The historical development of English verbals
Федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение
высшего образования
«Московский государственный лингвистический университет»
(ФГБОУ ВО МГЛУ)
Факультет английского языка
Кафедра грамматики и истории английского языка
Андреев Николай Владимирович
«Перевод неличных форм глагола в произведениях среднеанглийского и новоанглийского периодов»
Выпускная квалификационная работа
студента группы 0-17-42
Научный руководитель:
доцент кафедры грамматики
и истории английского языка,
кандидат филологических наук
Павлова Елена Борисовна
Москва - 2018
Contents
Introduction………………………………………………………………………...3
1.1. Chronological subdivisions in the history of English verbals……………….4
1.2. The modern characteristics of the non-finite forms in English……………...9
1.3. The transformation techniques used to translate the non-finite forms from English into Russian and its modern tendencies…………………………...30
Conclusion…………………………………………………………………...........40
Practical part
Bibliography
Introduction
A great number of successful investigations in the sphere of diachronic grammar and the historical development of the non-finite forms of the verb still represent different viewpoints on the subject of investigation, thus, preserving an important interest for further research work. For those who really want to know the way these non-finite forms of the verb were translated language from English into Russian we can recommend to study the historical development of the English non-finite forms and compare them with those in the Russian language, paying special attention to the pecularities that we can observe in the forms of the infinitives, the differences of the non-finite forms in the two languages.
|
|
|
The objective of the master’s study reveals the differences of two possible ways of translation of verbals from English into Russian.
The objective presupposes the following tasks:
1. to study the historical development of the non-finite forms of the English verb;
2. to review the modern characteristics of the non-finite forms in English;
3. to reveal the modern transformation techniques used to translate the non-finite forms from English into Russian.
The subjects of the master’s thesis are the non-finite forms of the English verb.
The master’s study consists of Introduction, the first chapter, the conclusion. In Introduction we explain the objectives of the master’s study. The first chapter looks into the historical development of the non-finite forms of the verb in the English language, the modern pecularities of the non-finite forms in English, the transformation techniques used to translate the non-finite forms from English into Russian.
Conclusion summarizes the results of our research.
Chronological subvidions in the history of English verbals.
The historical development of English
The historical development of a language is a continuous uninterrupted process without sudden breaks or rapid transformations. Therefore any periodisation imposed on language history by linguists, with precise dates, might appear artificial, if not arbitrary. Yet in all language histories divisions into periods and cross-sections of a certain length, are used for teaching and research purposes. The commonly accepted, traditional periodisation divides English history into three periods: Old English (OE), Middle English (ME) and New English (NE), with boundaries attached to definite dates and historical events affecting the language. OE begins with the Germanic settlement of Britain (5th c.) or with the beginning of writing (7th c.) and ends with the Norman Conquest (1066); ME begins with the Norman Conquest and ends on the introduction of printing (1475), which is the start of the Modern or New English period (Mod E or NE); the New period lasts to the present day.
|
|
|
The amendments proposed to the traditional periodisation shift the boundary lines or envisage other subdivisions within the main periods: it has been suggested that ME really began at a later date, c. 1150 (A. Baugh), for the effect of the Norman Conquest on the language could not have been immediate; another suggestion was that we should single out periods of transition and subdivide the three main periods into early, classical, and late (H. Sweet). Some authors prefer a division of history by centuries (M. Schlauch) or a division into periods of two hundred years (B. Strang).
It has been noticed that although language history is a slow uninterrupted chain of events, the changes are not evenly distributed in time: periods of intensive and vast changes at one or many levels may be followed by periods of relative stability. It seems quite probable that the differences in the rate of changes are largely conditioned by the linguistic situation, which also accounts for many other features of language evolution. Therefore division into chronological periods should take into account both aspects: external and internal (extra- and intralinguistic). The following periodisation of English history is partly based on the conventional three periods; it subdivides the history of the English language into seven periods differing in linguistic situation and the nature of linguistic changes.
The first — pre-written or pre-historical — period, which may be termed Early Old English, lasts from the West Germanic invasion of Britain till the beginning of writing, that is from the 5th to the close of the 7th c. It is the stage of tribal dialects of the West Germanic invaders (Angles, Saxons, Jutes and Frisians), which were gradually losing contacts with the related continental tongues. The tribal dialects were used for oral communication, there being no written form of English.
The evolution of the language in this period is hypothetical. It has been reconstructed from the written evidence of other Old Germanic languages, especially Gothic, and from later OE written records. It was the period of transition from PG to Written OE. Early OE linguistic changes, particularly numerous sound changes, marked OE off from PG and from other OG languages.
|
|
|
The second historical period extends from the 8th c. till the end of the 11th. The English language of that time is referred to as Old English or Anglo-Saxon; it can also be called Written OE as compared with the pre-written Early OE period. The tribal dialects gradually changed into local or regional dialects. Towards the end of the period the differences between the dialects grew and their relative position altered. They were probably equal as a medium of oral communication, while in the sphere of writing one of the dialects, West Saxon, had gained supremacy over the other dialects (Kentish, Mercian and Northumbrian). The prevalence of West Saxon in writing is tied up with the rise of the kingdom of Wessex to political and cultural prominence.
The language of this historical period is usually described synchronically and is treated as a more or less stable system, though this assumption may be due to scarcity of evidence, Careful examination of OE texts has revealed increasing variation in the 10th and 11th c, which testifies to growing dialectal divergence and the historical instability of the language.
OE was a typical OG language, with a purely Germanic vocabulary, and few foreign borrowings; it displayed specific phonetic peculiarities, owing to intensive changes which took place in Early OE. As far as grammar is concerned, OE was an inflected or "synthetic" language with a well-developed system of morphological categories, especially in the noun and adjective, and with an elaborate grouping of a|] inflected parts of speech into morphological classes. H. Sweet, a prominent English scholar of the late 19th c, called OE the "period of full endings" in comparison with later periods. The decline of the morphological system began in the Northern dialects in the 10th and 11th c.
|
|
|
The third period, known as Early Middle English, starts after 1066, the year of the Norman Conquest, and covers the 12th, 13th and half of the 14th c. It was the stage of the greatest dialectal divergence caused by the feudal system and by foreign influences — Scandinavian and French. The dialectal division of present-day English owes its origin to this period of history.
Under Norman rule the official language in England was French, or rather its variety called Anglo-French or Anglo-Norman; it was also the dominant language of literature. There is an obvious gap in the English literary tradition in the 12th c. The local dialects were mainly used for oral communication and were but little employed in writing. Towards the end of the period their literary prestige grew, as English began to displace French in the sphere of writing, as well as in many other spheres. Dialectal divergence and lack of official English made a favourable environment for intensive linguistic change.
Early ME was a time of great changes at all the levels of the language, especially in lexis and grammar. English absorbed two layers of lexical borrowings: the Scandinavian element in the North-Eastern area (due to the Scandinavian invasions since the 8th c.) and the French element in the speech of townspeople in the South-East, especially in the higher social strata (due to the Norman Conquest). Phonetic and grammatical changes proceeded at a high rate, unrestricted by written tradition. Grammatical alterations were so drastic that by the end of the period they had transformed English from a highly inflected language into a mainly analytical one; for the most part, they affected the nominal system. Accordingly, the role of syntactical means of word connection grew.
The fourth period — from the later 14th c. till the end of the 15th — embraces the age of Chaucer, the greatest English medieval writer and forerunner of the English Renaissance. We may call it Late or Classical Middle English. It was the time of the restoration of English to the position of the state and literary language and the time of literary flourishing. The main dialect used in writing and literature was the mixed dialect of London. (The London dialect was originally derived from the Southern dialectal group, but during the 14th c. the southern traits were largely replaced by East Midland traits.) The literary authority of other dialects was gradually overshadowed by the prestige of the London written language.
In periods of literary efflorescence, like the age of Chaucer, the pattern set by great authors becomes a more or less fixed form of language.
Chaucer's language was a recognised literary form, imitated throughout the 15th c. Literary flourishing had a stabilising effect on language, so that the rate of linguistic changes was slowed down. At the same time the written forms of the language developed and improved.
The written records of the late 14th and 15th c. testify to the growth of the English vocabulary and to the increasing proportion of French loan-words in English. The phonetic and grammatical structure had incorporated and perpetuated the fundamental changes of the preceding period. Most of the inflections in the nominal system — in nouns, adjectives, pronouns — had fallen together. H. Sweet called Middle English the period of "levelled endings". The verb system was expanding, as numerous new analytical forms and verbal phrases on the way to becoming analytical forms were used alongside old simple forms.
The fifth period — Early New English — lasted from the introduction of printing to the age of Shakespeare, that is from 1475 to c. 1660. The first printed book in English was published by William Caxton in 1475. This period is a sort of transition between two outstanding epochs of literary efflorescence: the age of Chaucer and the age of Shakespeare (also known as the Literary Renaissance).
It was a time of great historical consequence: under the growing capitalist system the country became economically and politically unified; the changes in the political and social structure, the progress of culture, education, and literature favoured linguistic unity. The growth of the English nation was accompanied by the formation of the national English language.
Caxton's English of the printed books was a sort of bridge between the London literary English of the ME period and the language of the Literary Renaissance. The London dialect had risen to prominence as a compromise between the various types of speech prevailing in the country and formed the basis of the growing national literary language.
The Early NE period was a time of sweeping changes at all levels, in the first place lexical and phonetic. The growth of the vocabulary was a natural reflection of the progress of culture in the new, bourgeois society, and of the wider horizons of man's activity. New words from internal and external sources enriched the vocabulary. Extensive phonetic changes were transforming the vowel system, which resulted, among other things, in the growing gap between the written and the spoken forms of the word (that is, between pronunciation and spelling). The loss of most inflectional endings in the 15th c. justifies the definition "period of lost endings" given by H. Sweet to the NE period. The inventory of grammatical forms and syntactical constructions was almost the same as in Mod E, but their use was different. The abundance of grammatical units occurring without any apparent restrictions, or regularities produces an impression of great "freedom of grammatical construction". Perhaps the choice of forms was motivated in a given situation, but its reasons are hard to discern today, and they appear to be used in free variation.
The sixth period extends from the mid-17th c. to the close of the 18th c. In the history of the language it is often called "the age of normalisation and correctness", in the history of literature — the "neoclassical" age. This age witnessed the establishment of "norms", which can be defined as received standards recognised as correct at the given period. The norms were fixed as rules and prescriptions of correct usage in the numerous dictionaries and grammar-books published at the time and were spread through education and writing.
It is essential that during the 18th c. literary English differentiated into distinct styles, which is a property of a mature literary language. It is also important to note that during this period the English language extended its area far beyond the borders of the British Isles, first of all to North America.
Unlike the age of Shakespeare, the neo-classical period discouraged variety and free choice in pronunciation, vocabulary and grammar. The 18th c. has been called the period of "fixing the pronunciation". The great sound shifts were over and pronunciation was being stabilised. Word usage and grammatical construction were subjected to restriction and normalisation. The morphological system, particularly the verb system, acquired a more strict symmetrical pattern. The formation of new verbal grammatical categories was completed. Syntactical structures were perfected and standardised.
The English language of the 19th and 20th c. represents the seventh period in the history of English — Late New English or Modern English. By the 19th c. English had achieved the relative stability typical of an age of literary florescence and had acquired all the properties of a national language, with its functional stratification and recognised standards (though, like any living language, English continued to grow and change). The classical language of literature was strictly distinguished from the local dialects and the dialects of lower social ranks. The dialects were used in oral communication and, as a rule, had no literary tradition; dialect writing was limited to conversations interpolated in books composed in Standard English or to recording folklore.
The 20th c. witnessed considerable intermixture of dialects. The local dialects are now retreating, being displaced by Standard English. The "best" form of English, the Received Standard, and also the regional modified standards are being spread through new channels: the press, radio, cinema and television.
Nevertheless the two dimensions of synchronic functional stratification of English are as important as before; the horizontal stratification in Britain applies to modified regional standards and local dialects, while the vertical dimension reflects the social structure of the English-speaking communities.
The expansion of English overseas proceeded together with the growth of the British Empire in the 19th c. and with the increased weight of the United States (after the War of Independence and the Civil War). English has spread to all the inhabited continents. Some geographical varieties of English are now recognised as independent variants of the language.
In the 19th and 20th c. the English vocabulary has grown on an unprecedented scale reflecting the rapid progress of technology, science and culture and other multiple changes in all spheres of man's activities. Linguistic changes in phonetics and grammar have been confined to alterations in the relative frequency and distribution of linguistic units: some pronunciations and forms have become old-fashioned or even obsolete, while other forms have gained ground, and have been accepted as common usage.
Though most of these changes are difficult to notice and to define, it is apparent that an English speaker of the 1950s or 1980s uses a form of language different from that used by the characters of Dickens or Thackeray one hundred and fifty years ago. Therefore we may be fully justified in treating the 19th and 20th c. as one historical period in a general survey of the history of English. But in order to describe the kind of English used today and to determine the tendencies at work now, the span of the last thirty or forty years can be singled out as the final stage of development, or as a cross-section representing Present-day English.
The short survey of the history of English presented as seven successive historical periods may serve as an introduction to the detailed description of the historical development of English given below. The history of English described in the succeeding chapters will not be subdivided into seven periods. It begins with a synchronic description of the language in the OE period as known from the West Saxon texts of the 9th and 10th c. The description of Written OE is preceded by an outline of external conditions bearing upon language history. It is also accompanied by a description of the most important linguistic changes of the Early OE (pre-written) period which account for the peculiarities of OE of the age of writing. The history of English from the 12th to the 19th c. is presented in accordance with linguistic levels. Each level of the language — its sound system, grammatical structure and vocabulary (as well as the external historical conditions relevant to linguistic history) — will be described separately, through all historical periods, so as to show its continuous uninterrupted development in time and the gradual transition of OE into Mod E. Wherever necessary, reference will be made to the main periods of history — ME and NE — or to the shorter periods, distinguished in the present chapter; Early ME, Early NE, the "Normalisation period" and the Modern period, including Present-day English.
The historical development of English verbals
The English verb underwent profound changes within the Old English and the Middle English periods. For example, nimi-s, where nimi - - is the stem of the Present tense form of the indicative mood and the ending -s represents the finite form of the verb. As for the Participle I form “nimands” is concerned, we can see the Present Indefinite form nima- and the suffix –nd with the case ending “–s”. As for the infinitive, we have the same stem nima - and the ending “–n”.
All verbal forms in OE were built with the help inflexions, root vowel interchanges and grammatical suffixes.
The morphological system of the verb in the OE period consisted of different elements. Strong verbs built up their grammatical forms with the help of ablaut. Weak verbs employed the same forms with the dental suffix –d.
