ocur with unexpected increase in the price of raw materials(сырье)
» cost-push: experince has shown that rising prices and unemployment can exist together, it's called stagflation
»mild inflation(<3%) – it may be a healthy by product of a prosperous economy or it may have an undesirable impact on real income
»creeping inflation(ползучая)- turning into hyperinflation which can cause speculation reckless spending and more inflation
13. Phases of the business cycle
- Peak(бум) there is an expansion of output, income, employment, prices and profits, there is also a rise in the standard of living.
- Recesion (рецессия) the economic activities slow down
- Trough (депрессия) there is a continuous decrease of output, income, employment, prices and profits, there is a fall in the standard of living
- Recovery (оживление) there are expansions and rise in economic activities
14. Reasons and results of business cycles
Reasons:
- Changes in interest rate affect consumer spending and economic growth. See: Interest rate cycle
- Changes in house prices. A rise in house prices creates a wealth effect and higher consumer spending. A fall in house prices causes lower consumer spending and bank losses. (house prices and consumer spending)
|
|
|
- Consumer and Business confidence. People are easily influenced by external events. If there is a succession of bad economic news, this tends to discourage people from spending and investing making a small downturn into a bigger recession. But, when the economy recovers this can cause a positive bandwagon effect.
Results: ?
Economic growth: definition and ingredients.
Economic growth - is achieved when there is an increase in a nations real income and output in a given year - an increase in real GDP occurring over some time period.
Ingredients of growth
Supply factors (факторы предложения) - related to the physical ability of the economy to expand.
They are:
-Improvement in technology:
-Increase in the quantity and quality of:
>Natural resources;
>human resources
>capital goods
Demand factors - to fully employ production potential expanding supplies of resources it is necessary to increase level of aggregate demand
Efficiency factor: the country must use its resources:
- in the least costly way - productive efficiency
- in producing the specific mix of goods and services that maximizes society’s well-being – all locative efficiency
Definition - a positive change in the level of production of goods and services by a country over a certain period of time. Nominal growth is defined as economic growth including inflation, while real growth is nominal growth minus inflation. Economic growth is usually brought about by technological innovation and positive external forces.
Aggregate demand (AD). AD curve.
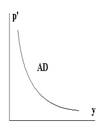 The total amounts of nation’s output that buyers collectively desire to purchase at each possible price level.There is an inverse relationship between a nation’s price level and the amount of output demanded
The total amounts of nation’s output that buyers collectively desire to purchase at each possible price level.There is an inverse relationship between a nation’s price level and the amount of output demanded
p'- price level
y - real output or income
2 economic explanations for the inverse relationship between the price level and real output or income:
|
|
|
Wealth effect - Higher price levels reduce the purchasing power or real value of the nation's wealth or accumulated saving.
Net export effect - With an increase in the domestic price level, consmers and firms find foreign goods and input more attractive, thus the quantity of domestic output demanded decreases.
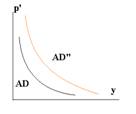 |
17. Determinants of AD.
·Consumption - Wealth (If wealth increases, consumption increases and savings decrease.)
- Expectations (If household expect prices to rise tomorrow, then today C will shift up, Sdown)
- Real interest rates (Lower real interest rates lead to more C, less S and vise versa.)
- Household debt (if debt gets too high, C will have to shift down as households try to pay off their loans.) - Taxation (Increase in taxes shifts BOTH C and S curves downwards, Decrease in taxes shifts BOTH C and S curves upwards)
·Investment
- Refers to the expenditures by firms on new plants, capital equipment, inventories etc.
- a firm's decision to invest is a COST and BENEFIT decision.
- Costs of investment: the interest rate changed by the bank on a loan to buy new capital
- Benefit of investment: the expected rate of return the investment will earn for the firm.
- expectations
- technology
- business taxes
- inventories
- degree of excess capacity
·government spending
·net export - Exchange rates,tastes and preferenees
A change in one of the four expenditures will cause the AD curve to shift.The distance between the old AD and the new AD represents the amount of new spending plus the multiplier effect: The ultimate change in output(GDP) will be greater than the initial change in spending.
Дата добавления: 2018-08-06; просмотров: 268; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