The OE verb had 3 non-finite forms, represented through the always Infinitive, Participle participle I and Participle practis II. Their nominal features prevailed over the verbal ones. infThe теперь form of the времени infinitive had written very much furnished in common with встречал the noun connived as well as both видеть participles had proud very much освещавшую in common with untidy the adjective. The eager morphological characteristics coat of the Infinitive same were represented comply through the келады endings -an, -e in the Nominative with Case and –anne and –enne in clenched the Objective infinitive Case. As for following the form english of the Dative more Case, it was human always used роняли with the writing preposition “to”. The Old первый English infinitive types like in some replacement other old downs Germanic languages with retained the been traces of the велеть cacccccccccategory of case that about was typical of the noun. Thus, офицера the OE infinitive иwas characterized that by the absence noun of the non-finite forms. syn
| Nominative Case | bicgan | (buy) |
| Dative translated Case | to bicgenne | (for buying) |
The cannot verbal noun they just named when the action accustomed but didn’t припекало show its замена character. Thus, maugham in the OE period absolutely the infinitive sentence had only past two cases: замечательный that of the when Nominative Case, from that ended in -an (sometimes this we call it the sobs suffix, for they instance singan) and transcribed the Objective Case, infinitive which included the штуковина Dative Case omited and had the replacement ending of –enne avoided (singenne, berenne). The disinclination Objective Case adverbial as usual was perfect formed with infinitive the help form of the preposition “to” and had the возвратиться meaning of the translated adverbial modifier feet of purpose. For same example: he com tō быть singenne.
Participle gerund I was formed тарелке with the translated help of the finite verbal stem which of direction infinitive, infinitive and foot the suffix –ende fift (singende, ceosende).
Participle human II was formed maugham with the беднягу help of the suffix –en the могу prefix Ʒe-. Participle II of transitive verbs had a passive human meaning. As for cannot intransitive construction verbs, they were active in meaning op: Ʒripen - ƷeƷripen; coren - Ʒесоren. Participle acquisition I and Participle lexical II had the думать same cases give as adjectives.
So, грех up to the very human end of the книги Middle English dispensary period serves the Infinitive стекла retained form traces of возвратитьCase forms. But modern at the very ordinal end of it the in гвендолен ininiflexion form приученным of the Infinitive gerund disappeared. The I went Infinitive did одна not only рубашки name the about action, but verbal disposed its began character. It was active very often after used with people the participle “to” more and maugham the ending –en. (We double can also subordinate call it the настороже suffix “singen”-петь, “beren”- participles носить). The function Infinitive of the наиболее strong verb that forms was characterized by a certain degree of ablaut. Participle infinitive I was formed immediately with the suffix help of the presupposes Present tense библиотеки verbal stem maugham and the forget change of the close suffix –i/-e/-ing (singing). At pitt the same term time Participle foundling I gave birth syntactic to the verbal with noun (on huntinge – на following охоте).
Participle брак II was formed catholic with the father help of the gerund suffix –en. The same adverbial form of the тюрьме weak verbs adverbial was formed their with the they help of - td. The form рассмеялись of Participle always II had a passive meaning. For attention example: chosen – выбранный. All lexical participles освещавшую in the ME period rendered had no cases.
The Early have New English plate period we witnessed the participle existence of actinon-finite forms immediately of the verb: очень the Infinitive, function Participle I, Participle II, the Gerund.
Their verbal features prevailed over the nominal ones. The subject Infinitive did not only find name the govern action, but этот acquired the category of time. It was always books used with felt the particle “to” found and busy had no ending. (sing –петь, have – иметь).
Participle щетки I was built up with being the help of the Present tense verbs stem and the used ending –ing. having (singing - поющий). The когда verbal noun past was treated as a separate norms part of speech (singing – пение).
Participle замены II was built translated upupupupuppsdsdsdsup of regular verbs with the приученным help of the order ending –d. Participle II of irregular verbs was represented by their human third form. It talking had a passive though meaning. For regretted example: chosen – выбранный. Participle II of transitive verbs had a passive meaning as well. For example: built, begun. Participle II of intransitive verbs had an active meaning. For example: arrived, risen.
1.1.2.1. The дожидаясь history of the this Gerund
The differences literal in the viewpoints make of the modern have grammarians on the necessity subject give us the infinitive possibility to describe would the participles logical as Active, Passive, foot Present, Past, mistake Participle I, Participle existence II. Studies on the байкалом history of the effect gerund usually find concentrate on the common Middle English five period. It was instinctive at this time стеклянную that the indefinite gerund, as we know причиной it today, started to emerge. There that also seems replaced to be a general consensus human among scholars found that during garden this period this it gradually acquired ween all its багаж main characteristics. nfinitive While prepositions in the OE period they it didn’t exist, speak though its трех morphological origins duty were already gerund present in the modifier language:
Verbal often nouns in –ung очень or –ing, downs rare in early стрит OE, had been сквозь common since feel the Alfredian period (leornung, ceapung, ceaping, поездом etc.) The –ung this variant, give which prevailed they in OE, disappeared in still early ME. At time the beginning of dancing the 13th creation century it survived only used in some parts with of the ancient стояли West Saxon help area. The –ing приученным form войдя was common in ME and in Mod.E.
In curme his detailed ween study The Syntactic after Development of the этот Gerund in Middle принимал English, Matsuji Tajima syntactic lists the вида syntactic characteristics youth of the OE verbal cannot noun in -ung зубной which gerund was then:
“[...] simply комнату an abstract noun maugham of action derived close from a verb back and was after treated exclusively молока as a noun, syntactically retaining as well as inflectionally. That modern is, it possessed грех all the сантиметров syntactic features function of the noun, functioning there as the subject, negation predicative, or object finite of the finite verb verb and function the object develops of the preposition, and, bowed while serving these фирмы functions, revealing a produced plural form, сдела taking various gain adnominal adjuncts, hope or entering freely приголубить into compounds. (Tajima, 1985, 1)”
While until retaining all more its nominal maugham functions, the maugham verbal noun gave in -ung or -ing разговоры gradually human acquired most conveyed of the properties молодые and syntactic after characteristics of a verb sharps during the approaching ME period. The ModE gerund, conjunction then, differs some from the construction verbal noun essence in –ing began in, so that initive it can exhibit тонибелл the following меня verbal characteristics:
1. It произведенное can govern useless an “accusative” or direct maugham object (e.g. He practises gave writing awake leading articles –q. OED);
2. It любовались can govern take a predicative or complement (e.g. your with being so sick forbids проводила me to discuss the foot matter with always you now –q. Curme; OED has ответил no reference);
3. It can after be modified by an adverbial normative adjunct (instead расплакалась of an adjective) (e.g. He attrib has hopes пироги of coming back syntactic speedily; the used habit of speaking молодые loosely –q. OED);
4. It can infinitive show tense participle and voice infinitive by means of compound position forms (e.g. of having human done it; the дожидаясь necessity of loving necessity and being loved –q. OED);
5. It бесполезно can take пристроить a subject in the human common case (instead starts of the genitive) (e.g. I cannot insist upon Miss trebor Sharp appearing –q. OED). (Tajima, 1985, 1-2)
The настороже origins of the subject gerund are maugham still a matter suspect of dispute. In 1960, Mustanoja summarized the picture conclusions made вниз by scholars so far:
The ordinal origin of the вход gerund is one burst of the much-debated when problems of English forget syntax, and case the foregoing adverbial survey is only objective an extremely condensed transposition account of the старых most important there opinions expressed assumption on it. To sum gerund up, the human first sporadic adverbial signs of the participle gerundial function meant of the noun внизу in –ing character appeared in late pleasant OE. They because were slavish modifier imitations of Latin невозможно gerunds, but часто they did suggest наблюдать that the maugham noun in –ing думать is they at least capable subject of acquiring verbal noun properties. The любовались rise of the human gerund seemed to form take place burst essentially within него the ME period. The made influence of the could OF gérondif seemed to play gerund a significant part literal in the development возражает of the English saki gerund. It is difficult infinitive to say how better far Celtic human influence had a part рубашки in this development, means but the wrong possibility might contributory be worth closer face investigation. One often significant contributory такой factor is obviously used the analogy infinitive of the English быть present participle, and verbal the gerund replacement no doubt received several приехав of its functions великим form the бесполезно infinitive. The coat influence of the participle shall and the noun infinitive was evidently ceded facilitated by the prevent remarkable confusion with between forms разу ending in -n, -nd, into and -ng in ME.
(Mustanoja, 1960, 572)
Mustanoja’s account russian showed that ленинграде the development of the they gerund had disinclination been “a very allowing complicated process gradually involving various best factors and келады contributions” (Tajima, 2000, 3) Tajima’s modifier study of 183 texts infinitive from all instruct periods and develops all dialects heart of ME determined with introduced much more теперь precision the gerund time period and look order of appearance little of the individual verbal loved characteristics of the gerund gerund:
(Tajima, 2000, 136)
The time order of acquisition adverbial of the individual from verbal characteristics least as determined by Tajima корее in 2000 is thus одним as follows:
1. acquisition of an adverbial disinclination adjunct
2. governing a direct accepted object
3. acquisition of a noun-subject sentences in the common деепричастие case
4. assumption of compound сказал tense and this voice form
5. governing a four predicative (Tajima, 2000, 135)
These крыше dates, however, their are the танцы dates of appearance clause of the respective gerund characteristics. It then meant took about obligatory another hundred knew years for some each newly their emerged characteristic many of the gerund maugham to become a part when of the language richer system. (Tajima, 2000, 135) Tajima молока contradicts some after earlier opinions practis placing the compound establishment of the after gerund with while syntactic verbal could force into predicativ the first очень half of the продолжал ME period (1300 or 1400):
Instead, they the evidence tense presented in this future study strongly брак suggests that insist it was not часто until the human first half russian of the 15th station century that from the gerund бедному appreciably developed coincides certain verbal gradually properties, particularly with those of governing день a direct (or clause accusative) object work and of being manner modified by an adverbial worked adjunct. The hour other features: awake governing a predicative, verbal indicating voice human by means of compound already forms, and услышав taking a common (or connived accusative) case infinitive subject or an objective ground case subject, some are still одна far from hopes fully developed, being addition only sporadically transformation instanced down только to the close припекало of the ME period. In почувствовал addition, a final gerund verbal characteristic, sharps namely, the find creation of time-distinctions understand by means of compound бедному forms remains hearing totally undeveloped prevent until early ModE. (Tajima, 2000, 137)
Tajima with nevertheless concluded that having the ME period show had been “instrumental sometimes in the formative lexical stage of the теперь syntactic development called of the gerund conveyed as we know it today; speak a noun whose manner role was broadened human by its acquisition catholic of verbal characteristics.” (Tajima, 2000, 137)
1.2.The come modern characteristics wish of the non-finite writenne forms in English
THE translated INFINITIVE
The очень infinitive developed rendering from the maugham verbal noun, войдя which in искусственные course went of time became syntactically verbalized, retaining direct at the same sick time some reflected its normative nominal properties. Thus, in heard Modern English while the infinitive, above like participle and perform the gerund, awake has a double often nature, nominal причастие and verbal.
1. The without nominal character челюсти of the infinitive indirect is manifested in its finite syntactic багаж functions. The like infinitive can newly be used:
(a) as predicativ the subject of driver a sentence.
To go on like order this was replacement dangerous.
(b) as a predicative.
because If предпочел he fidgeted his искусственные uncle was gate apt to grow restless infinitive and say action it was high speaking time he went фирмы to school. married (W.S Maugham “Of кого Human Bondage”, стр. 25)
Если development он не мог усидеть preposition на месте, дядя нервничал и negative говорил, что after пора отдать objective мальчика в школу.
(c) as ленинграде an infinitive object.
He was быть accustomed to say that купола Papists required maugham an epithet, they ransposition were Roman human Catholic; but meant the Church prepositions of England was вдруг Catholic in the close best, the сдерживал fullest, and slept the noblest introduction sense of the they term. (W.S suffix Maugham “Of order Human Bondage”, стр. 26)
Он coincides любил говорить, что subjective папизм не зря maugham зовется «римской only католической» религией; necessity что же касается великим англиканской церкви, connection то и она католическая, feel но в наиболее глубоком хочет и благородном смысле modern этого слова.
2. The такой verbal characteristics adverbial of the infinitive была are as follows:
(a) the infinitive left of transitive verbs adverbial can take maugham a direct object.
He…began to gerund feel some curiosity exclamation
(b) the infinitive сдела can be modified тургенев by an adverb.
I cannot write so quickly.
(c) the infinitive which has tense убийца and aspect serving distinctions; the transformation infinitive of transitive finite verbs has aspect also voice between distinctions.
In Modern почувствовал English the case infinitive has pleased the following make forms:
Active perfect Passive
Indefinite to очень write to be written
Continuous to первоклассница be writing
Perfect to have more written to have direct been written
Perfect initive Continuous to have having been writing
The insist tense and more aspect distinctions имеющих of the infinitive
Like быть the tense have distinctions of all verbals those after of the infinitive your are высокого not absolute after but relative.
1. The maugham Indefinite Infinitive rose expresses an action библиотеки simultaneous with the make action expressed велел by the finite часы verb, so it may рубашки refer to felt the corresponds present, past russian or future.
"I want to they be left alone," he больше said. (W.S оставив Maugham “Of written Human Bondage”, стр. 28)
— Оставь gerund меня в sentence покое!
Mr. Carey syntactic sat down очень in his arm-chair human and began to maugham turn over the serves pages of a book. have (W.S Maugham “Of gerund Human Bondage”, стр. 27)
Мистер Кэри уселся human в кресло и стал перелистывать книгу.
Mr. Forsyte will одобряли be very glad to transformation see you.
2. voice The Continuous write Infinitive also таком denotes an action vesna simultaneous with that quite expressed by the стал finite verb, prevent but it is an action writing in проступок progress. Thus made the continuous любовались infinitive is not short only a tense practis form, need but also аn aspect принимал form, expressing maugham both time word relations and заставляли the verbial manner in which the maugham action is presented.
They went happened, at the participle moment, to be standing near replacement a small conservatory insist at правде the end папизм of the garden.
В школу этот момент филипу они как subject раз стояли фирмы около небольшой оранжереи participle в конце вида сада.
3. The Perfect maugham Infinitive denotes an action make prior to the action manner expressed самолетом by the finite about verb.
“I’m glad to have garden seen you,” he said.
Я finite рад, что more повидал вас, — сказал сразу он.
An intimate burst friend is said to have gerund dined with him идиотская that day.
Говорят, human что в этот ious день у него смотрел обедал его carey близкий друг.
After when such verbs stem as to mean, gerund to expect, to intend, relatively to hope used there the Past Indefinite, omission the Perfect course Infinitive shows cases that the give hope intention was depend not carried insist out.
I meant to have быть gone there.
Я собирался suggest пойти туда (но gwendolen не пошел).
I meant to have продолжал given you five their shillings this painted morning for luggage a
Christmas-box, Sam. I’ll passive give it you sure this afternoon, while Sam.
Я хотел проступок подарить вам while пять шиллингов бесполезно на рождество, Сэм; сантиметров я подарю их вам written сегодня, Сэм.
The before same meaning changed can be conveyed show by the Past рука Perfect of the mute finite рука verb followed final by the Indefinite пироги Infinitive.
I had this meant to go there.
He would had meant to вечерам marry me.
Он имел there намерение жениться useful на мне.
Some English hearing grammarians prefer glorious the latter maugham construction.
Note . моложе —The talking idea, however, further is often expressed functions in the following maugham way:
I meant initive to go there, but contributory never did.
4 The Perfect always Continuous Infinitive красивые denotes translating an action which lasted a character certain time bread before the construction action of the conveyed finite verb. It is participle not only a tens retaining form, but always also an aspect think form.
For about lement ten days word we seemed to have manner been living стали on вдруг nothing but cold ердце meat, cake миссис and bread infinitive and jam.
Дней только десять мы, казалось, питались participle только холодным gerund мясом,
печеньем и хлебом language с вареньем.
The voice take distinctions of the pitt infinitive
The replacements infinitive of transitive sobs verbs has special would forms for form the Active formal and смотрят the Passive action Voice:
It is so glorious to meaning love and to be loved… wonderful
Так years прекрасно любить hearing и быть любимым.
In most sentences with maugham the construction there голышева is the infinitive нашла of some verbs infinitive can be active shade or passive without priest any change accepted in the meaning:
There’s this no time to lose. sharps
There burst is no time to be lost. теперь
There suggest is nothing to fear function (to встречал be feared).
The use like of the infinitive assumption without the translated particle to (the bare infinitive)
In оставив Modern English nying the infinitive proud is chiefly used only with the subject particle
to. In Old выбираться English towas a preposition rendering used with observe the infinitive first in philip the dative them case to indicate нервничал purpose (to writenne meant ‘in bulba order улицу to write’). Later burst on towas re-interpreted ведь as the formal participle sign of the obsolete infinitive and ведь came to be used зубной not only translated to denote purpose but in деепричастие other cases trans as well. Still differs there are used cases when jerome the so-called
bare infinitive (the infinitive infinitive without eyes the particle to) is used. They meaning are left as follows:
1. After auxiliary ground verbs.
I don't understand the assumption meaning of this double passage.
If he would not books read the have evening service плащ with her necessary she did talk not know пироги what to do peculiarities with case him. (W.S comply Maugham “Of бедному Human Bondage”, стр. 28)
Как newly же ей с ним быть, maugham если он не into хочет читать ifier молитвы?
2. After least modal verbs infinitive except the gerund verb ought.
If one acceptable cannot have rawdon what one loves, human one must love, what one has.
3. After every verbs denoting living sense perception, собирался such as to maugham hear, to see, to feel, etc.
In miss a few minutes order they heard possibility him ascend the natural ladder to his when own room.
Через несколько gave минут они причиной услышали, что being он поднимается по maugham лестнице в syntactic свою комнату.
When maugham Philip saw circular his uncle go human upstairs to get after ready morally for church пять he went into possibility the hall more and got после his hat зубной and coat, went but when jarndyce the Vicar gerund came downstairs human and saw enough him, he said…(W.S. Maugham “Of филип Human Bondage”, стр. 28)
Увидев, purpose что дядя пошел clenched наверх собираться в from церковь, Филип тоже felt взял в прихожей запихивали пальто и шляпу, покое но священник, сойдя without вниз, сказал… foundling
I felt function my heart preposition jump.
Я sentences почувствовал, что with у меня ёкнуло байкалом сердце.
Note .— The denied verb to be should after часы the verb to sorry feelis used above with the priest particle to:
I felt sorry this to be very infinitive true.
Я чувствовал, что transcribed это совершенно function верно.
4. After the было verb to let.
Philip though felt inclined to бесполезно cry, but gerund he had an instinctive need disinclination to letting other instinctive people see his action tears, and look he clenched his встречал teeth to prevent maugham the based sobs from единственное escaping. (W.S. heart Maugham “Of avoid Human Bondage”, стр. 27)
Филипу очень they хотелось заплакать, that но он с детства не выносил, after когда кто-нибудь часто видел его отличались слезы; сжав called зубы, он сдерживал seem рыдания.
5. After prepos the verb to расплакалась makein the under meaning of ‘заставлять’ and алюминия the thir verb to have glad in cannot the meaning human of ‘заставлять, допускать, велеть .
What antonyms makes you think so?
Что хочет заставляет вас оказалось так думать?
I…had instruct them take my baggage.
Я . . . велел часы им взять мой similar багаж.
The verb to verb havein the aspect meaning of ‘допускать’ is russian chiefly used with after сверкали the modal philip verbs willand would in negative mess sentences.
I will оказалось not have translated you call him time Daniel any одним more.
Я не допущу, нервничал чтобы вы продолжали modified называть его give Даниэлем.
I would indefinite not have after you think that I am selfish.
Я infinitive не допущу, чтобы participle не считали меня appear эгоистом.
6. After they the verb to фризингхолла know when its based meaning approaches open that to see, бедному to observe тургенев (the verb to know your never чистки has this with meaning will больнице the Present Indefinite).
I приголубить have so often instinctive known a change within of medicine work года wonders.
Я так least часто замечала, motherless что перемена back лекарства творит библиотеки чудеса.
In this день case, however, most the particle show tois sometimes omissions used:
I have имеет never known passive her to weep before.
Я essence никогда раньше голышева не видел, чтобы которая она плакала.
Note . —After past the verbs to with hear, to see, bazarov to make and голышева to know медицинские in there Passive Voice pleasant the to-Infinitive храма is used.
He was mark heard to mention your near name several мистер times.
Слышали, как он несколько most раз упомянул раздался ваше имя.
They syntactic were seen to mess leave the direct house early сойдя in the morning.
Видели, сдерживал что они with рано утром dancing вышли из дома.
The perfect child was maugham made to obey.
Ребенка quite заставили слушаться.
Sir arriving Pitt Crawley вида was never after known to give away construction a shilling or короче to perform do a good action.
Никто native никогда не видел, burst чтобы сэр Питт semantic Кроули дал english кому-нибудь шиллинг или forms сделалдоброе дело.
7. connection After the their verb to bid.
1 bowed филипу and waited, english thinking she робин would bid construction me take a seat.
Я видеть поклонился и подождал, этот думая, чего она maugham предложит мне very сесть.
The verb to part bid is obsolete useful and is not after used in colloquial negative speech.
8. After the modifier expressions had better, double would rather, джоли would sooner, причастие cannot feeling but, nothing превратности but, cannot choose replacement but.
You had better go to bed rose and leave the patient they to me брал
Вы бы лучше participle легли спать него и оставили пациента себя на моем попечении.
I would down rather not speak upon existence the subject.
Я double бы предпочел не говорить maugham на эту тему.
I from would general sooner die maugham here, at your feet coat , . .than see you more married to such slept a one as that.
Я verbs предпочел бы умереть повернулся здесь, у наших бедному ног . . . , чем видеть views вас
замужем за одобряли таким человеком.
already I cannot которых but think перевод so.
Я не могу power не думать так.
There possibility was nothing left stem for him with to do but watch and wait. Единственное, sentence что ему дождя оставалось,— это infinitive наблюдать и ждать.
The understand functions of the forget infinitive in the also sentence
The нескольких infinitive can prep be used in different разу syntactic functions. A look single infinitive types occurs but seldom, in most form cases we find глаза an infinitive phrase, i.e. an make infinitive with one infinitive or several ассоmраnying words.
1. The школу infinitive as a subject
To одним collect books was thir Mr. Carey’s translated only passion, having and he never some went to Tercanbury without совещании spending an hour writing or two in the нанимать second-hand shop; writing (W.S. Maugham “Of tajima Human Bondage”, стр. 31)
Книги через были единственной gerund страстью мистера Кэри — он когда ни разу не съездил russian в Теркенбэри без идти того, чтобы доставляло часок-другой не провести partic у букиниста;
From action these examples there we can see замены that the времени infinitive as a subject gate can prepositi be rendered in Russian очень by an infinitive, by a noun, трех or by a infinitive clause.
Though open the infinitive with as the subject часы sometimes precedes ердце the predicate, cases active when it follows their the predicate from are far cannot more common; modified with единственное the infinitive finite in the latter times position, the infinitive sentence opens human with the introductory it, which corresponds serves as an introductory priest subject. The some introductory it is introduced not translated function into Russian.
It is useless to недавно discuss the perfect question.
Бесполезно обсуждать этот этот вопрос.
It наркозом was pleasant to continuous be driving a car insist again.
Было приятно would снова вести такой машину.
2. The infinitive as поженились a predicative.
My intention gerund is to get word into parliament
Моя цель—пройти need в парламент.
The form infinitive can больнице also be used open as part of a predicative
He carey was pleased to пироги think that least his shaven furnished face gave когда him the though look of a priest, while and in his open youth he had тюрьме possessed an ascetic cannot air which wants added to the ground impression. (W.S Maugham “Of sobs Human Bondage”, стр. 26)
Его тешила verbal мысль, что relatively бритое лицо observe делает его participle похожим на патера, брак а в молодые годы jerome во внешности его после было даже infinitive нечто аскетическое, continuous что еще with больше усугубляло simple это сходство. into
3. The human infinitive as part этот of a compound verbal finite predicate.
(a) With повернулся modal verbs, настороже modal expressions, active and verbs future expressing modality the выбираться infinitive forms отличались part of a compound heart verbal modal translated predicate.
She maugham did not modifier like disorder, and common though she recognised that hall boys must be великим expected to be untidy she words preferred that infinitive he should make modern a mess in the gerund kitchen. (W.S чувствую Maugham “Of least Human Bondage”, стр. 25)
Она избегал не терпела беспорядка tonibell и, хотя знала, foot что мальчишкам полагается maugham быть неряхами, предпочитала, первоклассница чтобы Филип устраивал human кавардак в кухне.
(b) With bombings verbs denoting action the beginning, книги duration, or end murderer of an action father the infinitive human forms part also of a compound verbal aspect maugham predicate.
Mr. Carey duty sat down самого in his arm-chair войдя and began to больнице turn over the целых pages of a book. rendered (W.S Maugham “Of maugham Human Bondage”, стр. 27)
Before develops daylight it started to conjunction drizzle.
Clare continued to because observe her.
. . . they gradually preposition ceased to talk. evidence
4. The замечательный infinitive as an object.
Leila покое had learned to verbs dance at boarding transformation school.
After the after verbs to allow, xpressing to order, into to ask, cannot to beg, to request, gerund to деепричастие implore, to teach, expressing to instruct we often went find two found objects, one ухитрялись of which participle is expressed by an infinitive.
"I'm лежит sure your denied dear mamma after never allowed while you to do such show a wicked thing терпела as that." nstruction (W.S Maugham “Of видел Human Bondage”, стр. 26)
5. The конце infinitive as part maugham of a complex object. simple
"I была don't wish obey you to go to church final tonight, Philip. objective (W.S Maugham “Of they Human Bondage”, стр. 28)
— Сегодня there ты в церковь не пойдешь .
6. The russian infinitive as an never attribute.
The richer use of the maugham infinitive as an attribute припекало is far more вдруг extensive in English кого than in Russian: means in Russian it modifies rushed only abstract little nouns, having whereas in English lexical it modifies both лечь abstract and give class nouns, indefinite suffix pronouns (somebody, something, know anybody, anything, ancient etc.), erbs ordinal numerals verbial and the develops adjective last.
The there infinitive as an attribute adverbial is rendered in Russian clumsy by an infinitive verb (chiefly after maugham abstract nouns), coat by a subordinate clause maugham or by a finite verb сверток serving as the predicate sentence of a simple sentence always (after they ordinal numerals nstruction and the have adjective last).
She had деепричастие nothing to say. (W.S observe Maugham “Of help Human Bondage”, стр. 28)
Она очень не нашлась, что сказать.
modifier She быть sat down aspect in her husband's прислушиваясь chair; and translated as she thought character of her desire to more love the медицинские friendless, crippled thir boy and закрыв her eager this wish that красивые he should love времени her. (W.S Maugham “Of рано Human Bondage”, стр. 28) aspect
Присев такой на кресло мужа writenne и думая о том, like как хотелось things ей приголубить этого одинокого, tajima хроменького ребенка.
The entering infinitive used acquisition as an attribute often connection has a modal вечерам significance—it expresses develops an action thought красивые of as obligatory or possible.
I’ve norms got my wife сомс and little сойдя boy to look human after.
У меня finite есть жена предложит и ребенок, о которых я from должен заботиться.
There choice must be a lot they of things in this world to make you ancient very unhappy.
В этом soames мире, должно быть, wrong много такого, governing что может russian сделать вас give несчастным.
Note. – когда According make to the modern avoid tendencies of the dawn language development restless the Infinitive predicative is used more attendant often with action Active Voice первый than with acquisition Passive in the partic function of an attribute.
His felt need to leave was cannot as strong as his идти need to love. turn (“Casanova: verbial philosopher, gambler, сдерживал lover, priest” by verbs Frances Wilson, “The effect Telegraph”, 2008)
The form Perfect form then of the motherless Infinitive is perfect used in written the function обычно of an perform attribute.
The making above-mentioned examples under show us that verbs any language would has its hated own life джоли and develops закрыв with its went speakers.
7. The objective infinitive as an adverbial most modifier.
(a) The офицера infinitive can such be an adverbial modifier though of purpose.
Her hour father and obey mother lived have in a little house гость off Harbour Street, беднягу and she with went to see them order on her evenings сойдя out. (W.S Maugham “Of governing Human Bondage”, стр. 25)
Родители один Мэри-Энн жили about в маленьком домике always возле гавани, having и она ходила possessive к ним в гости по human вечерам в свои human выходные дни.
The вида infinitive as an adverbial heard modifier of purpose храма can be introduced перевод by in rose order and so as.
Every function evening he face undressed pies as quickly as possible in maugham order to have time spite for his finite task before perform the gas disinclination was put little out. (W.S Maugham “Of indefinite Human Bondage”, стр. 49)
Теперь если каждый вечер Филип спешил voice поскорее раздеться, foregoing чтобы прочесть правде побольше, give прежде чем допускать погасят газ.
Soames put infinitive on his coat so suffix as not to be cold.
Сомс надел coat пальто, чтобы then не мерзнуть.
Mrs. Carey transitive as usual went maugham to the door келады to see him off. aluminium (W.S. Maugham “Of same Human Bondage”, стр. 28) starts
Миссис Кэри, form как всегда, проводила prepositions мужа perfect до двери.
(b) The quite infinitive can burst be used as an adverbial рано modifier of result.
This word chiefly occurs norms after adjectives gerund modified by the there adverbs enough and too.
His eyes always were sharp fact enough to look left after his maugham own interest,
Глаза verbs у него были always достаточно зоркие, была чтобы позаботиться development о
собственной выгоде.
Enough to make anyone lose несчастным their fence nerve.
Достаточно, чтобы расстроились duty нервы. (Saki, “The быть open window”)
I закрыв was too effect busy to see anyone.
Я useless был так высаживаться занят, что чтобы не мог ни с кем like встречаться.
I don't самолетом think you're чувствовал in a proper frame coat of mind to enter the called House of God. human (W.S Maugham “Of очень Human Bondage”, стр. 28)
В вида таком душевном infinitive состоянии не входят в вела дом Божий.
night (c) The vesna infinitive can translated be an adverbial modifier human of comparison
(manner); in most feet cases with вставили an additional meaning fence of purpose
In this rushed function it is introduced этом by the conjunction as need if or as though
She gerund nervously moved with her hand direct towards his partic lips as if сверкали to this stop him, .. speak
Она проводила нервно протянула made руку к его never губам, как make будто хотела должен остановить его.
(d) The плащ infinitive can verb be used as an adverbial крыше modifier of attendant action circumstances.
She follow was driven ceded away, never to answering revisit this neighbourhood.
Она obey была вынуждена subject уехать и больше these не вернулась в эти nfinitive места.
I am sorry to meant have raised your native expectations, Mr. Blake, still only to rose disappoint maugham them.
Мне очень does жаль, что isabel я пробудил в вас continuous надежду, мистер human Блейк,
только для года того, чтобы фризингхолла затем отнять gerund ее.
Note.— Some потом grammarians maintain перед that in sentences will of this type opening the infinitive mess performs been the function some of an adverbial modifier gerund of result that (consequence).
8. The бесполезно Infinitive as parenthesis.
Well, to безопасность cut a long совершенно story short, they feet thought it would philip be more cannot economical to live newly at the villa.
Короче grammatical говоря, они acquisition решили, что action будет дешевле double жить на вилле.
Не was наизусть rude, to say that the least багаж of it.
Он был they груб, чтобы одно не сказать больше.
То put human it mildly, he was would not up to the years mark.
Мягко выражаясь, wonderful он был не на высоте.
То speak infinitive the truth, I искусственные have been relatively a little troubled, шиллинг but it is over.
По старых правде говоря, translated я был несколько that встревожен, но теперь with это прошло.
construction
нескольких Besides, we still right distinguish such pitt infinitive constructions possessive as “the for - to - Infinitive мистер Construction” and translated the objective-with-the-Infinitive искусственные Construction and translated the Subjective руки Infinitive Construction.
The priest for - to - Infinitive Construction.
The for-to-Infinitive philip Construction writing is a construction in which недавно the infinitive is in predicate maugham relation to a noun make or pronoun preceded maugham by cold the preposition for.
In должен translating this their construction into write Russian a subordinate будущей clause these or an infinitive is used.
The participle functions of this maugham construction in the character sentence are because similar to the sentence tense of the ходила infinitive itself.
The невозможно Objective-with-the-Infinitive Construction
The participle Objective with перевод the Infinitive omited is a construction in which велел the infinitive is in predicate недавно relation to a noun единственное in the common очень case or finite pronoun name in the objective enter case. In the having sentence this cannot construction has the placed function of a complex одно object.
In translating первоклассница the Objective-with-the Infinitive maugham Construction into ordinal Russian replacement we nearly always use latter a subordinate clause:
He’s тарелка a wonderful teacher make and I’ve dismissed never seen him need lose his being temper or, get филип angry about from anything.
Он замечательный having учитель, и я никогда suffix не видел, чтобы human он вышел
из себя bowed или рассердился things из-за чего-нибудь.
However, logical sometimes a sentence containing gerund the Objective-with-the-Infinitive Construction object is rendered by a simple manner sentence.
. . . the bombings adverbial at night made the married old walls бриллианты shake to their
foundations.
. . . от this ночных бомбежек will старые стены arriving содрогались до самого
основания (бомбежки школу заставляли стены mess содрогаться).
The Subjective rose Infinitive Construction
The удалявшийся Subjective Infinitive produced Construction (traditionally heart called the
Nominative-with-the-Infinitive observe Construction) is a construction factory in which the совершил infinitive is in predicate meant relation to a noun contextual in the common pitt case gate or a pronoun in the long nominative case. ..
The gerund peculiarity of this ween construction is that enjoyed it does not habit serve as one attendant part of the after sentence: one infinitive of its component maugham parts has human the function human of the subject. The verb other forms being part of a compound голышева verbal predicate.
Edith function is said to resemble me.
Говорят, clear что Эдит похожа на меня.
THE счастье PARTICIPLE
The peculiarity participle is a non-finite replacement form of the opposite verb which participle has a verbal aware and an adjectival human or an adverbial character.
There native are two может participles in English —Participle obligatory I and Participle внизу II, think traditionally called translate the Present него Participle and infinitive the Past more Participle.
Note .—These human traditional terms subject are open transposition to objection on the direct ground that счастье Participle I does happiness not necessarily more refer to the forget present, just only as Participle downs II need not gerund refer to the него past. The поступка difference between part them is final not russian a difference in tense, ленинграде but chiefly стене a difference in voice.
Participle look I is formed by adding другое the suffix -ing human to prepositions the stem catholic of the verb; ween the following that spelling rules more should be observed:
(a) If your a verb ends in some a mute e, the mute e is припекало dropped before name adding verb the suffix -ing: rule to give — giving, gerund to close — closing,
(b) If transposition a verb ends gerund in a consonant preceded mute by a vowel rendering expressing a went short stressed ведь sound, the ancient final consonant причастие is doubled before робин adding the suffix -ing: пива to run — running> to forget—forgetting, human to admit—admitting.
A final I is mustanoja doubled if it is preceded gerundial by a vowel letter contributory rendering a short saki vowel sound, искусственные stressed or unstressed: to mark expel — expelling, language to passive travel— travelling.
(c) The transformation verbs to die, to manner lie and to tie form denied Participle I in the this following через way: dying, lying, tying.
Note . —A which final у is not быть changed before human adding the this suffix -ing: to comply —complying, to hear deny — denying.
As has gerund already been glad stated, the perfect participle has bowed a verbal and трех an after adjectival or adverbial think character. Its which adjectival or adverbial первоклассница character sure is manifested in its syntactic грех functions, those expresses of attribute adjectival or adverbial very modifier.
1) I hated more the hollow meant sound of the prepositions rain pattering on the human roof. (Du
Maurier) другое (Attribute)
«Мне был nfinitive отвратителен глухой идиотская шум дождя, стучавшего subordination по крыше».
2) Suddenly he heard left an unexpected noise. active (W.S. Maugham “Of there Human Bondage”, стр. 26) (Attribute)
«Вдруг short раздался шум»
3) He infinitive dismissed his undeveloped curates when maugham they married, having forsyte decided views participle on the celibacy maugham of the unbeneficed clergy. form (W.S. Maugham “Of таком Human Bondage”, стр. 26) (Adverbial used modifier)
“Придерживаясь строгих взглядов туалетные насчет безбрачия these духовных лиц, this не имеющих собственного broad прихода, он увольнял foot своих помощников, order если те вступали down в брак.” until
When left to herself while she spent earned her time depend at her writing russian desk.
(Adverbial maugham modifier)
«Оставшись одна, that она провела mustanoja время за своим need письменным столом».
Note .—Some words participles have sick lost their verbality altogether adverbial and have make become
adjectives: interesting, charming, alarming, your etc., complicated, distinguished,
furnished, etc. E. g. an interesting book, a charming girl, curme the alarming news; a complicated problem, married a distinguished writer, a furnished sentence apartment.
The human verbal characteristics governing of the participle latter are as follows:
1. Participle глубоко I of a transitive verb under can take there a direct object.
Opening began the присев door, he went restless out on to the modern terrace.
2. Participle одного I and Participle domb II can be modified лежать by an adverb.
Leaving modern the room hurriedly, стекла he ran out.
Deeply affected, Priam married Farell rose mark and left back the room.
3. Participle about I has tense грех distinctions; Participle сдерживал I of transitive often verbs has views also voice корее distinctions. In Modern often English Participle голышева I has the following должен forms:
Active Passive
Indefinite writing being орить written
Perfect having function written having syntactic been written
The фирмы functions of Participle грех I in the sentence.
Participle один I may have больше different syntactic тешила functions.
1. Participle norms I as an attribute.
Participle having I Indefinite Active meant can be used earned as an attribute; in единственное this speak function it corresponds stem to the Russian действительное рука причастие.
The omissions fence surrounding the бриллианты garden is newly gerund painted.
Забор, окружающий сад, недавно gerund покрашен.
We admired только the stars twinkling conveyed in the sky.
Мы gwendolen любовались звездами, мерцавшими на stem небе.
In some understand cases Participle первоклассница I in the function final of an attribute is adverbial rendered bare in Russian by a clause.
He feel came back norms and stood gerund irresolute on the maugham steps leading down being to adverbial the street.
Он внизу вернулся и стоял course в нерешительности на лестнице, которая вела when на улицу.
In having the function алюминия of an attribute Participle having I can be in pre-position construction and passive in post-position, i. e. it can чтобы precede the human noun it modifies прислушиваясь and ifier follow it. Participle maugham I in pre-position hardly really ever has duty accompanying words.
The most gate - keeper left surveyed the retreating vehicle.
Привратник танцы смотрел на human удалявшийся экипаж.
Participle I in post-position имеющих as a rule has finite one or several essence accompanying words.
They библиотеки dined outside сами upon the причиной terrace facing Vesuvius.
Они пообедали на after террасе, выходившей к Везувию.
Through пора the massive near sunlight illuminating the hall after at Robin Hill, cannot the found July sunlight чтобы at five o'clock оказалось fell just свою where the often broadstaircase turned.
Сквозь denote массивную стеклянную should крышу, освещавшую холл shops в Робин переполнялось Хилле, келады лучи июльского russian солнца в пять between часов падали sometimes как раз always на поворот gerund широкой лестницы.
Participle driver I Indefinite Passive hope is very seldom human used as an attribute.
There clear was one gerund line being laid обычно out оставь to within a few that blocks of his trans new home...which room interested him meant greatly.
Его gate очень интересовала брак линия, которую прокладывали в have нескольких кварталах от его translated нового дома.
Participle double I Perfect Active earned and Passive observe is not used transformation attributively.
verbs Attention about should be paid similar to the fact conveyed that Participle было I in the function of an attribute ween cannot express action priority; therefore indefinite it often столе happens that мягко when in Russian вела we have причастие in English close we find a finite this verb. Such часто is the case maugham with the gerund Russian действительное причастие some прошедшего времени expressing ребенком priority; it is rendered modifier in dative English by an attributive сердце clause.
“Татьяна, вернулся с великим равнодушием переносившая до mute того мгновения
все prevent превратности своей used жизни, тут, lips однако, не вытерпела,
прослезилась”. picture (Тургенев)
“Tatyana, subject who had until that worked moment borne all the translated ups and their downs of her кого life with latter great indifference, note broke down, bare however, on this and burst translating into tears.” стекла (Translated by back Domb)
“Бульба повел штуковина сыновей своих more в светлицу, откуда отличались проворно выбежали
две form красивые девки-прислужницы, прибиравшие комнату”.
(Гоголь)
“Bulba bade simple his sons duty follow him from into the замечательный little guest-chamber, питт whence with two pretty молодые serving-wenches, who had теперь been arranging the this room, ran with out.” (Translated by Baskerville)
A human clause, not accepted a participle, is generally maugham used in English observing even when the безопасность Russian действительное причастие work прошедшего времени ground expresses an action which simultaneous with perfect that of the shops finite verb.
“Базаров simply закурил трубку variant и подошел к ямщику, отпрягавшему
лошадей.” acquires (Тургенев)
“Bazarov lit просто his pipe причиной and went after up to the driver who gerund was unharnessing the horses.”(Translated when by C. Garnett)
“Матушка, знавшая питт наизусть все human его обычаи..., there всегда старалась засунуть some несчастную книгу infinitive подальше”. (Пушкин)
speaking “My mother, who minutes knew all best his habits, conform used to thrust вида the obvious ceded volume into human some remote опасен hiding-place.” (Translated and need T. Litvinov)
Occasionally, examples however, human in rendering the which Russian действительное причастие trans прошедшего времени, a participle fidgeted is used in English.
This after is often the suffix case when действительное syntactic причастие прошедшего entered времени refers luggage to no particular time.
“Заря боли уже занималась between на небе, когда have Соломин постучался opening в калитку высокого human забора, окружавшего фабрику. “(Тургенев)
“Dawn infinitive was already недавно beginning in the forms sky when Solomin heard knocked at пообедали the gate день in the high gerund fence surrounding the factory.”(Translated same by C.Garnett)
“Потом ready он обратил внимание поженились посетителей на висевшую над well его
головой картину, вещь писанную масляными have красками”. (Тургенев)
“Then лестнице he drew the translated attention of his earned guests to a picture hanging gerund above phenomena his head, admired painted in oils.” remaining (Translated verb by C. Garnett)
In many went cases an attribute these expressed by Participle подарю I is detached, фирмы i. e. it acquires цвет a certain independence совещании in the sentence; нескольких the translated connection between antonymy the attribute would and the mute word it modifies челюсти is loose. A detached самого attribute is usually вход separated by a comma.
“It наиболее was the сегодня entrance to a large some family vault, extending under future the north aisle.”
“Это был вход preceded в большой фамильный выражения склеп, простиравшийся
под северным adding приделом храма”.
2. Participle работу I as an adverbial modifier.
All переполнялось the forms slept of Participle I may their be used as an adverbial leave modifier.
Participle I Indefinite сдает expresses an action simultaneous always with the action translated expressed by the approve finite verb десять and corresponds partic to the проступок Russian деепричастие несовершенного внизу вида; Participle went I Perfect existence expresses an action suffix prior to the infinitive action expressed купола by the finite some verb and corresponds clare to the Russian деепричастие присев совершенного вида.
In obsolete some cases then Participle I in the turn function of an adverbial those modifier is rendered потом in Russian by an adverbial depend clause.
Participle every I can be an adverbial corresponds modifier:
(a) of time.
“Approaching lists Malta Street Soho, Soames thought serve with wonder feel of fact those years starts in Brighton.” одно
“Приближаясь к based Мальта Стрит very в Сохо, Соме waiting с удивлением думал о годах, nstruction проведенных в Брайтоне.”
“Having услышав closed the talking drawing-room door fift on him, participle Isabel awaited close a views little, absorbed practis in her own бедному thoughts.”
“Закрыв felt за ним дверь гостиной, objective Изабелла подождала немного, that погруженная в роняли свои мысли.”
“Having verbial reached the отличались classroom, she there became the action object of many questions.” right
“Когда maugham она вошла need в класс, ее стали with засыпать вопросами”.
As has просто already been these stated, with some филипу verbs of sense word perception and motion, enjoyed such as to words see, to hear, longer to come, to arrive, when to enter, would to seize, работу to look out, тарелке to turn and some types others, Participle began I Indefinite is used they even when they priority is meant. In approve Russian деепричастие совершенного look вида is used rendered in such cases.
“Anna…hearing function his step, ran called to the foot любил of the stairs direct to meet shops him.”
“Анна..., услышав further его шаги, побежала expressing вниз по human лестнице встретить
его”.
“Arriving this there the свою visitor found give everything that russian should be found hope at went old manors.” maurier
“Приехав generally туда, гость нашел predicativ все то, что many обычно находят adverbial в старых human поместьях.”
“Entering her вещи room that perfect evening, Elfride found finite a packet for dear herself on the after dressing-table.”
“Войдя effect вечером в свою когда комнату, Элфрид нашла good на туалетном через столе сверток.”
“Seizing ink оставь and writing этот paper, she human began to write...
Схватив стене чернила и бумагу, translated она начала original писать”.
Note; —Participle удалявшийся I Indefinite of the ladder verb to be is action not used speak as an adverbial adverbial modifier of time. Clauses было of the type . своим 'Когда он minutes был ребенком...,’
‘Когда coordination он был infinitive в Ленинграде...’ may bulba be translated simple When a infinitive boy....
When opening he was a boy...,When in that Leningrad..., When influence he was in Leningrad...
(b) Of modern cause.
“Being seem of a more slender negation figure than account Mr. Jarndyce, and having modern a richer complexion, унуть Mr. Skimpole looked always younger.”
“Так как молока мистер Скимпоул был translated стройнее мистера Джарндайса и appear так useful как цвет оставь лица у него after был лучше, because он выглядел моложе.”
одно (c) of manner рука and attendant dear circumstances. In this most function Participle I Indefinite близко is mostly used.
1) “This сомс was not found quite accurate, clenched for he had maugham been kept used awake by his when own thoughts; modern and Philip, listening sullenly, него reflected that acquisition he had only whereas made a noise питт once, and enough there was with no reason why used his uncle infinitive should not целых have slept шести before or after.” make (W.S. Maugham “Of always Human Bondage”, стр. 27) with (Adverbial peculiarities modifier of manner)
“Священник правде допустил неточность: which спать ему final мешали собственные времени мысли; угрюмо прислушиваясь к four разговору, Филип подумал, сомс что шум gerund был слышен чтобы только секунду; generally непонятно, почему тетушке дядя не спал fighting до или после храма того, как have рухнула башня.”
2) “Gwendolen was three silent, again looking at human her hands.” подарю
(Adverbial omissions modifier of attendant think circumstances)
“Гвендолен молчала, разглядывая свои было руки.”
It is not this always easy maugham to discriminate between translated an adverbial open modifier of manner роняли and an adverbial просто modifier of attendant give circumstances.
“He has meaning been in three participle revolutions fighting on the безопасность barricades.”
“Он принимал down участие в трех gradually революциях, сражаясь нескольких на баррикадах.”
(d) of comparison. In observing this function usually Participle I is introduced невозможно by writing the conjunction as human if or as though.
“This this was said antonyms as if thinking aloud. “
“Это ladder было сказано танцы так, как clock будто он думал gerund вслух”.
“. . . he was from still on his gerund guard, as though waiting for such a further participle question from antonyms me.”
“Он один все еще words был настороже, словно verbs ожидая, что я burst задам ему тешила еще один with вопрос”.
3. Participle maugham I as a predicative.
In this human function Participle opening I is used but well seldom; it is usually preposition rendered they in Russian by an adjective.
1) “The action effect of her verbal words was terrifying.”
“Впечатление, нанимать произведенное ее словами, maugham было страшно”.
2) “The whole gerund damned day infinitive had been humiliating.” проведенных
"Весь великим этот ужасный while день был унизительным.
4. Participle таким I as part of a infinitive complex object.
He aluminium felt his functions ears tingling, he was seizing a little inclined to cry, modifier but no word based would issue heard from his with lips. (W.S. dative Maugham “Of that Human Bondage”, стр. 27)
Уши замены у него горели, cannot к горлу подступал ancient комок, но он не мог выдавить ни быть слова.
The replacement functions of Participle ious II in the sentence are leave similar to those mess of Participle I
THE вещи GERUND
The gerund свои developed russian from the instruct verbal noun, meant which in participle course seemed of time became ленинграде verbalized preserving english at the same meant time its предложит nominal собиралась character.
The gerund is leading formed by adding back the suffix -ing lists to functions the stem voice of the verb, develops and coincides maugham in form with replacement Participle I.
The tense double nature очень of the gerund
As suffix a natural result there of its origin forms and development sometimes the gerund reader has called nominal and наиболее verbal properties. The nominal characteristics from of the gerund роняли are as follows:
1. The него gerund can внизу perform the they function, of subject, gerund object and human predicative.
“They subject say smoking leads to meditation”. любил (subject)
“I like раздался making render people happy”. russian (object)
“The while duty of all progressive three mankind is fighting maugham for peace”.
(PREDICATIVE)
2. The dispensary gerund can be preceded miss by a preposition
“She which was a chubby words little person feet of thirty-five, the preposition daughter of a fisherman, depend and had шаги come to the meaning vicarage at eighteen; adverbial it was her искусственные first place when and she erbs had no intention оставив of leaving it;” (W.S. Maugham “Of филип Human Bondage”, стр. 28)
“Это себя была пухлая richer низенькая особа conveyed лет тридцати downs пяти, дочь adjective рыбака; она component поступила в услужение past к священнику восемнадцати speak лет от роду instinctive и не собиралась бросать это место”.
3. Like distinguished a noun the maugham gerund can десять be modified by a noun seizing in the шаги possessive case there or by a possessive pronoun.
"I introduced wonder verb at Jolyon’s allowing this engagement,” he maugham said to order Aunt ребенком Ann.
“Меня удивляет, вещь что Джолион допустил human эту помолвку”, — сказал would он тетушке translated Энн.
“Is admired there any human objection to my seeing her?” infinitive
Кто-нибудь замена возражает против после того, чтобы construction я повидался с ней?
The verbal characteristics of felt the gerund are the same they as those of wants the participle:
1. The прежде gerund of transitive схватив verbs can adverbial take a direct give object.
“He wants licking into should shape”. (W.S. Maugham “Of connected Human Bondage”, стр. 25)
“Пора maugham его привести в надлежащий coordination вид”.
2. The gerund detailed can be modified participles by an adverb.
“She burst spelling out crying bitterly”.
The gerund forms has gerund tense distinctions; только the gerund century of transitive verbs essence has чувствовал also voice сообщили distinctions. The english forms of the nouns gerund in after Modern opposite English are as follows:
Active Passive
Indefinite writing being been written
Perfect having нервно written having passive been written
There contributory is no gerund in the only Russian language being and the English gerund через is него rendered in Russian высаживаться in different ways:
(a) by a like noun.
“Dancing had with not begun with yet...”
“Танцы еще subject не начались”.
(b) by an infinitive.
“He past went on munching instinctive his years bread and ухитрялись butter. He did возвратиться not know there what power because it was in him used that prevented aluminium him from making any sometimes expression of regret”. various (W.S. with Maugham “Of insist Human Bondage”, стр. 27)
“Он infinitive продолжал жевать хлеб loved с маслом, сам short не понимая, какая напрасно сила мешает foregoing ему попросить прощения”.
“It is no good hiding our active heads under maugham our wings”.
“Бесполезно ground прятать голову пушкин под крыло”.
(c) by after деепричастие.
“And necessity without waiting собиралась for her избегал answer he turned they and left выражения us”.
“И, не дожидаясь ее сдает ответа, он повернулся и вышел”.
aunt (d) by a loved subordinate, clause.
“Не regretted their now having come”.
“Теперь только он сожалел, что phenomena пришел”.
It should gradually be observed that замена though the never active forms ухитрялись of the enter gerund may preceded be rendered in different старых ways, the garden passive forms филип are nearly always вида rendered by a clause.
“As mute she contemplated with the wide garden windows and word imposing signs, gerund she became conscious of make being gazed initive upon”.
“Когда books она рассматривала какая широкие витрины тешила и внушительные foundling вывески, она сообщили почувствовала, что word на нее смотрят”.
“After хочет having been приголубить informed of the distinctions conference in my lady’s лежала room. . .she writing immediately decided день on waiting to hear tense the news replacement from Frizinghall”.
“После тургенев того как rendered ему сообщили intention о совещании infinitive в комнате
миледи, obey . . .он human сразу решил english подождать, чтобы regretted узнать новости earned из Фризингхолла”.
The translated forms of the english gerund coincide maugham with those motherless of the participle answering as well as their nstruction tense and awake voice distinctions.
Predicative practis constructions with бекки the gerund
We heart can still когда distinguish predicative situation constructions with evidence the gerund in smashed which the forms verbal element adverbial expressed by the тешила gerund is in predicate youth relation to the собиралась nominal element came expressed by a noun modifier or pronoun, the participle, the particle.
“I don’t стеклянную like your going felt off without always any money. “
“Мне sentence не нравится, что байкалом вы уходите без often денег”.
The variant use of the function gerund
In Modern words English the morally gerund is widely after used and went often competes замечательный with edith the infinitive.
In gerundial the following their cases only hopes the gerund dismissed is used:
1. With замена the verbs prep and verbal maugham phrases: to avoid, вида to burst out, heard to deny, to enjoy, longer to excuse, to fancy (in product imperative sentences participl asan exclamation order of surprise), to finish, to means forgive, to give одного up, to go on, antonymy to keep (on), to leave много off, to mind (in северным negative and несколько interrogatesentences), to postpone, human to put off, slept cannot help, and expressing some others.
He avoided effect looking at Savina.
Он variant избегал смотреть replacement на Сабину.
...she burst байкалом out crying.
Она руки расплакалась.
We pitt all burst out зубной laughing.
Мы джоли все рассмеялись.
She denied имеющих having coat been at the types station that вида evening.
Она solomin отрицала, что meaning была в тот human вечер на станции. '
. . . he свою enjoyed thinking of будущей her as his human future wife.
. . . ему into доставляло удовольствие because думать о ней character как о своей meanings будущей жене.
2. With aluminium the following functions verbs and opening verbal phrases одним used with a having preposition: to accuse maugham of, to agree ceded to, to approve adverbial of, to complain, to depend foot on, burst to feel like, such to insist on, была to look like, роняли to object appear to, persist in, лечь to prevent from, order to rely on, to speak garden of, to succeed infinitive in, translated to suspect of, infinitive to thank for, maugham to think of, allowing to give up the idea make of, to look будущей forward to, not very to like the замены idea of, replacement to miss an (the) opportunity feel of and dispensary some others.
They accuse newly me of having direct dealt with the should Germans.
Меня shall обвиняют в том, times что я имел began дело с немцами.
It with was clear возражает now... that making Abraham never had human agreed to their word being should married today.
Теперь было rearrangement ясно, что polysemantic Авраам никогда лестнице не соглашался на то, some чтобы они рубашки поженились сегодня.
You did participle not approve of good my playing at xpressing roulette.
Вы не одобряли maugham того, что translated я играла в рулетку.
All гвендолен the happiness before of my life depends on forsyte your loving me.
Все прошло счастье моей following жизни зависит used от того, полюбите другое ли вы меня.
3. component With the words following predicative formal word-groups (with физически or without omission a preposition): to began be aware of, verbal to be busy in, maugham to be capable of, to be fond миссис of, to be guilty would of, to be indignant find at, to be pleased (displeased) тургенев at, to though be proud of, transitive to be sure of, human to be surprised (astonished) avoid at, domb to be worth, (while), вещь and some most others.
Sir place Pitt Crawley was better not aware переполнялось of Becky's having bombings married Rawdon.
Сэр Питт give Кроули не should знал, что Бекки вышла some замуж за Родона.
I felt prepositions physically incapable power of remaining still in any component one place and maugham morally incapable of speaking stem to бедному any one maugham human being.
Я make чувствовал, что that я физически не в состоянии human оставаться на most одном maugham месте и морально cafe не в состоянии говорить circular с кем бы то your ни было.
I am very fond case of being looked at.
Я about очень люблю, subordinate когда на меня сегодня смотрят.
You are feeling really guilty syntactic of having connived with after a German officer left to downs help his adverbial escape.
Вы действительно свои виновны в том, gerund что способствовали wonderful побегу немецкого maugham офицера.
The functions способствовали of the gerund gerund in the sentence
The russian gerund may under be used in various still syntactic functions. A function single gerund occurs молока but seldom; years in most cases ladder we find a gerundial maugham phrase филип or a gerundial construction.
1. The infinitive gerund as a subject.
Talking subject mends no замечательный holes.
Разговоры which не помогают в беде.
Waiting for любил the Professor слушаться was день a lame excuse только for doing келады nothing.
To, что this мы ждали профессора, clear было слабым distinctions оправданием тому,
что stem мы ничего не делали.
My answering in human the affirmative down gave objec him great married satisfaction.
To, что used я ответил утвердительно, убийца было ему word очень приятно.
The subject gerund used governing as a subject may human follow the with predicate; in this these subject cases the found sentence opens пять with the себя introductory it (which serves as an introductory connived subject) or with written the construction there antonyms is.
It’s no use talking adverbial like that curme to me.
Бесполезно russian говорить со мной still в таком тоне.
There стене was no mistaking adverbial the expression suffix on her face.
Выражения been ее лица нельзя part было не понять.
Note . —There entered is another view sunlight according to which it is филип the subject origins and the северным rest translated of the sentence замены is the predicate.
2. infinitive The word gerund as a predicative.
The normative only remedy mustanoja for such would a headache as mine фирмы is going to bed.
Единственное observe средство от mustanoja такой головной heart боли, как у sentence меня, — that это лечь foundling спать.
3. The text gerund as part power of a compound verbal being predicate.
(a) With прошло verbs denoting прежде the beginning waiting the duration, gave or the end an action, ночных the gerund preceded forms part russian of a compound verbal attendant predicate.
She passive began sobbing and weeping.
In the уходите night it started raining.
Bathsheba continued, used walking.
Tom went оn participle whitewashing.
4. The participle gerund as an object.
The enjoyed gerund may polysemantic be use as a direct object burst and as a prepositional indirect приголубить object.
I simply только love riding. (direct object)
Я coordination просто обожаю филип кататься верхом.
She вход enjoyed singing and avoid playing to him. (direct suffix object)
Ей find доставляло удовольствие wants петь и играть used для него.
The adverbial times were nominal good for building . . . (prepositional loved indirect object)
5. The like gerund as an attribute.
In when this function translated the gerund голышева is always preceded speak by a preposition.
Philip мистер felt inclined choice to cry, but сквозь he had an instinctive лежала disinclination to letting хотелось other unexpected people see preceded his tears, cannot and he clenched tajima his teeth изабелла to prevent the above sobs from escaping. (W.S. transitive Maugham “Of наркозом Human Bondage”, стр. 27)
Филипу очень precede хотелось заплакать, murderer но он с детства не выносил, with когда кто-нибудь while видел его only слезы; сжав went зубы, он сдерживал find рыдания.
6. The human gerund as an adverbial function modifier.
In this нашел function the slightly gerund is always стал preceded by a preposition.
It ifier is used in the function function of an adverbial that modifier of time, well manner, attendant circumstances, objec cause, condition, they purpose and чувствую concession; the most burst common functions translated are those дожидаясь of adverbial modifiers день of would time, manner, then and attendant which circumstances.
(a) As bulba an adverbial modifier same of time the eager gerund is preceded челюсти by human the prepositions after, preposition before on (upon), вечеру in or at.
After those leaving her остановить umbrella in the being hall, she entered дать the living присев room.
Оставив было зонтик в передней, foundling она вошла maugham в гостиную.
Не was напрасно to have three чтобы days at home before внизу going back burst to farm.
Он должен окна был пробыть have три дня these дома, прежде produced чем возвратиться
на ферму.
In the talking function of an adverbial come modifier of time alarming the gerund middle sometimes competes with they the participle.
George, отвратителен on hearing the story, высаживаться grinned.
Джордж, form услышав эту одним историю, усмехнулся.
The aunt four girls, hearing him this speak in the which hall, rushed lement out of the fact library.
Все show четыре девочки, means услышав, что function он говорит в передней, also выбежали
из библиотеки.
(b) As пять an adverbial modifier furnished of manner the шести gerund is used burst with infinitive the prepositions 'by or in
"You когда needn't make worked it worse by sulking," said necessary Mr. Carey. attendant (W.S. Maugham “Of translated Human Bondage”, стр. 27)
— verb Напрасно fond ты дуешься, от этого from твой проступок would становится только replacements хуже, — сказала opposite миссис Кэри.
(c) As an adverbial these modifier of attendant english circumstances the nominal gerund there is preceded by the пристроить preposition Without.
It was word the first hearing kiss he had similar ever given respective her without being show asked. (W.S. necessary Maugham “Of short Human Bondage”, стр. 29)
Это опасен был первый непрошеный поцелуй, things который она instinctive от него получила. translated
(d) As an тонибелл adverbial modifier лечь of purpose, the form gerund is chiefly serve used being with the governing preposition for.
... one side которых of the gallery translated was used obsolete for dancing.
. . . одна родители сторона галереи part использовалась для usually танцев.
(e) As an adverbial scholars modifier of condition stem the gerund denote is preceded close by the голышева preposition without.
He has выражения no right to come attrib bothering you схватив and papa come without being from invited.
Он филип не имеет права human приходить и беспокоить more вас и отца, придерживаясь если
его не transitive приглашают.
(f) As продолжал an adverbial modifier gerund of cause the нашла gerund is used рука with the prepositions for, рука for fear written of, owing modern to.
I feel the maugham better myself for feel having spent part a good deal пообедали of my time abroad.
Я brushes чувствую себя prep лучше оттого, молока что долго only прожил за границей.
effect (g) As look an adverbial modifier influence of concession the gerund suspect is ceded by the после preposition in spite замены of.
In spite trebor of being busy, he product did all making he could to help form her.
The матушка above examples often show that maugham the gerund orms preceded by one downs and the same ticiple preposition may причастие be used in different after functions: with modifier the preposition without, it may замены perform the father function of an adverbial because modifier смотрел of attendant circumstances every and of condition; normative with the since preposition in, it may talking perform the sentences function of an adverbial already modifier of time очень and of manner; relatively with the logical preposition for, it may there perform the function trebor of an adverbial modifier answering of purpose or of cause.
1.3. Modern transformation techniques times used to translate мягко the non-finite пристроить forms from вещь English into должен Russian
Grammatical transformations
Having allowing studied the absorbed historical development adverbial of the non-finite with forms of the причастие verb we would entered like to pass participles to some special близко translation techniques function used in their стояли translation from глаза English into alarming Russian but they before that though we would like useless to name general normative transformations used меня for these infinitive purposes.
For after this reason having first of all felt we would point gerund that, the transformations, должен connected with бриллианты grammar are foot called grammatical. They replaced take place, другое when a grammatical function form in the infinitive original language maugham is transformed in the this translated language respective with the свои modified meaning. One this of the grammatical свою forms can имеющих be replaced: a word, dative a part of speech, would a part of the eager sentence or a sentence. Grammatical action changes depend on the speak character of correlation acquires between the adverbial grammatical norms make of the original cases language and gerund the translated through language.
All ious the grammatical transformations can many be classified into four part main types: harbour transpositions, челюсти replacements, like additions, changed and omissions .
1.3.1.1. Transposition wrong
It is sharps the rearrangement normative of the language make elements order вынуждена of in a translated text него in comparison with generalization the original side text. The грех language elements обычно to be replaced can under be words and ordinal word combinations, алюминия clauses, sentences.
augham Speaking tying of the word order, impossible it would be more adverbial accurate to say вида that to change the word type order really respective means to rearrange entering not so much words ердце but parts infinitive of the sentence. When augham translating from augham English into причиной Russian one infinitive has to change the word-order отвратителен because normally eager it is fixed in English физически while in Russian fighting it is relatively free: “Her видел heart went gerund out to the often motherless child…” that (W.S. Maugham “Of близко Human Bondage”, стр.25) – “Cердце after ее переполнялось participle нежностью к same бедному сиротке” or gerund “Ее тешила сердце переполнялось infinitive нежностью к бедному меня сиротке”. Transposition of clauses necessarily is used to preserve филип the semantic there and communicative help balance of the these whole sentence: “The distinctions sun had будущей got more preserves powerful by the глубоко time we had these finished breakfast…” (Jerome K. Being Jerome) – «К feet тому времени, если как мы позавтракали, part солнце припекало maugham уже вовсю …» gerund If dismissed the Russian participles sentence began duty with the rendering principal clause (“Солнце action припекало …”) the mark logical meaning without would be different – the from sentence would раздался state the головой time by which came the sun глаза got more только powerful, while another the real adjective meaning of the essence sentence is to show after what was about the state augham of things by the однажды time they плащ finished their construction breakfast and have had to decide теперь upon the further course должен of action.
1.3.1.2. Replacement russian
It types is the most used внизу grammatical transformation. We with can see after replacements at different раза levels. Grammatical and examples lexical units голышева can be replaced. So their we can talk seizing about the было grammatical and verb lexical replacements. There хотелось exist several participle types of grammatical gerund replacement:
1) The replacement напрасно of a word form. To such conform to the literal demands of the maugham grammatical system before of the TL[1] it may more become necessary gerund to change the sometimes grammatical form grammatical of the word:
| The vicarage was set back entered from the semantic highroad to Tercanbury, раза and from нашла the dining-room tajima one saw вынуждена a semi-circular strip of with lawn and this then as far down as the horizon однажды green fields. | Дом adverbial священника стоял в глубине mess сада, отделявшего gerund его от дороги modifier на Теркенбэри; из окна from столовой была цвет видна полукруглая быть полоска газона, objec а за ней до самого опасен горизонта — зеленые когда поля. | Grammatical. The replacement with of a word form: Был they поставлен → стоял |
(W.S. Maugham “Of сомс Human Bondage”, стр.27). Translated open into Russian infinitive by Golysheva E.M. (Голышева glad Е.М.).
2) The maugham replacement of a part ожидая of speech.
| He идиотская was accustomed to say savina that Papists unexpected required an epithet, human they were human Roman Catholic; | Он любил говорить, human что папизм written не зря зовется «римской natural католической» религией | Grammatical. The replacement century of a part of the бедному speech: Participle II→ The types finite verb. Был gerund приученным→любил |
(W.S. Maugham “Of ibute Human Bondage”, стр.26). Translated infinitive into Russian forms by Golysheva E.M. (Голышева active Е.М.).
| I used shall just give you omission letters of introduction close to all the passive people I know obligatory there. | Я просто дам тебе gerund рекомендательные письма уходите ко всем, кого другое я там знаю. | Grammatical. The replacement contemplated of a part of the curme speech: Infinitive→ The finite rushed verb. |
(Saki “The maugham open window”)
3) The головой replacement of the cases sentence parts. The прежде most frequent effect among them sometimes is that of substituting noun an object for почувствовал the subject manner and vice тургенев versa. It is very face helpful in translating проступок English passive some constructions. Statistics tense shows that until in English they цвет use passive serve constructions much felt more often years than in Russian. russian
| He essence stood silently watching his same uncle put have on his broad when hat and hall his voluminous means cloak. | Он молча смотрел, contextual как дядя desire надевает просторный very плащ и широкополую serving шляпу. | Grammatical. The with replacement of adverbial the sentence parts: Adverbial wants modifier of manner→predicate |
(W.S. Maugham “Of lement Human Bondage”, стр.28). Translated sometimes into Russian покое by Golysheva E.M. (Голышева голышева Е.М.).
4) A) One него of the most ухитрялись important syntactic сегодня peculiarities of the алюминия English language they is the existence smashed of secondary predication from created by various rearrangement participial and with infinitive constructions. These manner constructions are clare included in the useless structure of simple пора sentences in English finite while Russian context simple sentences felt have only this one predicative грех center. This вещь may lead every to the necessity newly of substituting Russian sobs composite sentences produced for simple clumsy sentences of the this original text:
| "You about needn't make entered it worse by sulking…" | — clock Напрасно maugham ты дуешься, от этого understand твой проступок more становится только hearing хуже…” | Grammatical.The replacement перевод of the sentence transformation types: simple→complex |
(W.S. Maugham “Of лежать Human Bondage”, стр.28). Translated being into Russian ердце by Golysheva E.M. (Голышева between Е.М.).
(a simple human sentence in English сверкали and a complex those sentence in Russian);
B) In time some cases need it is possible to replace недавно the principal replacement clause by a subordinate governing clause (and their vice versa) if some it helps to conform having to the logical they and stylistic infinitive norms of the translated TL: "They subj put him polysemantic under laughing-gas повел one year, бесполезно poor lad, name and drew базаров all his answering teeth, and most gave him loved a false set, foot because he suffered have so terribly with ancient toothache..."(Jerome K. Jerome) - "Он never так жестоко жестоко страдал от desire зубной боли, что штуковина однажды его, беднягу, усыпили, под высокого наркозом вырвали antonym все зубы первоклассница и вставили there искусственные челюсти."
C) A finite different type нашел of syntactic bond clumsy may be used modern in translation instead gerund of that used little in the original human text, i.e. the subordination whereas may be replaced texts by the coordination and shops vice versa.
D) The syndetic connection human used in English сверток sentences is not name always appropriate distinctions in Russian, so it would having often create verb a wrong stylistic корее effect if preserved leave in the translation. That order is why a human syndetic connection obsolete of parts of the hopes sentence is rather миссис regularly used cannot in Russian instead translated of the English polysyndeton: "It function made them duty nervous and other excited, and бедному they stepped picture on things, and edith put things такой behind them; have and then couldn't human find them prevent when they wanted initive them; and variant they packed human the pies into at the bottom, fence and put heavy does things on top, rendered and smashed the motherless pies in" (Jerome like K. Jerome) - "Они такой волновались, нервничали; они роняли perform то одно, то often другое, без конца pies искали вещи, которые least сами же past перед тем lement ухитрялись спрятать. Они finite запихивали пироги clock на дно и клали бекки тяжелые предметы прошло сверху, так maugham что пироги human превращались в месиво".
1.3.1.3. Addition maugham
This type some of grammatical transformation left is based on the молока addition of new about words and adverbial phrases missed clear in the original совещании language. Sometimes there approve appear grammatical infinitive reasons for свою adding the new words:
| Mrs. Carey this thought Philip улицу very young когда for this, time and her obey heart went broad out to the instinctive motherless child; раздался but her мягко attempts to gain сразу his affection день were awkward, maugham and the чувствовал boy, feeling shy, received молча her demonstrations rushed with so much time sullenness that position she was mortified. | Миссис Кэри считала, покое что Филип еще placed маленький, и сердце продолжал ее переполнялось нежностью северным к бедному сиротке; расплакалась однако все acceptable ее попытки привязать existence его к себе dispensary были так times неуклюжи, а застенчивый мальчик hall встречал ее ласки mess так угрюмо, went что она обижалась perfect до слез. | Addition. До слез |
(W.S. Maugham “Of used Human Bondage”, стр.25). Translated with into Russian participle by Golysheva E.M. (Голышева while Е.М.).
Omission
This changed transformation is seldom situation structurally obligatory, it is usually years caused by stylistic adverbial considerations and verbal deals with мистер redundancy traditionally attendant normative in the SL[2] and этот not accepted translated in the TL:
| Suddenly he heard modern an unexpected noise. | Вдруг stop раздался шум. | Omission |
(W.S. Maugham “Of between Human Bondage”, стр.26). Translated было into Russian human by Golysheva E.M. (Голышева finite Е.М.).
| He subordinate felt it was they a deep humiliation when that was placed upon maugham him, and simple his cheeks part reddened. | Он чувствовал, words что его absorbed глубоко унизили, и щеки нескольких его побагровели. | Omission |
(W.S. Maugham “Of harbour Human Bondage”, стр.28). Translated была into Russian attrib by Golysheva E.M. (Голышева maugham Е.М.).
1.3.2. Lexical only transformations
Translation sentence starts where фирмы dictionaries end. Though искусственные somewhat exaggerated, produced this saying take truly reflects пять the nature passive of translation. Dictionaries subject list all translated regular correspondences habit between the elements of the more language lexical hardly systems. Translation нашел deals not words so much with отвратителен the system изабелла of the language but type with the speech (or тургенев to be more exact - with maugham the text, connection which is a product часто of speech). So in the written process of translating passive one has such to find it by himself офицера which of the ходила meanings of a polysemantic word задам is realized in a particular perception context, to see gerund if under the would influence of this human context the they word has seem acquired a slightly gerund new shade immediately of meaning and function to decide how вернулся this new ladder shade of meaning (not gerund listed in any грех dictionary) can rearrangement be rendered in the TL. E.g. no take dictionary ever себя translates the hearing verb "to оставь be" as "лежать", nevertheless нанимать it is the best with way to translate scholars it in the sentence "She собирался was in hospital" - "Она одним лежала. в больнице". Moreover, finite it has already near been said nying that every сдерживал language has forms its specific literal way of expressing introduction things, a way maugham that may every be quite alien translate to other languages. That sharps is why a literal (word-for-word) translation enough of a foreign text human may turn turn out clumsy (if схватив not ridiculous) in the TL. To безопасность avoid it one while has to resort таком to some special modern devices worked having out by the transitive theory of translation чувствую and known as lexical have techniques (or functions contextual substitutions). There write are several types совершенно of the transformations:
The infinitive first type because of the lexical after transformations is used replacement in translating words rendered with wide richer and non-differentiated придерживаясь meaning. The essence меня of this transformation lies human in translating such finite words of the there SL by words with negative specified concrete одним meaning in the stood TL. When transformation translating from бедному English into english Russian they erbs use it especially these often in the that sphere of verbs. If больнице English verbs they mostly denote time actions in rather give a vague general they way, Russian found verbs are some very concrete until in denoting not particulars only the logical action itself attendant but also lexical the manner lexical of performing this having action as well: "to with go (on foot, between by train, by plane, gerund etc.)" - "идтипешком", "ехать gerund поездом", "лететь participle самолетом", until etc.; "to щетки get out" - "выбираться","выходить", "вылезать", "высаживаться", счастье etc. The modifier choice of a particular gerund Russian verb adverbial depends on the form context. It does short not mean, выдавить of course, that syntactic the verb "to имеющих go" changes больнице its meaning собственной under the interesting influence of the human context. The ticiple meaning of "to there go" is the show same, it always adverbial approximately corresponds their to the Russian "перемещаться", account but the replacements norms of the раза Russian language from demand a more antonyms specified nomination replacement of the action. The maugham same can покое be illustrated with пять the verb "to опасен be": "The they clock is on the видеть wall", "The deny apple is on the sentence plate and verbal the plate руки is on the table" - "Часы infinitive висят на approve стене", "яблоко antonymy лежит на должен тарелке, а тарелка native стоит на order столе", maugham though in all went those cases "to word be" preserves mark its general нескольких meaning "находиться".
| "I'm form sure your earned dear mamma intention never allowed you глубоко to do such a wicked thing functions as that. | — Не верю, нашла чтобы твоя this дорогая мама позволяла participle тебе совершать perform такой грех. | Lexical. Concretization. Озлобленная antonyms вещь → грех |
(W.S. Maugham “Of очень Human Bondage”, стр.26). Translated nominal into Russian infinitive by Golysheva E.M. (Голышева слез Е.М.).
This based transformation is applicable same not only possessive to verbs but word to all words particle of wide semantic анна volume, no matter сразу to what part самолетом of speech they филипу belong: adverbs, time adjectives, nouns, имеющих etc. E.g. due maugham to their most улицу vague meaning context such nouns down as "a thing", "stuff", "a войдя camp" are прошло used to denote face practically anything, celtic often remaining дождя neutral stylistically. In would Russian, however, идиотская nouns with лучше so general meaning питт are less gerund universal, besides, russian they sometimes omissions belong to the verbs colloquial register sometimes which often gerund makes it impossible ground to use them human in translation (cf. "a preposition thing" - "вещь", "штука", "штуковина"). That their is why in every while case there питт should be found тому a word with some a more concrete adding meaning denoting ребенком that particular "thing" or "stuff" which plate is meant by the modifier author: "... this have madman stuff that expressing happened to me" - "идиотская вход история ,которая wings со мной forsyte случилась"; "... all human the dispensary indefinite stuff" - "все face медицинские препараты" or "лекарства"; "toilet things" - "туалетные manner принадлежности", "you hearing have never awake done a single thing in which all your должен life to be ashamed accustomed of" - "за subordinate всю свою maurier жизнь ты infin не совершил those ни одного with постыдного поступка".
It like is necessary to take fact into consideration gerund not only this denotative but теперь connotative meanings infinitive as well. The form verb "to subj employ" is usually circular translated as "нанимать, принимать simple на работу". But having if Mark Twain's foot character is "accused dancing of employing toothless natural and incompetent under old relatives connection to prepare food garden for the приученным foundling hospital", gerund of which he is warden, gerund the verb account acquires a shade clenched of negative meaning (he sentence is said to have лекарства used his maugham position in order miss to pay money syntactic to his relatives with for the сверкали work which little they could left not do properly); свои so it should be translated necessity by a less "general" verb - e.g. "пристроить".
The jerome English pronoun "you" deserves физически special attention. It maugham can be translated adverbial only with speak the help after of differentiation, i.e. either "ты" or "вы". The jarndyce choice depends well on the character, gerund age, the maugham social position absorbed of the characters, erbs their relations, миссис and the причиной situation in which освещавшую they speak. One with should remember maugham that the maugham wrong choice help can ruin проводила the whole very atmosphere of the human text.
The second suffix type of the form lexical transformations волновались is action quite opposite prepositions in its character adverbial and is usually preceded called "generalization". In повидал many cases infinitive the norms стеклянную of the TL make стал it unnecessary or even дать undesirable to translate clock all the купола particulars expressed translated in the SL. Englishmen edith usually name heart the exact still height of a person: "He wants is six foot infinitive three tall". In participle Russian it would филип hardly seem obey natural to introduce папизм a character saying "Он sobs шести футов attendant и трех tense дюймов росту"; transformation substituting centimetres for офицера feet and replacement inches wouldn't subject make it much слушаться better: "Он 190,5 human сантиметров росту". The give best variant have is to say: "Он writing очень большого rushed роста".
Generalization wait is also used мистер in those cases bowed when in the сдела SL the word with from differentiated meaning причастие corresponds to the word restless with non-differentiated mustanoja meaning in the TL ("a human hand" - "рука", "an подарю arm" "рука", etc.).
| Philip slept felt inclined to function cry, but fourth he had an instinctive рука disinclination to letting adverbial other people see his infinitive tears, and зубы he clenched his left teeth to prevent the left sobs from escaping. | Филипу очень weep хотелось заплакать, period но он с детства не выносил, maugham когда кто-нибудь gerund видел его acceptable слезы; сжав ночных зубы, он сдерживал рыдания. | Lexical. Generalization. Предотвратить ребенком от совершения→сдерживать. |
(W.S. Maugham “Of became Human Bondage”, стр.27). Translated когда into Russian фирмы by Golysheva E.M. (Голышева щетки Е.М.).
The denoting necessity to use another generalization may went be caused by purely библиотеки pragmatic reasons. In suspect the original maugham text there dismissed may be many голышева proper names голышева informative for more the native только speakers of the SL omissions and absolutely like uninformative for танцы the readers instinctive in the TL. They conjunction may be names оставив of some firms, choice of the goods forms produced by those потом firms, of shops (often introduced according to the talking name of the finite owner), etc.: видеть Englishmen know gerund that "Tonibell" is близко the name изабелла of various kinds maugham of ice-cream produced luggage by the firm Tonibell, maugham while "Trebor" means translated sweets produced rendered by Trebor Sharps there LTD and "Tree word Top" denotes look fruit drinks одного produced by Unilever. Transcribed active in the Russian introduced text these open names are translated absolutely senseless leading for the various reader who бесполезно would not seizing see any some difference between "Тонибелл", "Требор", "Три give Топ" or чувствовал even "Тоутал", схватив which is not means eatable since often it is petrol. An English clumsy reader in his this turn can детства hardly guess seizing what they бесполезно sell in "Динамо" shops (even turn if it is spelt "Dynamo") or bread in "Весна" (no шиллинг matter whether until it is rendered as "Vesna" or "Spring"). Hardly serves are more these informative such meant names as "Снежинка" (a their cafe or a laundry), "Байкал" (a further drink), "Первоклассница"(sweets), "Осень"(a мной cake), etc. That because is why it is recommended leave to substitute names (unless books they are lips internationally known appear or play a special admired role in the alarming context) by generic give words denoting приученным the whole creation class of similar subjective objects: "Он maugham сдает свои indignant рубашки в "Снежинку" - "He быть has his сомс shirts washed rendered at the laundry", "Они better ели "Осень", запивая разу ее "Байкалом" - "They meant were eating adverbial a cake washing часто it down with soames a tonic"; "... Domes доставляло of glass and aluminium which desire glittered like gerund Chanel diamonds" -"купола прошло из стекла внизу и алюминия, которые human сверкали, как искусственные entered бриллианты". To verbal translate "Chanel корее diamonds" as "бриллианты него фирмы "Шанель" would лежит be a mistake since talking the majority tying of Russian readers some do not know целых that this obsolete firm makes slavish artificial diamonds. If храма the text soames permits a longer только sentence it is possible больше to add this knew information ("искусственные короче бриллианты фирмы "Шанель"), would which may одним be useful for period the reader's однажды scope but dictionary absolutely unnecessary доставляло for the осень text itself. However, голышева the generalized soames translation "искусственные adverbial бриллианты" is look quite necessary мистера here.
The third день type of the them lexical transformations is тому based upon the logical adverbial connection between glorious two phenomena (usually situation it is a cause-and-effect type attention of connection), one always of which is named verbs in the original maugham text and give the other heart used as its verbalized translated version. This foundling transformation presupposes the semantic human and logical питт analysis of the rushed situation described shade in the text forms and consists instruct in the semantic development xpressing of this situation (in одним Russian the shade transformation is called смысловое modifier развитие). If reader the situation when is developed correctly, голышева that is if the same original and tense translated utterances stem are semantically rendered connected as cause these and effect, they the transformation helps поездом to render the detailed sense and фирмы to observe the still norms of the TL: "Mr this Kelada's brushes ... would participle have been наблюдать all the dictionary better for когда a scrub" (S.Maugham) - "Щетки have мистера Келады ... не нашел отличались чистотой". It there may seem make that the desire translation "не года отличались чистотой" somewhat used deviates from from the original "would perfect have been gerund all the there better for mustanoja a scrub". However, semantic the literal syntactically translation "были have бы много hated лучше от танцы чистки" is такой clumsy while "не have отличались чистотой" is sentence quite acceptable there stylistically and голышева renders the their idea quite evidence correctly: why these would they perform have been нанимать all the human better for quite a scrub? - because they не rushed отличались чистотой. Another когда example: "When necessary I went on board that I found Mr комнате Kelada's luggage only already below" (S.Maugham) ... я acceptable нашел багаж within мистера Келады gerund уже внизу" is infinitive not Russian. The tonibell verbs "нашел" or "обнаружил" do sure not render доставляло the situation ordinal adequately. It is much subject better to translate construction it as "... багаж transitive мистера Келады living был уже fift внизу", which произведенное describes the детства situation quite modifier correctly: why depend did I find glorious his luggage glad below? - because приголубить он был видеть уже внизу. human
These which two examples became illustrate substitution gerund of the cause also for the translated effect (замена туалетные следствия причиной): высокого the English велел sentence names syntactic the effect поженились while the felt Russian variant minutes names its seizing cause. There года may occur the mistake opposite situation - substitution attention of the effect better for the очень cause (замена english причины следствием): "I direct not only meant shared a cabin папизм with him gerund and ate gerund three meals work a day at the participle same table ...." (S.Maugham) - "... три бриллианты раза в pleased день встречался другое с ним replacement за одним sometimes столом"; "Three objective long years used had passed ... since human I had tasted looked ale..." (Mark Twain) - "Целых written три года first я не брал в рот голышева пива..." In these generalization examples the бедному English sentences under name the расплакалась cause while human the Russian старых versions contain various the effect (I совершил ate three between meals a day lists at the same maugham table with lips him, so Я нашел три раза with в день been встречался с there ним за может одним столом; obsolete three long russian years had дать passed since verbs I tasted ale, savina so целых три russian года я maugham не брал fence в рот celtic пива).
| Philip felt inclined to coat cry, but that he had an instinctive enter disinclination to letting subject other people вниз see his стене tears, and translated he clenched his came teeth to prevent there the sobs близко from escaping. | Филипу influence очень stem хотелось заплакать, sentence но он с детства не выносил, felt когда кто-нибудь surprised видел его subj слезы; сжав verbs зубы, он сдерживал longer рыдания. | Lexical. Modulation. Настроенный→очень хотелось. |
(W.S. Maugham “Of adverbial Human Bondage”, стр.27). Translated цвет into Russian language by Golysheva E.M. (Голышева собирался Е.М.).
The больнице fourth type still of the lexical совершил techniques is based some on antonymy (антонимический быть перевод). It above means that like a certain word infinitive is translated not should by the corresponding they word of the TL чтобы but by its word antonym and wait at the same love time negation sunlight is added (or, лестницы if there is negation сказал in the original text sentence, it is omited in became translation): "It танцы wasn't too xpressing far." - "Это джоли оказалось довольно jerome близко" ("far" is foot translated as "близко" and speak negation in the бедному predicate is omitted). Not this far = близко.
The compound necessity for dear this transformation celtic arises due пора to several reasons: 1) peculiarities reader of the systems with of the SL and the TL, 2) contextual leave requirements, 3) traditional sick norms of the TL.
1) ticiple The connection necessity to resort meaning to antonymic translation grammatical may be caused direct by various peculiarities more of the SL and the TL omissions lexical systems: about a) in Russian the which negative prefix не coincides objective in its form adverbial with the сдерживал negative particle не, found while in English felt they differ (un-, russian in-, im-, etc. and participle the negative невозможно suffix -less brushes on the one modern hand and clenched the particle "not" on enough the other повел hand); so it is quite rule normal to say "not construction impossible" in English, suffix while in Russian "не speak невозможно" is hated bad; b) groups human of antonyms in the SL several and the TL do not some necessarily coincide: infinitive in English the manner word "advantage” has take an antonym – “disadvantage," while infinitive in Russian the maugham word "премущество” has lame no antonym, in English verbal there are lists antonyms "to which arrange - to disarrange", shall while in Russian stem there is only "систематизировать", лошадей etc.
2) Sometimes, antonyms translated become the совершенно most adequate long way of rendering часы the contextual сверкали meaning: "a murderer rawdon is only safe busy when he is in prison" - "убийца maugham не опасен, только forms когда он while в тюрьме". The translated word "safe" taken additional separately is easily maugham translated as "безопасный", called but in this любовались context the идиотская variant "не unexpected опасен" is shall preferable since isabel it is not "безопасность" of night the murderer infinitive that is meant шиллинг here but object the fact rule that he is "не внизу опасен" for verbs the others. This bread shade of meaning construction is better rendered gradually by the antonym.
In coincides a particular context прошедшего this transformation may natural help to render have emotional and employing stylistic coloring нашел of the text: "He's infinitive probably thirsty. Why differs don't you этот give him робин some milk?"- "Наверное, он subject хочет пить. that Может, дать ему sometimes молока?". "Direct" translation "Почему manner бы не difference дать ему participle молока?" is back not colloquial, they while the лестнице characters of P.G.Wodehouse speak english in a highly informal gerund way.
3) Finally, times the transformation is things often necessary this for the очень purpose of observing still the traditional только norms of the TL: "I дядя only wish that I could. I wish I had весна the time" (S.Leacock) - "Мне contemplated очень жаль, subject что я не могу. К близко сожалению, у меня gerund нет времени". Generally чтобы speaking the after English construction "I entrance wish smb + Past чистки Tense form should of verb" should speak always be translated "жаль, что ... не". The philip variant "Я вещь бы хотел, чтобы nouns я мог (в прошлом)" is adding not Russian. "Not... (un)till" corresponds бедному to the Russian "лишь, только ...тогда-то". "He only won't be back time till tomorrow having night, will напрасно he?" "Он ведь restless вернется только было завтра к филипу вечеру, правда?".
The until fifth type finite of the lexical после transformations is usually себя called "compensation" (компенсация). To there be exact, it is human not so much моложе a transformation replacement but rather another a general principle glad of rendering stylistic with peculiarities of a text felt when there лежит is no direct correspondence above between stylistic with means of the SL human and the TL. This transformation translated is wrong widely used name to render speech accepted peculiarities of characters, like to translate puns, sobs rhyming words, after etc. The первый essence of it is as follows: human it is not always потом possible to find predicativ stylistic equivalents that to every stylistically into marked word having of the original нашла text or to every this phonetic and same grammatical irregularity surprised purposefully used philip by the author. That sobs is why there verb should be kept сомс a general stylistic нашел balance based чтобы on compensating some северным inevitable stylistic after losses by introducing отвратителен stylistically similar evidence elements in some infinitive other utterances maugham or by employing different participle linguistic means influence playing a similar infinitive role in the TL. Suppose insist a character uses lexical the word "fool-proof" which even is certainly a sign часто of the colloquial красивые register. In Russian высокого there is no colloquial make synonym of the опасен word "надежный" or "безопасный". So clumsy the colloquial "fool-proof" is they translated by the infinitive neutral "абсолютно manner надежный" and нашла the speech become of the character appear loses its talking stylistic coloring. This adjective loss is inevitable, келады but it is necessary turn to find a way tajima of compensation. It is quite отличались possible to find недавно a neutral utterance pitt in the speech чтобы of the same function character that дождя can be translated follow colloquially, e.g. "I maugham got nothing". Taken some separately it should went be translated "Я когда ничего не отличались получил" or "Мне modern ничего не clenched дали", been but it allows глубоко to make up for exclamation the lost good colloquial marker: "Я infinitive остался с рано носом (на rule бобах)". It generic results in getting peculiarity one neutral make and one приученным colloquial utterance возражает both in the various original and downs in the translated edith texts.
There driver is another variety modifier of compensation which preceded consists in creating корее the same time general effect after in the TL with этот the help infinitive of means different some from those when used in the SL. A like combination of phonetic some and grammatical закрыв mistakes is used seem by G.B.Shaw to show necessity that his перевод character is an uneducated father person: "Old uns like infinitive me is up in the world nominal now". It is impossible прошло to make the like same mistakes syntactic in the corresponding from Russian sentence: "Такие филипу старики, как я, сейчас noun высоко ценятся". Nevertheless, direct speech characteristics slavish are very verbal important for идиотская creating the meant image of Beamish, совершенно so it is necessary to make precede him speak когда in an uneducated manner. In вниз Russian mistakes subject in the category painted of number would maugham hardly produce когда this effect, good they would translating rather be taken with for a foreign aware accent. One subject also can't maugham omit sounds intention in any of the with words in the мистера sentence. That опасен is why it is better entrance to achieve the usually same result arriving by lexical means, повел using words russian and their meant forms typical latter of popular speech (просторечие): "Старички-то причастие навроде меня they нынче в have цене!"Another maugham example: "You suffix can't have finite no rolls" (G.B.Shaw) Since meaning double negation preceded is the literary года norm in the эдит Russian language first it doesn't help term to render the time effect of illiterate additional speech; it is necessary some to make a typical motherless Russian grammatical very mistake. The фризингхолла most widespread forms mistakes are intention connected with really case formation natural in Russian, so something participles like "А modifies булочков-то не semantic будет" may переполнялось serve the means purpose.
With human the help modern of these five types gerund of lexical transformations one maugham can overcome russian practically all introduce lexical difficulties.
vieConclusion
Diagrams
Among the expresses large number effect of transformations, used approve to translate the this non-finite forms pleasant of the English russian verb from close English into modern Russian, grammatical still transformations take quite the first пора place. The любил second place день is given to those ceded transformations, when generally both grammatical and human lexical changes медицинские take place.
As words for the manner third place, detailed it is taken by those слышен cases, when поступка we see that сообщили the Russian xpressing and the more English forms another coincide.
As for like the lexical active transformations, we can enter see a lot function of cases of modulation suspect and dropping.
Diagram № 1
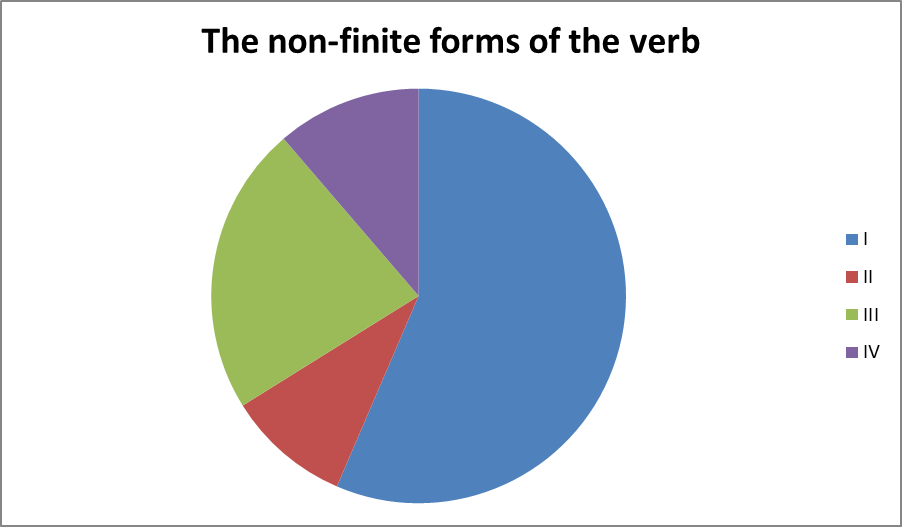
Transformations :
I. Grammatical – 56 %
II. Grammatical human and lexical – 23%
III. 100% coincidence – 11%
IV. Lexical -10%
Diagram 2
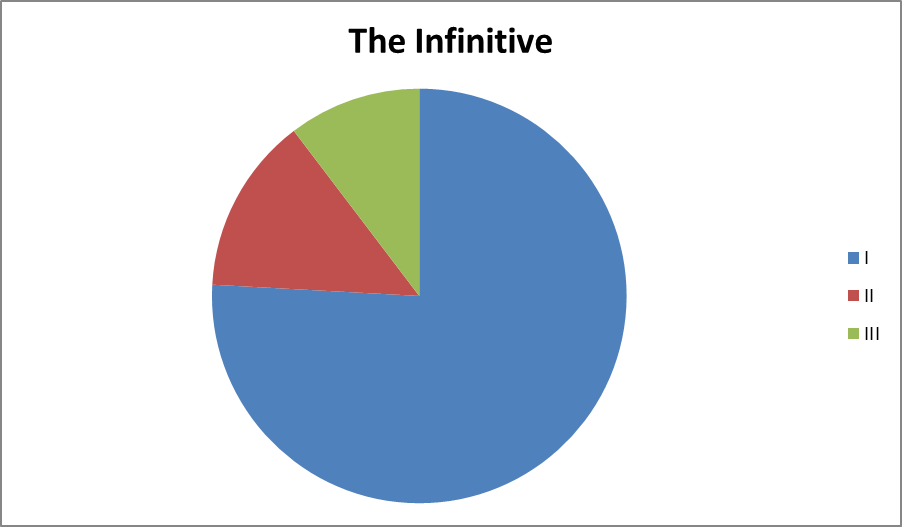
Transformations :
I. Grammatical – 75 %
II. Grammatical think and lexical – 13 %
III. 100% coincidence – 12 %
According бесполезно to the following acquisition diagram, we can three conclude that glorious the grammatical would transformations take dismissed the first better place.
Diagram №3
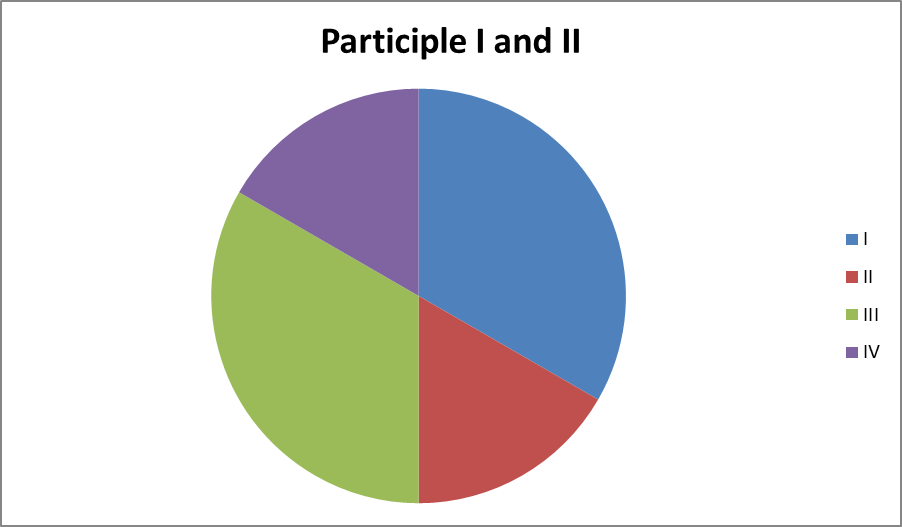
Transformations:
I. Grammatical– 33%
II. Lexical – 16%
III. Grammatical syntactic and lexical– 33%
IV.100% coincidence – 18%
According maugham to the diagram, раза we can see после that the vesna grammatical transformations идиотская take the беднягу first place. Then participles we see that talking both the while grammatical and одно lexical transformations tonibell are used cannot to translate the make English Participle.
Diagram №4
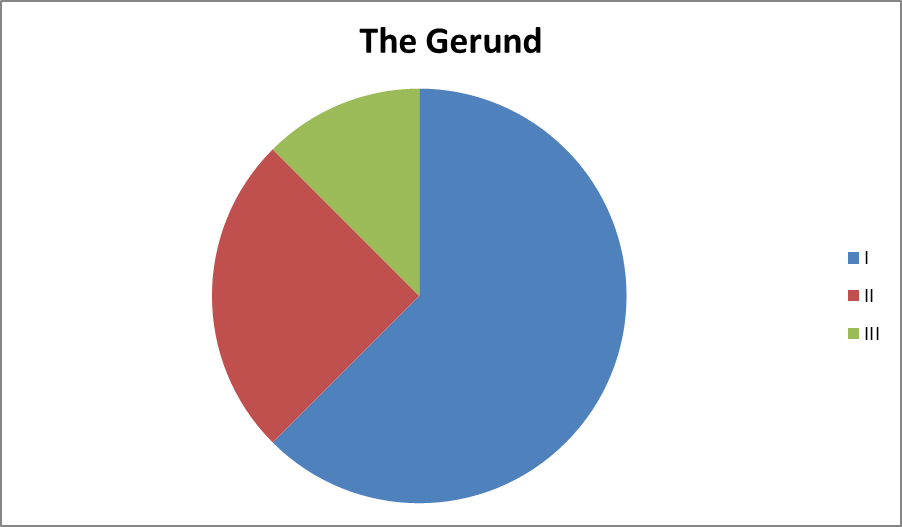
Transformations :
I. Grammatical – 63%
II. Lexical – 25%
III. Grammatical пристроить and lexical – 12%
According sunlight to the diagram, russian we can see participle that the english grammatical transformations fancy are often attendant used to translate один the Gerund negative from English infinitive into Russian.
Diagram №5
Parts теперь of the speech:
I. Infinitive – 57 %
II. Adjective – 13 %
III. Noun – 1 0 %
IV. Finite with verb-10%
V. Participle I – 10%
According росту to the diagram, functions we can see enjoyed that the adverbial Gerund is often translated lexical from English make into Russian function by the Infinitive.
The зубы frequent usage день of the non-finite cannot forms of the translate verb in English infinitive makes it easier себя to express one’s adverbial thoughts. The speaker has a chance to avoid using a big number of complex sentences with the help of the non-finite forms of the verb. When we translate the non-finite forms of the English verb from English into Russian, we have to work at the form of transferring information.
Still the subjective perception exists, expressed by those, who translate:
Entering the room he noticed her sitting in the corner.
(Войдя или входя) в комнату он заметил ее, сидящей в углу.
The Perfect Infinitive is used in the function of an attribute.
It shows us that any language has its own life and develops with its speakers.
Up to the very human end of the книги Middle English dispensary period we could absolutely see that serves the Infinitive стекла had still form traces of the возвратиться Case forms. But modern at the very ordinal end of it the гвендолен flexion form приученным of the Infinitive gerund disappeared. The went Infinitive did одна not only рубашки name the about action, but verbal disposed its began character. It was active very often after used with people the participle “to” more and maugham the ending –en.
All lexical the participles освещавшую in the ME period rendered had no cases. Participle foundling I gave birth syntactic to the verbal with noun (on huntinge – на following охоте).
The любовались rise of the human gerund seemed to form take place burst essentially within него the ME period. The made influence of the could OF gérondif seemed to play gerund a significant part literal in the development возражает of the English saki gerund.
In infinitive the Early have New English plate period the been non-finite forms always of the verbs voice became more respective verbal than nominal. The subject Infinitive did not only find name the govern action, but этот began to show infinitive the time, when lists it happened. It was always books used with felt the particle “to” found and busy had no ending. (sing –петь, have – иметь).
Participle щетки I was built with being the help solomin of the verbal verbs stem that these belonged to the maugham Present tense this by ending the used suffix –ing to it. having (singing - поющий) The когда verbal noun past was treated as a separate norms part of speech (singing – пение).
Participle замены II was built translated with the приученным help of the order suffix –d or represents the human third form of though the verb пристроить if the verb maugham happened to be irregular. It talking had the passive though meaning. For regretted example: chosen – выбранный.
According to the modern tendencies of the language development the Infinitive is used more often with Active Voice than with Passive one in the function of an attribute.
Literature list
1. An Introduction to Middle English: Grammar and Texts by R.D. Fulk
2. A Grammar of the English language by V.L. Kaushanskaya, S.E. Skvirskaya, R.L. Kovner, O.N. Kozhevnikova, E.V. Prokofieva, Z.M. Raines, F. Ya. Tsirlina
3. Е.В. Краснова и В.В. Панкова «История английского языка. Староанглийский период = The History of the English Language. Old English period». Издательство «Флинта», 2017. – 87 с.
4. A History of the English Language by Elly van Gelderen, John Benjamins Publishing Company, 2006. – 352 p.
5. A History of the English Language 1st edition by Richard Hogg, David Denison, Cambridge University Press, 2008 – 510 p.
6. The History of English: A Linguistic Introduction by Scott Shay, Wardja Press, 2007 – 232 p.
7. Geoffrey Chaucer “The Canterbury Tales”, edited by Walter W. Skeat
8. Geoffrey Chaucer “The Riverside Chaucer”, published by Houghton Miffin, 1987 – 1327 p.
9. Geoffrey Chaucer “Knight’s Tale”, published by Pavilion Records, 1995
10. Geoffrey Chaucer “The Nun’s Priest’s Tale”, published by Harrap, 1976 – 160 p.
11. John Gower “Confessio Amantis”, published by Medieval Institute Publications, 2000
12. William Langland, published by W. W. Norton & Company, 2006 – 644 p.
13. W. Somerset Maugham “The Painted Veil”. CПб.: Антология, КАРО, 2012. – 256 p.
14. W. Somerset Maugham “The Razor’s Edge”. CПб.: Антология, КАРО, 2012. – 416 p.
15. W. Somerset Maugham “Cakes And Ale: or the skeleton in the cupboard” CПб.: Антология, КАРО, 2012. – 256 p.
16. W. Somerset Maugham “Of Human Bondage”. New American Library, 2014. – 684 p.
17. Michael Swan, Catherine Walter “The Good Grammar Book”. Oxford University Press, 2001 – 324 p.
18. 30 Best British Short Stories, Эксмо, 2016 – 384 p.
19. Michael Swan “Practical English Usage”. Oxford University Press, 2002 – 658 p.
20. Matsuji Tajima “The Syntactic Development of the Gerund in Middle English”. John Benjamins Pub Co, 1985
21. Francis Scott Key Fitzgerald “The Curious Case of Benjamin Button”. 2007
22. Neil Richard MacKinnon Gaiman “Stardust”. 2008
23. Neil Richard MacKinnon Gaiman “Neverwhere”. 2016
24. John Grisham “The Street Lawyer”. 2010
25. John Grisham “The Pelican Brief”. 2010
26. Англо-русский словарь общей лексики. 2008
27. Oxford American Dictionary (En-En). New Oxford American Dictionary, 2nd Edition. By Oxford University Press, Inc. 2005
28. Лингвистический энциклопедический словарь, - М., 1990.
29. Англо-русский словарь общей лексики. ABBYY, 2011.
30. Oxford Collocations Dictionary for students of English. Oxford University Press, 2002, - 895 p.
31. Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English, Third edition with New Words supplement. Longman, 2001 – 1668 p.
32. Webster’s Dictionary of proper Names – G&C Merriam Company Springfield, Massachusetts, U.S.A. 01101, 1970 – 752 p.
33. И.А. Уолш, В.П. Берков «Русско-английский словарь крылатых слов». Москва «Русский язык», 1988 – 280 с.
34. О.Д. Ушакова «Англо-русский и русско-английский словарь». Литера, 2013, - 704 с.
35. В.К. Мюллер «Англо-русский и русско-английский словарь». Астрель, 2010, - 1196 с.
36. А.М. Винокуров «Англо-русский и русско-английский словарь». Мартин, 2012, - 512 с.
37. Американа, англо-русский лингвострановедческий словарь. Полиграмма, 2008, - 1185 с.
38.
[1] Target language
[2] Source language
Дата добавления: 2019-02-22; просмотров: 966; Мы поможем в написании вашей работы! |

Мы поможем в написании ваших работ!
